Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain FM-S-4 capable of improving color and luster stability of fruit wine and application
A strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, applied in the field of fruit wine processing, can solve the problems of color fading, browning, fading, etc., and achieve the effects of strong flocculation ability, safe source, and good alcohol fermentation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Screening of Saccharomyces cerevisiae FM-S-4
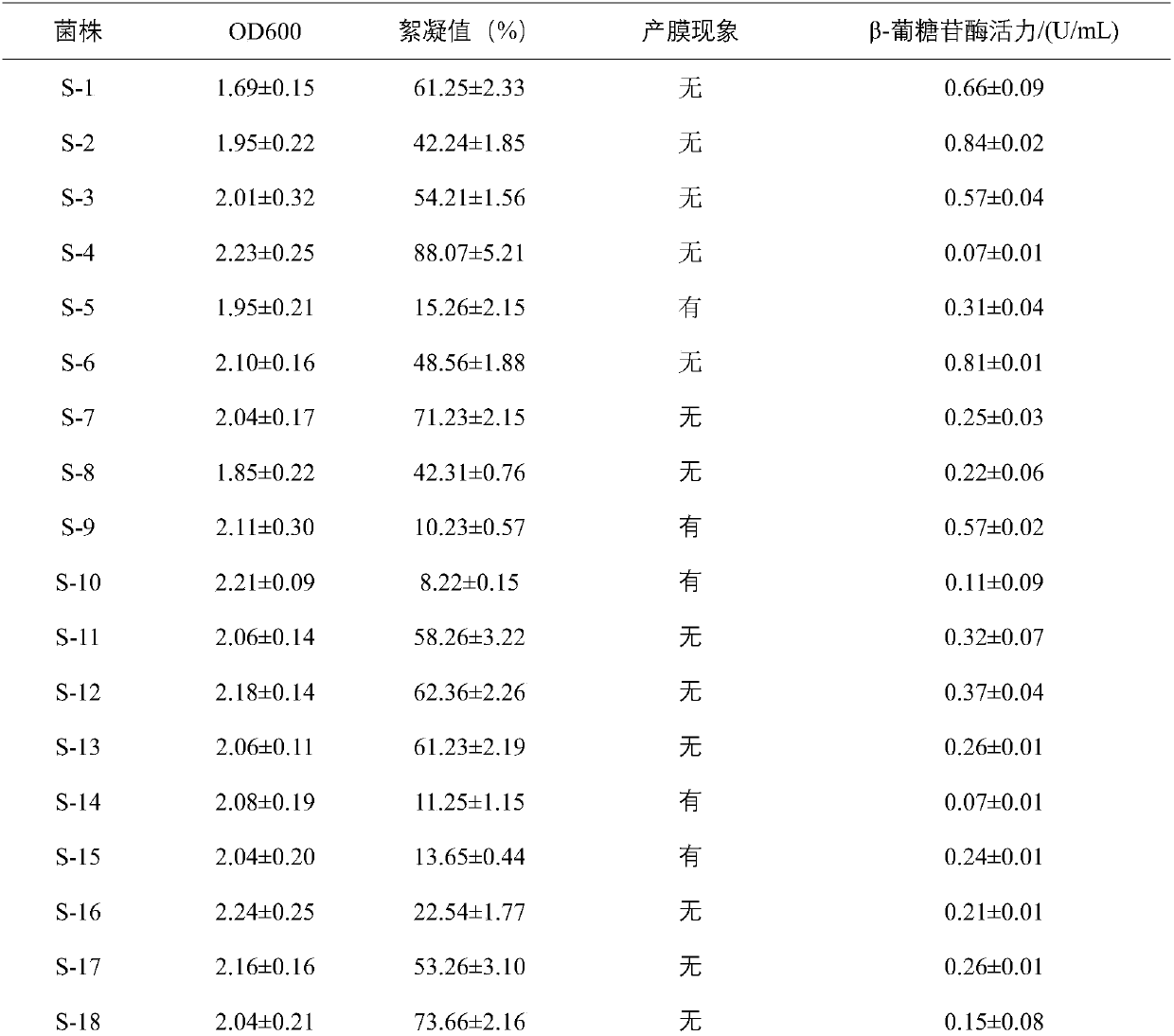
[0026] PDA medium was used to isolate yeast strains from traditional fermented foods, and 19 yeast strains were isolated according to the characteristics of colony morphology and cell morphology.
[0027] Nineteen strains of yeast were inoculated into PDA liquid medium respectively, cultured at 150 r / min for 12-14 h at 25°C, and the OD value at 600 nm wavelength was measured with a spectrophotometer.
[0028] Inoculate 19 strains of yeast into PDA liquid medium respectively, and culture them statically for 48 hours at 25°C, and observe whether there is a film on the surface of the culture medium.
[0029] Inoculate 19 strains of yeast into PDA liquid medium, culture at 25°C, 150r / min for 12-14h, collect the cultured yeast cells, wash twice with deflocculation buffer and sterile water, and suspend in flocculation buffer solution, placed in a 50mL shake flask at 30°C, and incubated at 100r / min for 2h. Take 20mL of...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: the tolerance of 5 yeast strains and the determination of fruit wine fermentation performance
[0041] Using the Dunbar tube fermentation method, the five yeast strains numbered S-4, S-7, S-13, S-17 and S-18 screened out through the above screening steps were respectively inserted into the PDA liquid medium and kept at 25°C. Measure the OD600 value after culturing for 28 hours, and adjust the OD600 value with sterile water, so that the OD600 value of the five strains is 2.01±0.05×10 8 , the adjusted 5 strains were inoculated into different ethanol volume fractions (8%, 10%, 12%, 14%, 16%, 18%), different SO 2 PDA liquid medium test tubes with Duchenne tubules with mass concentration (40, 70, 100, 130, 160, 190 mg / L) and different sucrose content (8%, 12%, 16%, 20%, 24%, 28%) , cultured at 25°C for 6 days, observed the generation of air bubbles in the Duchenne tube after the end of the culture, and compared the effects of the five yeast strains on ethanol,...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3: Identification of bacterial strain
[0054] The genome of S-4 was extracted, and 18S rDNA universal primers were used to carry out PCR amplification using the genome as a template. The amplified products were purified and then sent to Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd. for sequencing. The obtained 18S rDNA sequence was compared in the GenBank database, and the BLAST results showed that the strain S-4 had the highest homology with Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), and the homology was 100%, indicating that the strain S-4 was the genus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. member. The colony and cell morphology of S-4 are shown in figure 1 with figure 2 , the colony shape of the bacteria cultured on the PDA medium plate for 48 hours is regular round, raised, moist, milky yellow in color, and the diameter of the colony is 3-6 mm; the length of the bacteria is 5-18 μm, and the cells of the bacteria are mostly oval Shaped, unilateral or multilatera...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com