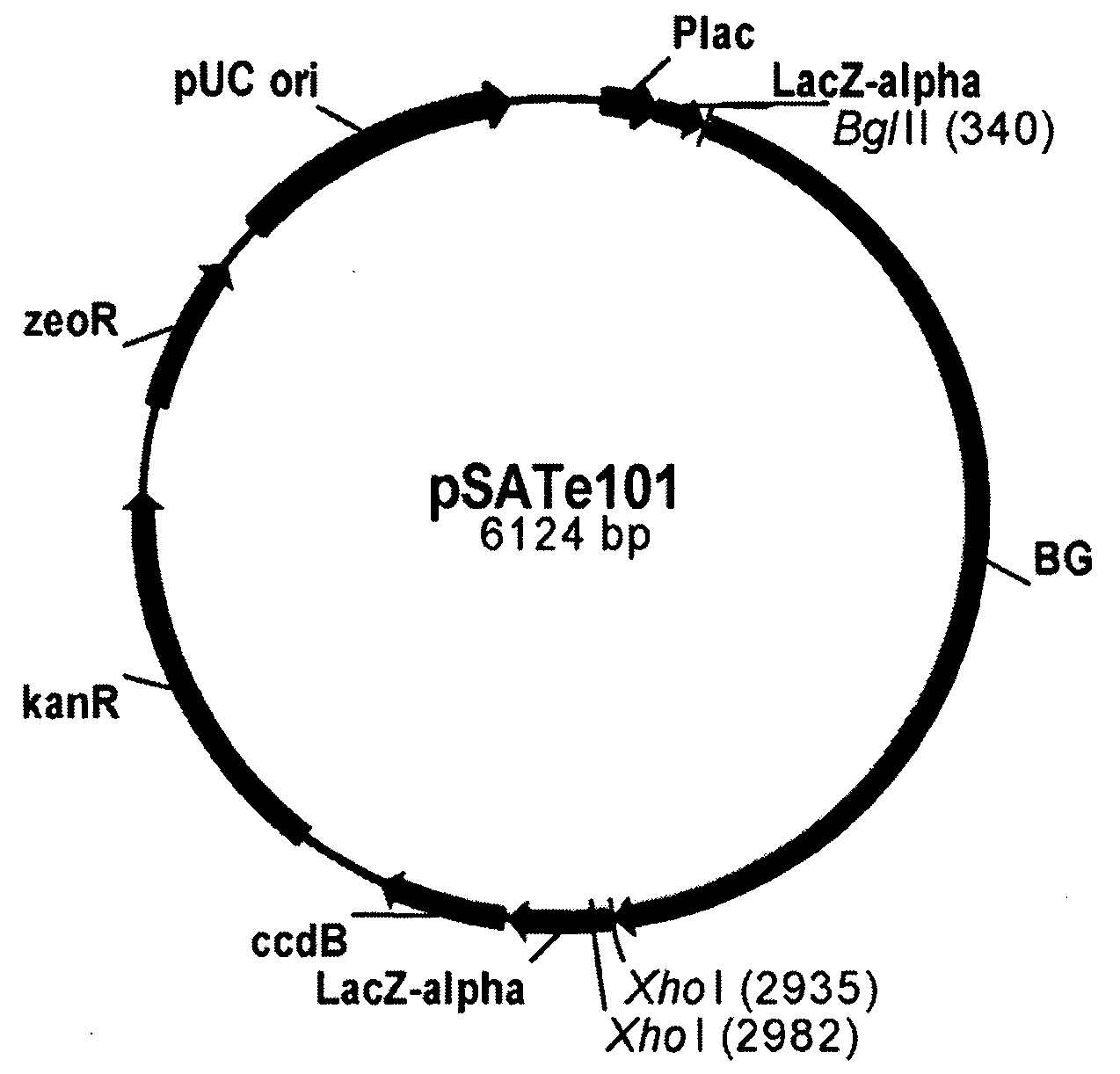
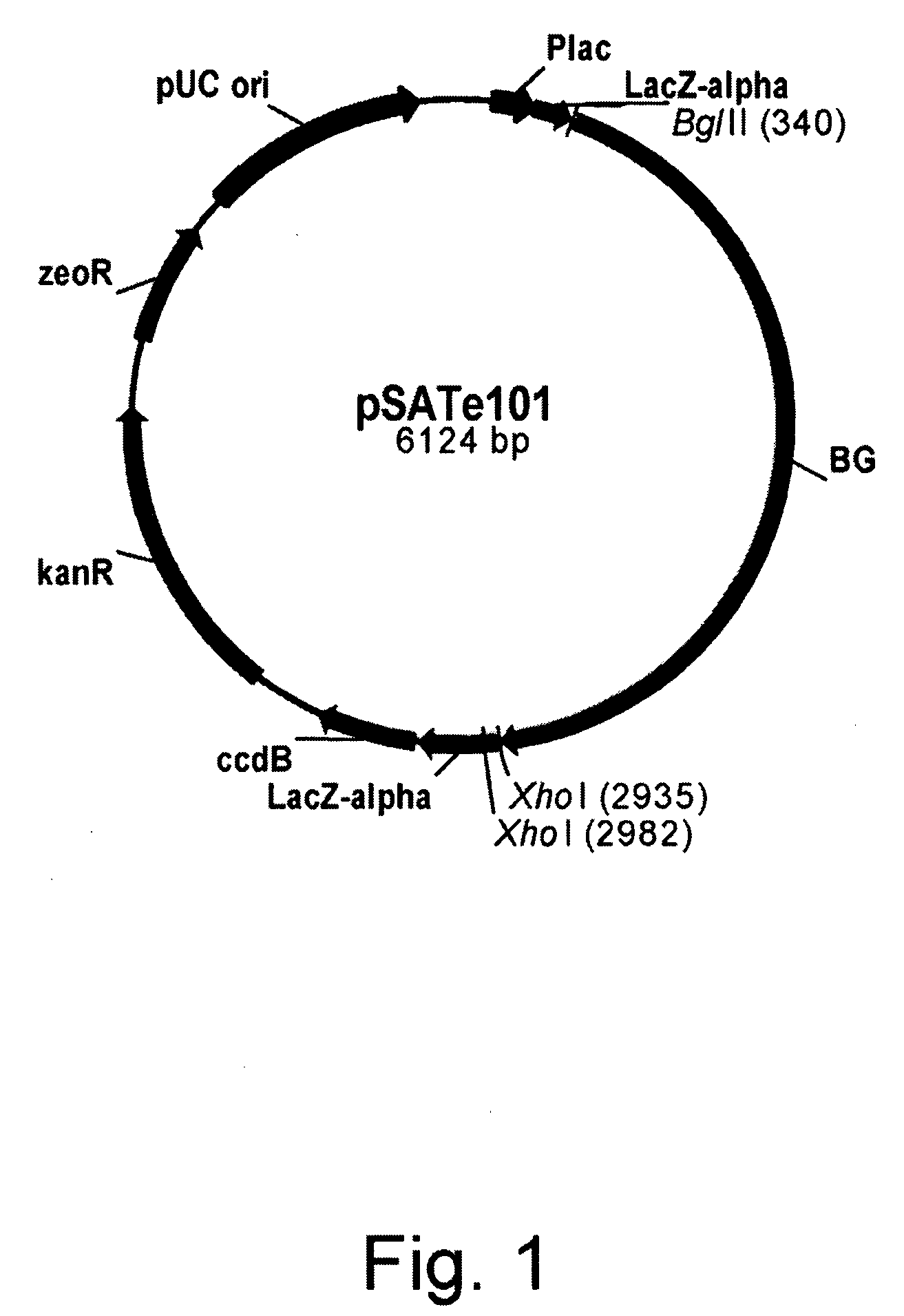
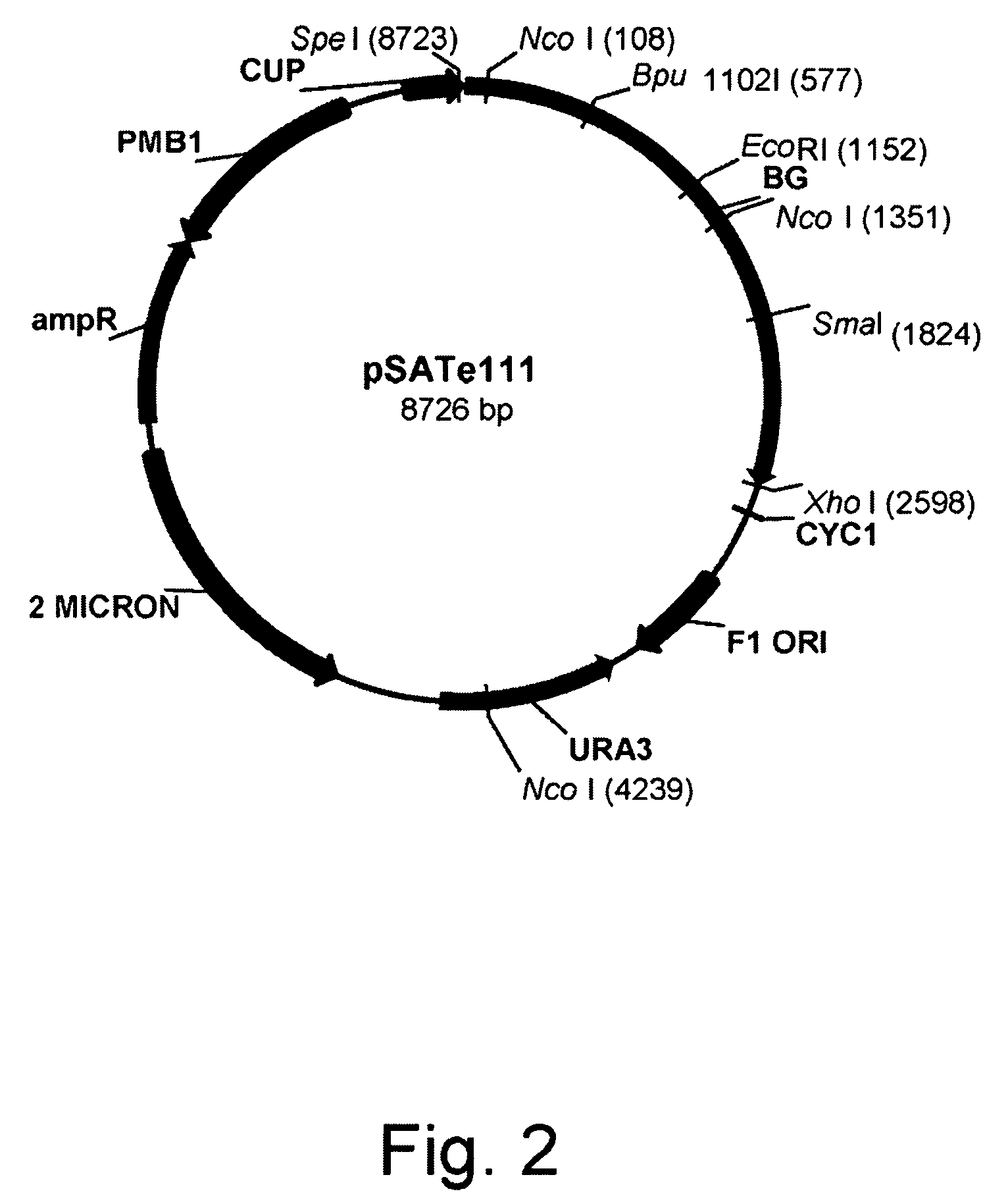
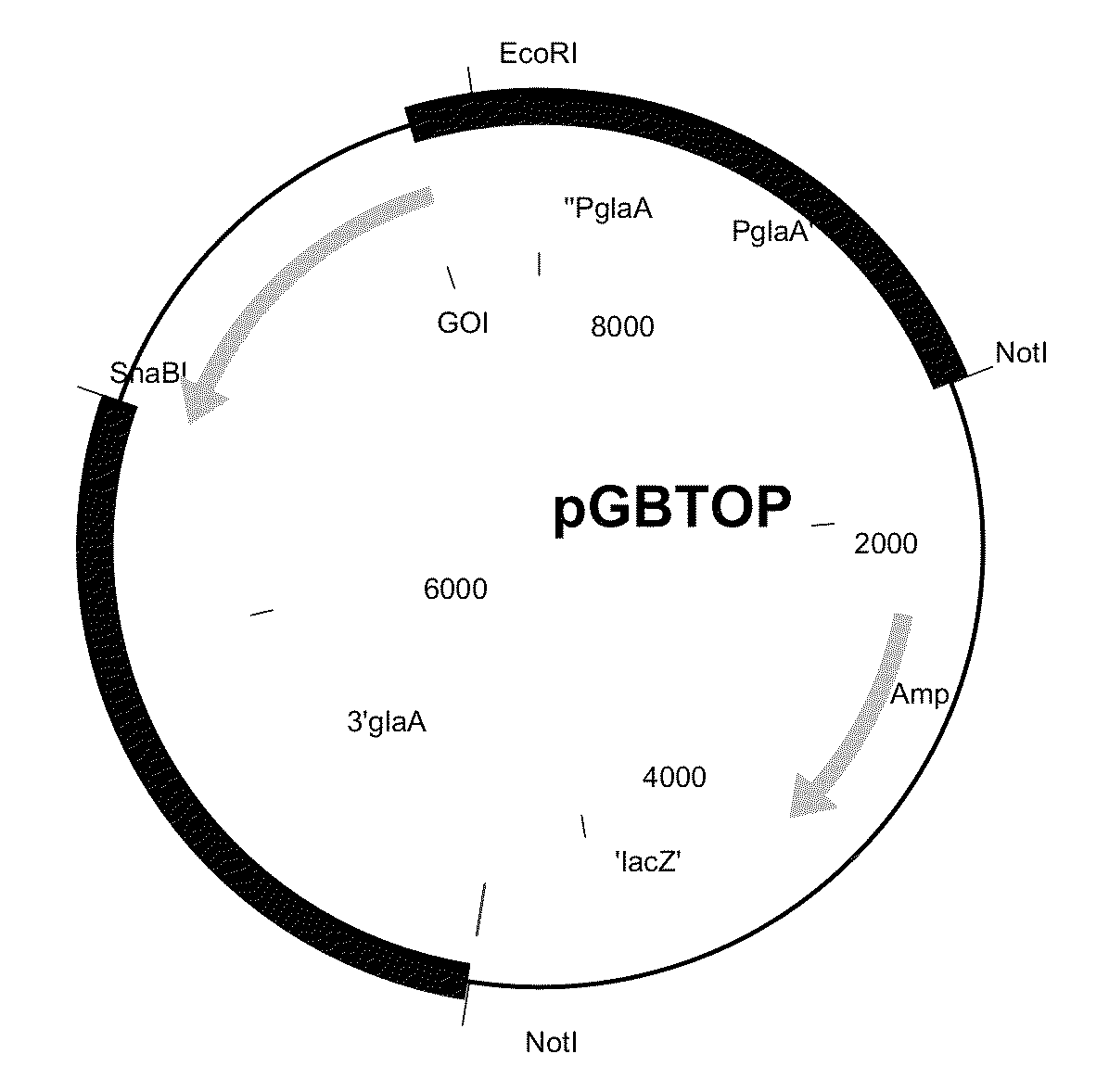
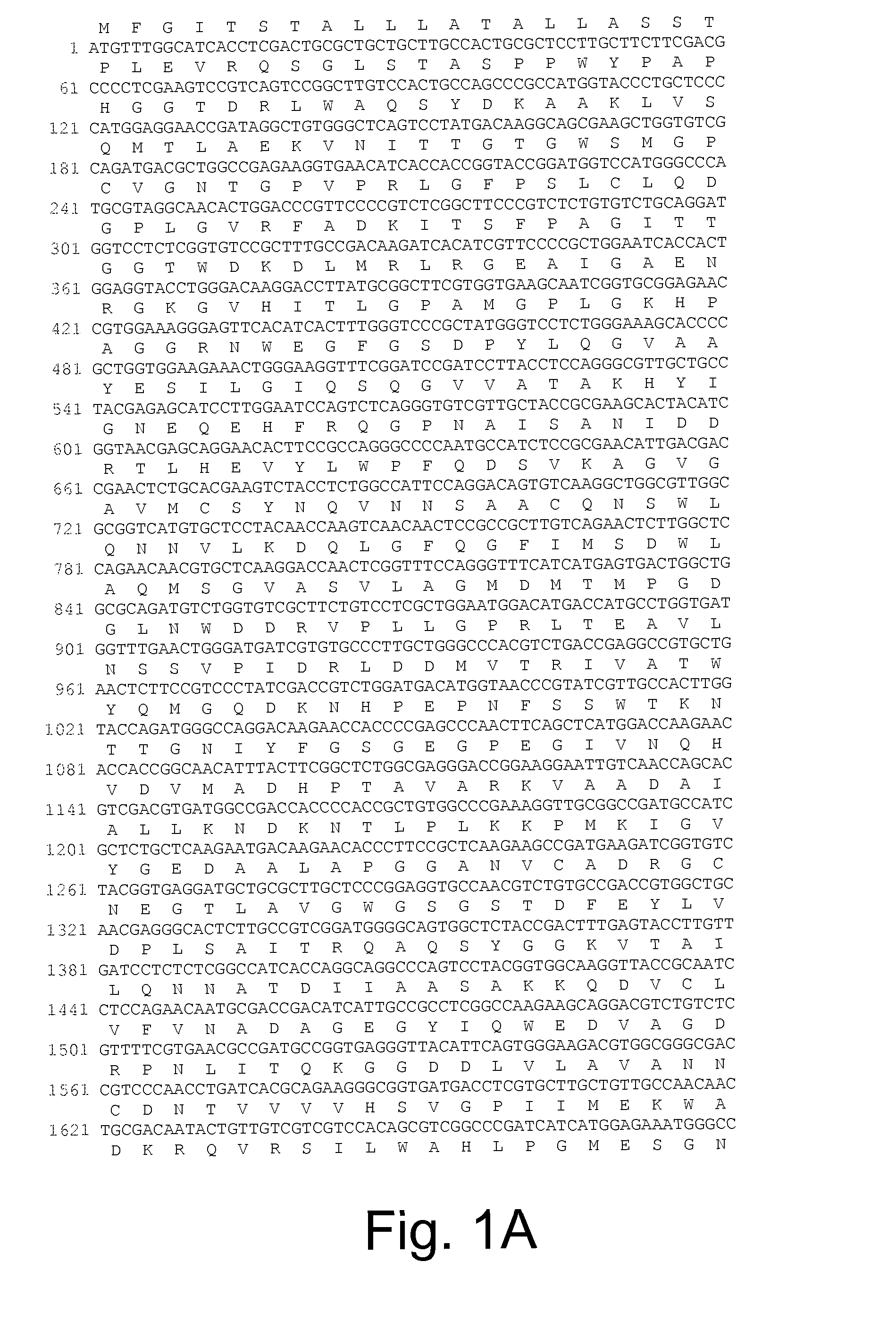
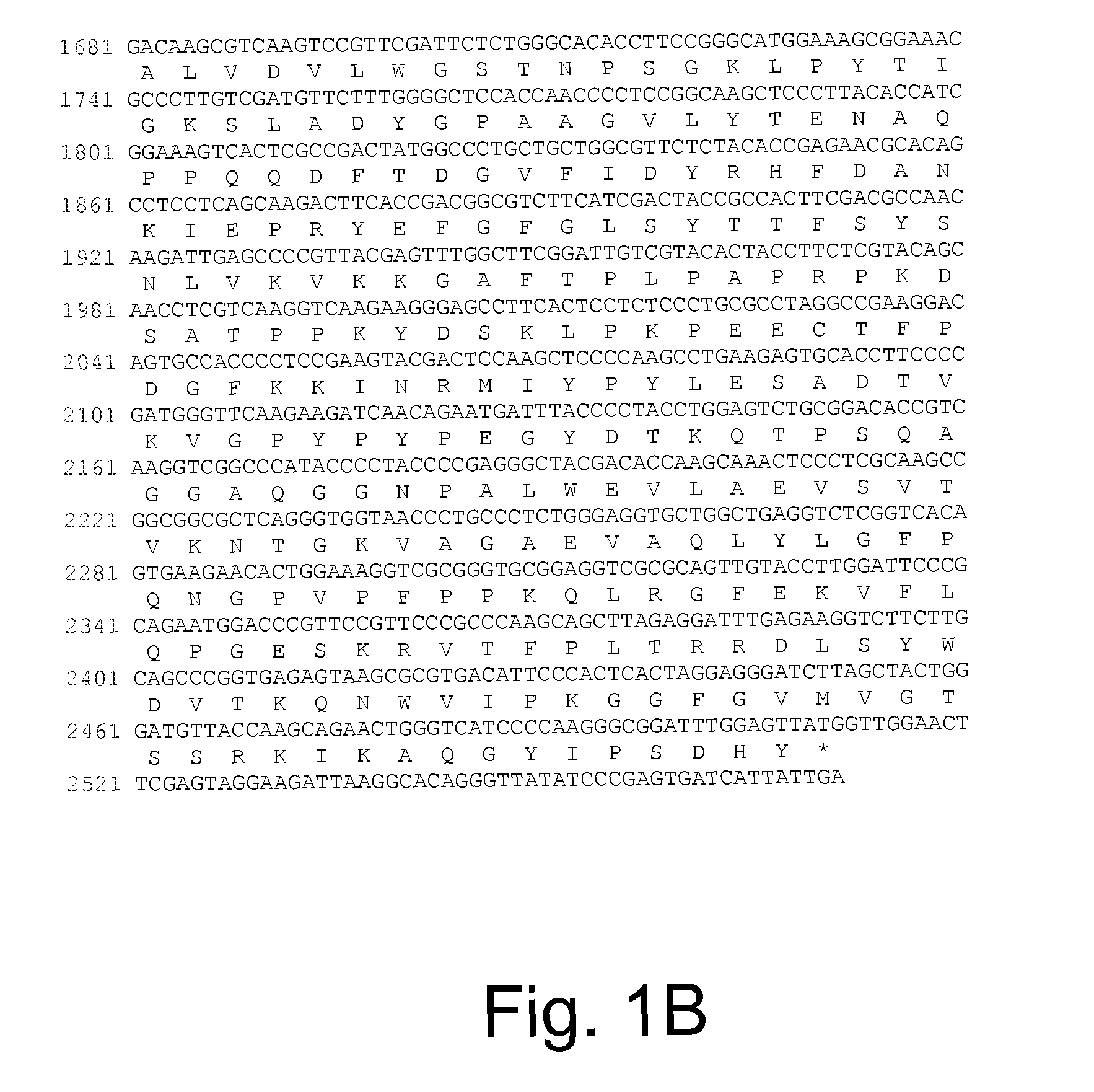
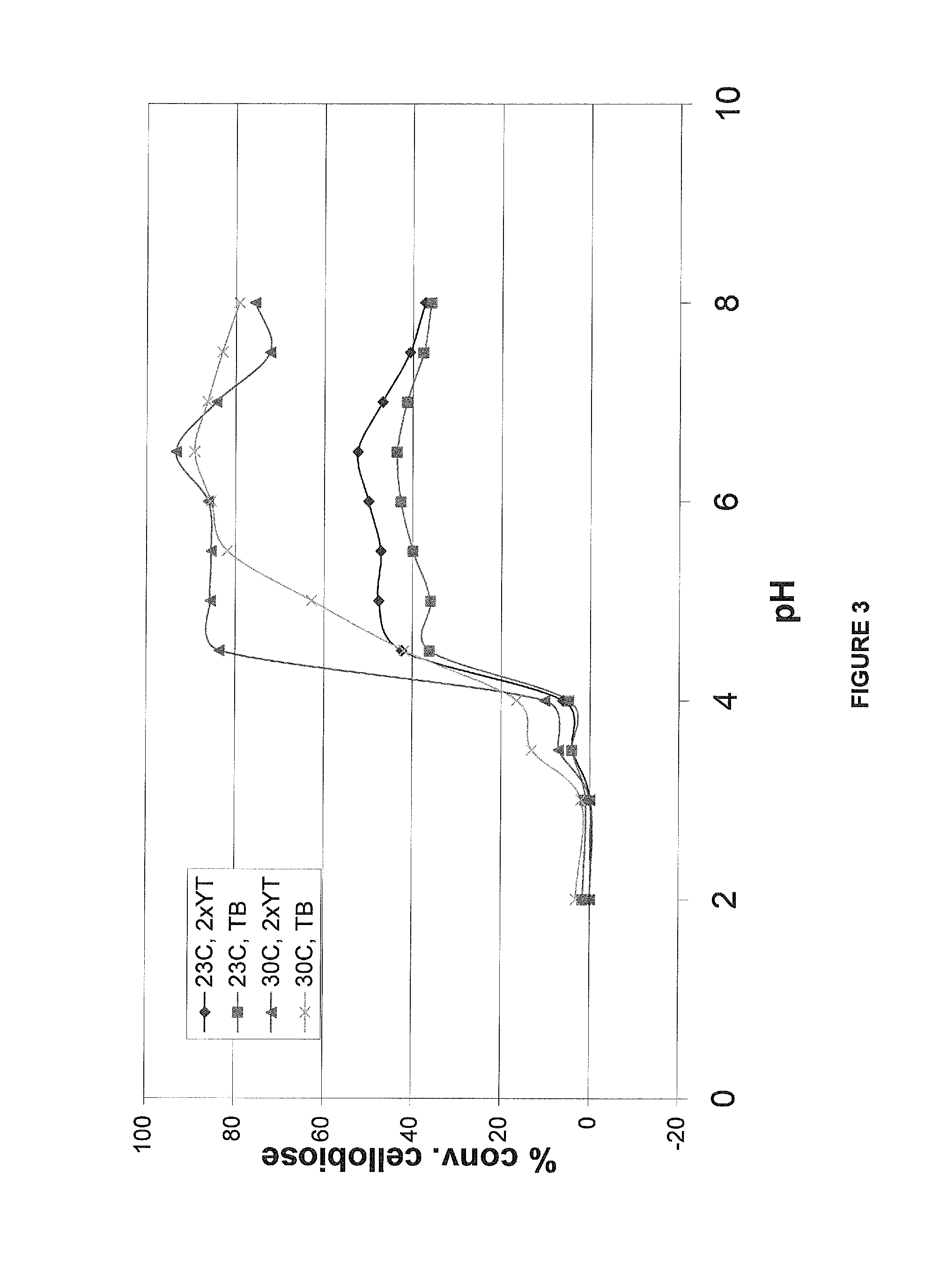
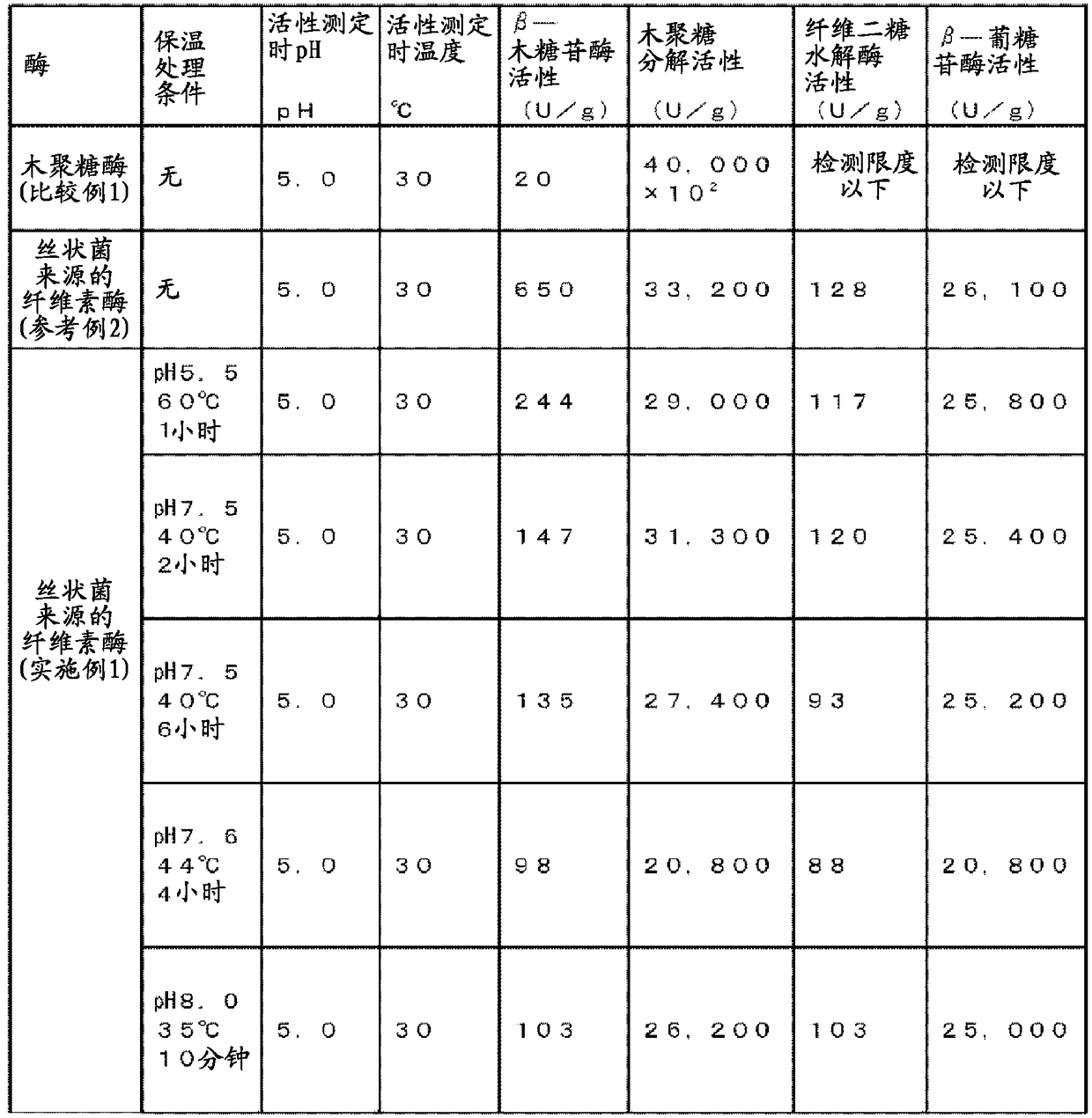
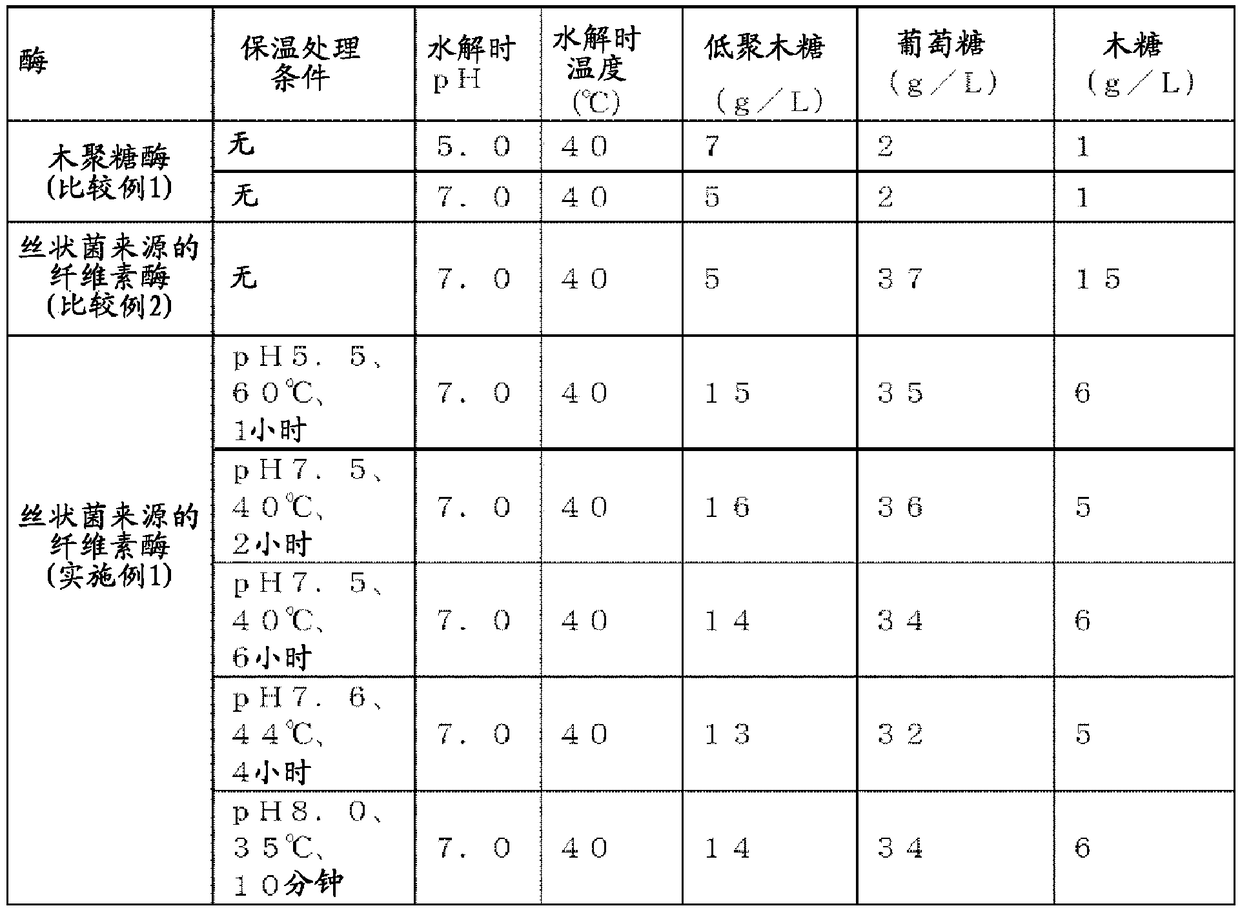
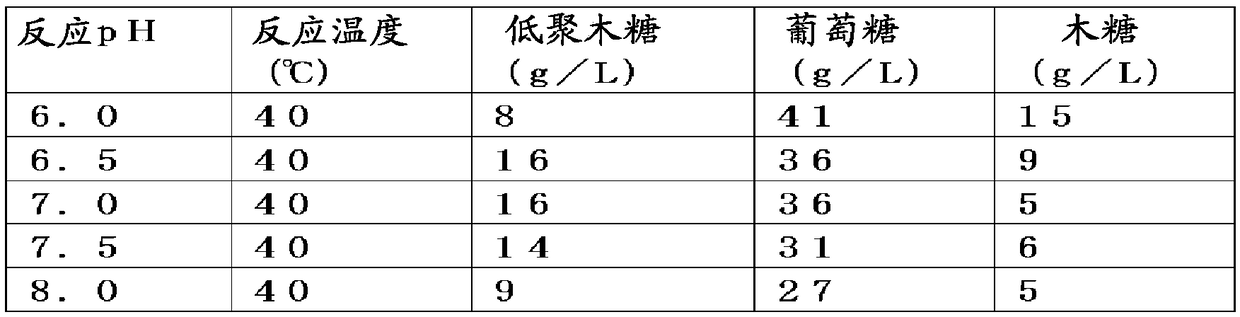
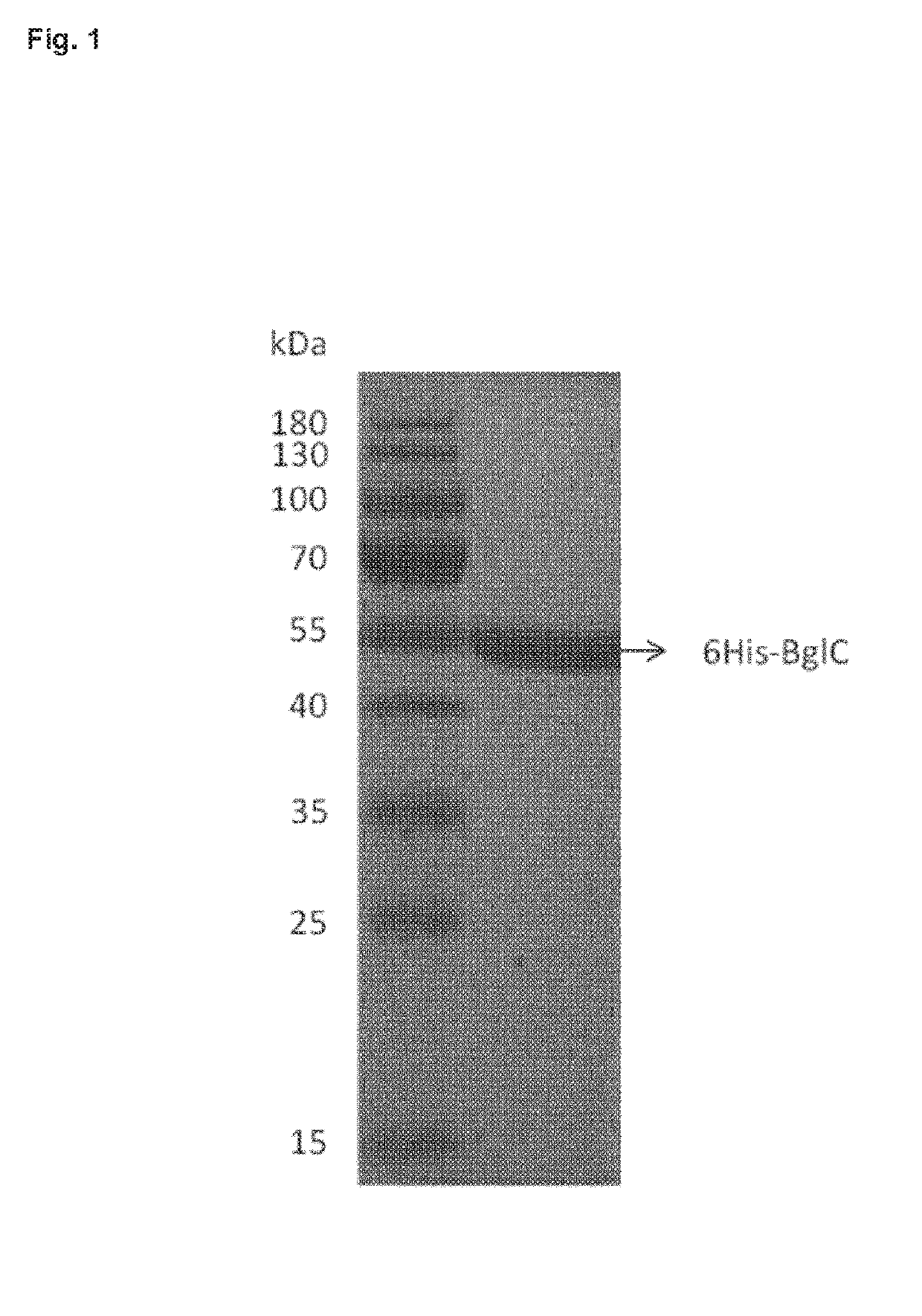
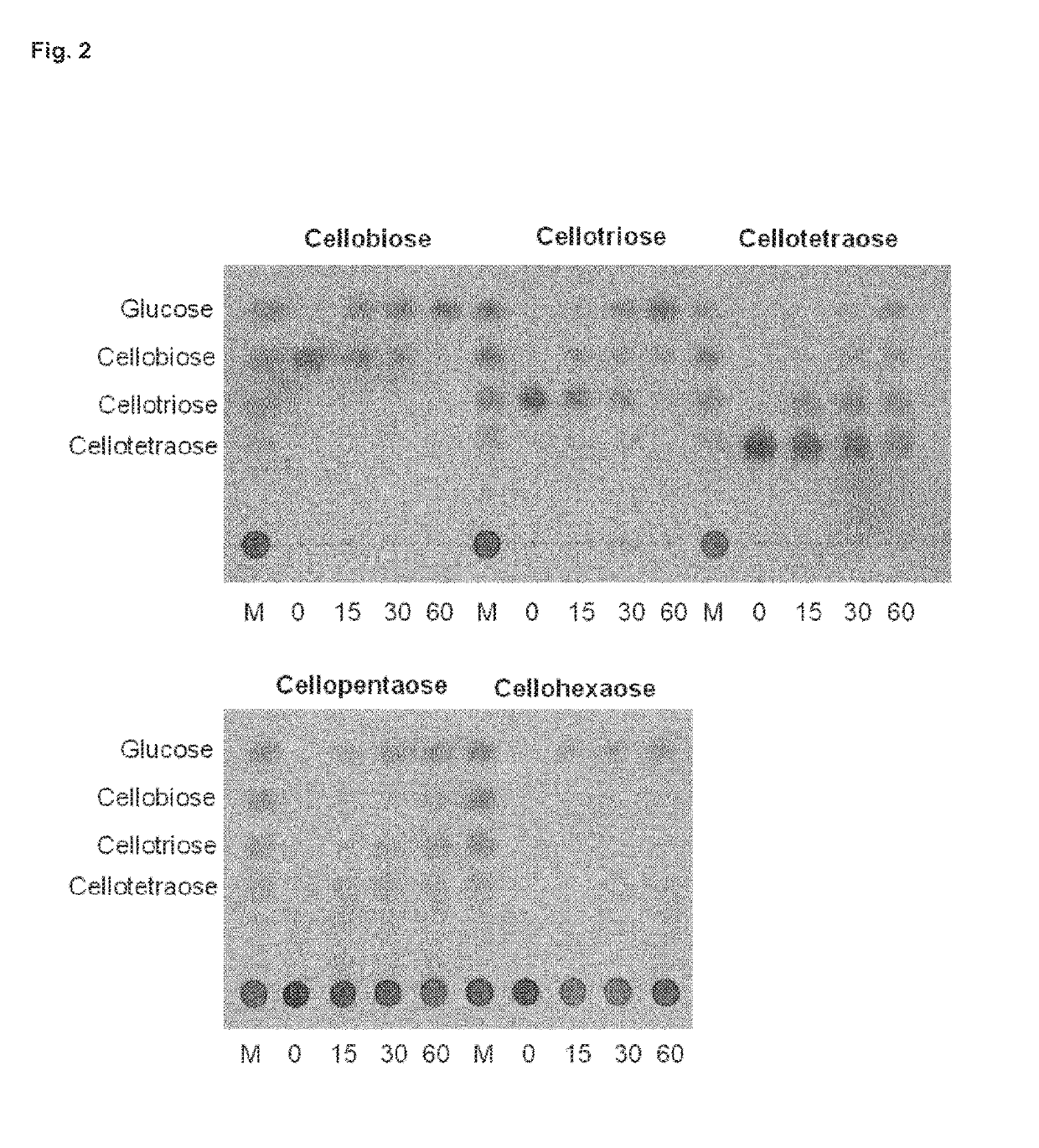
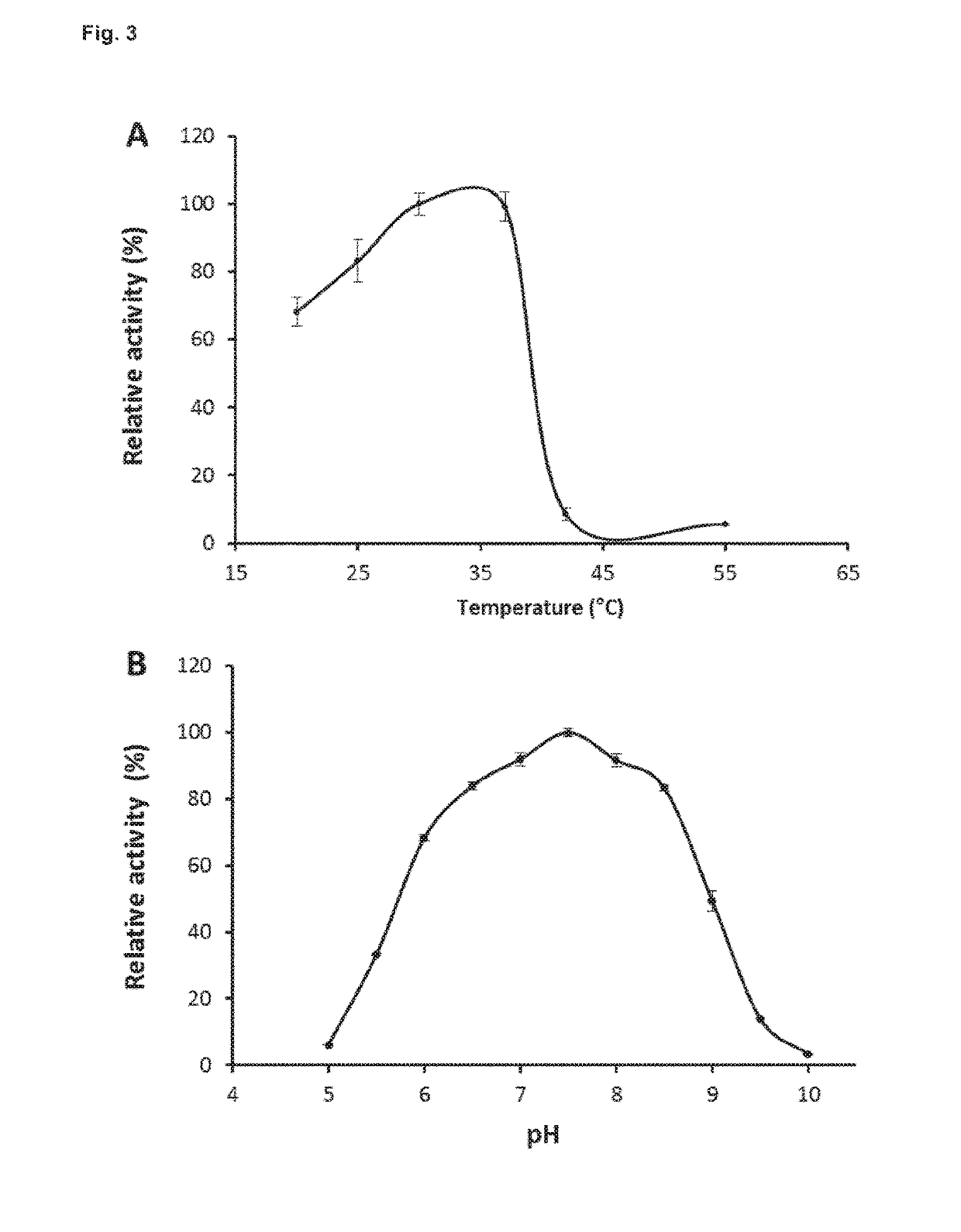
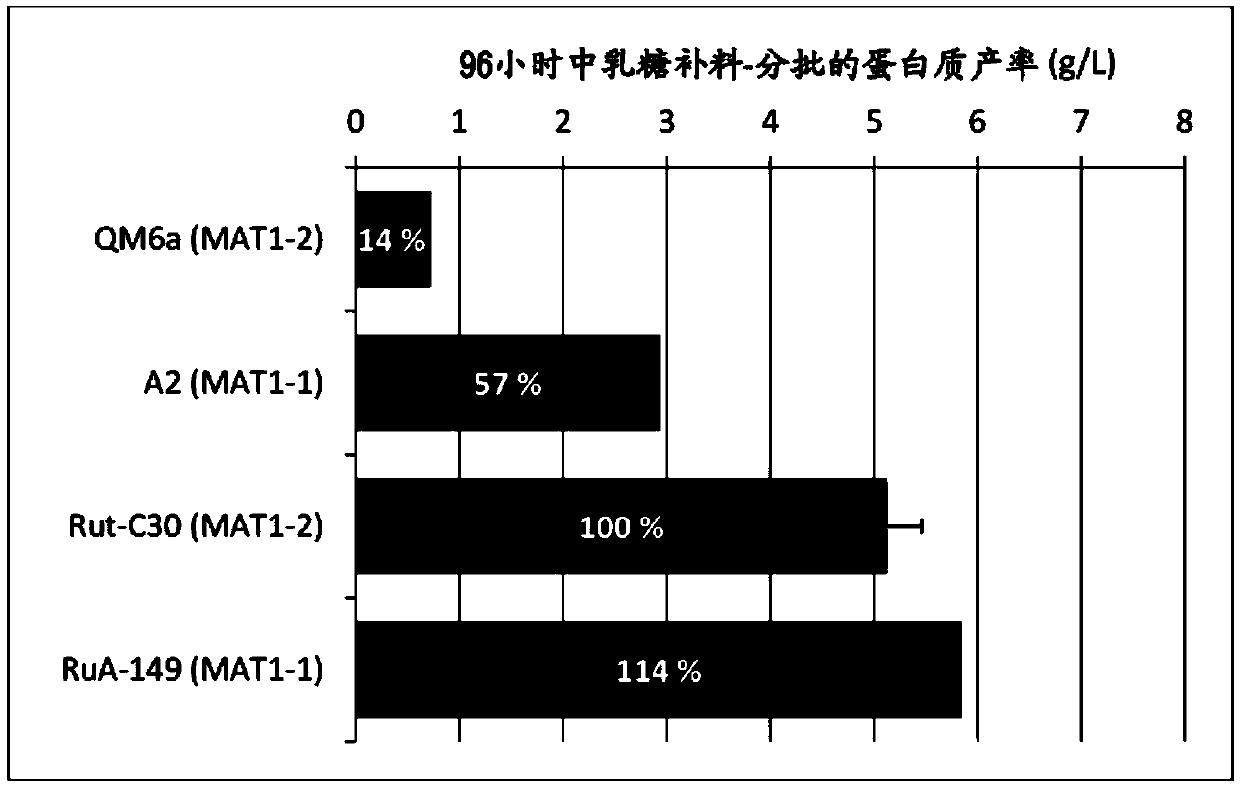
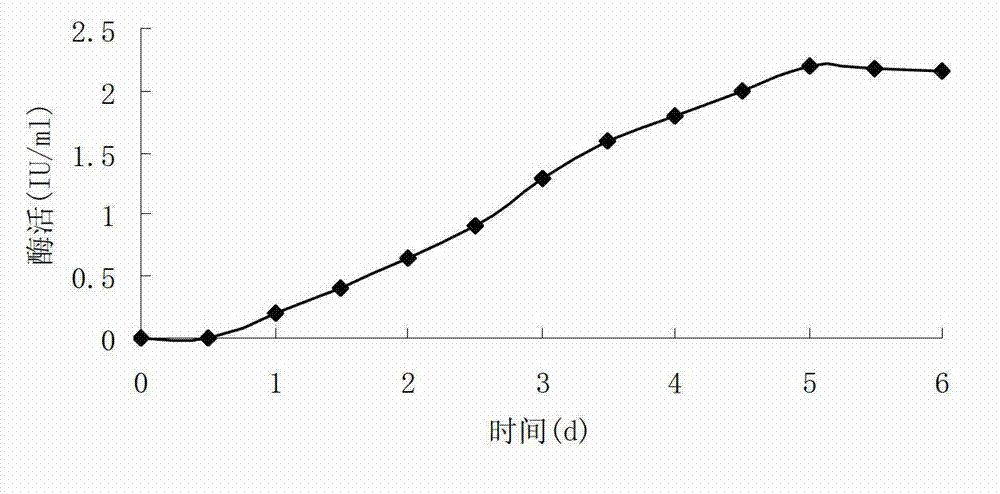Patents
Literature
38 results about "Beta-glucosidase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing beta-D-glucose residues with release of beta-D-glucose. [EC:3.2.1.21]
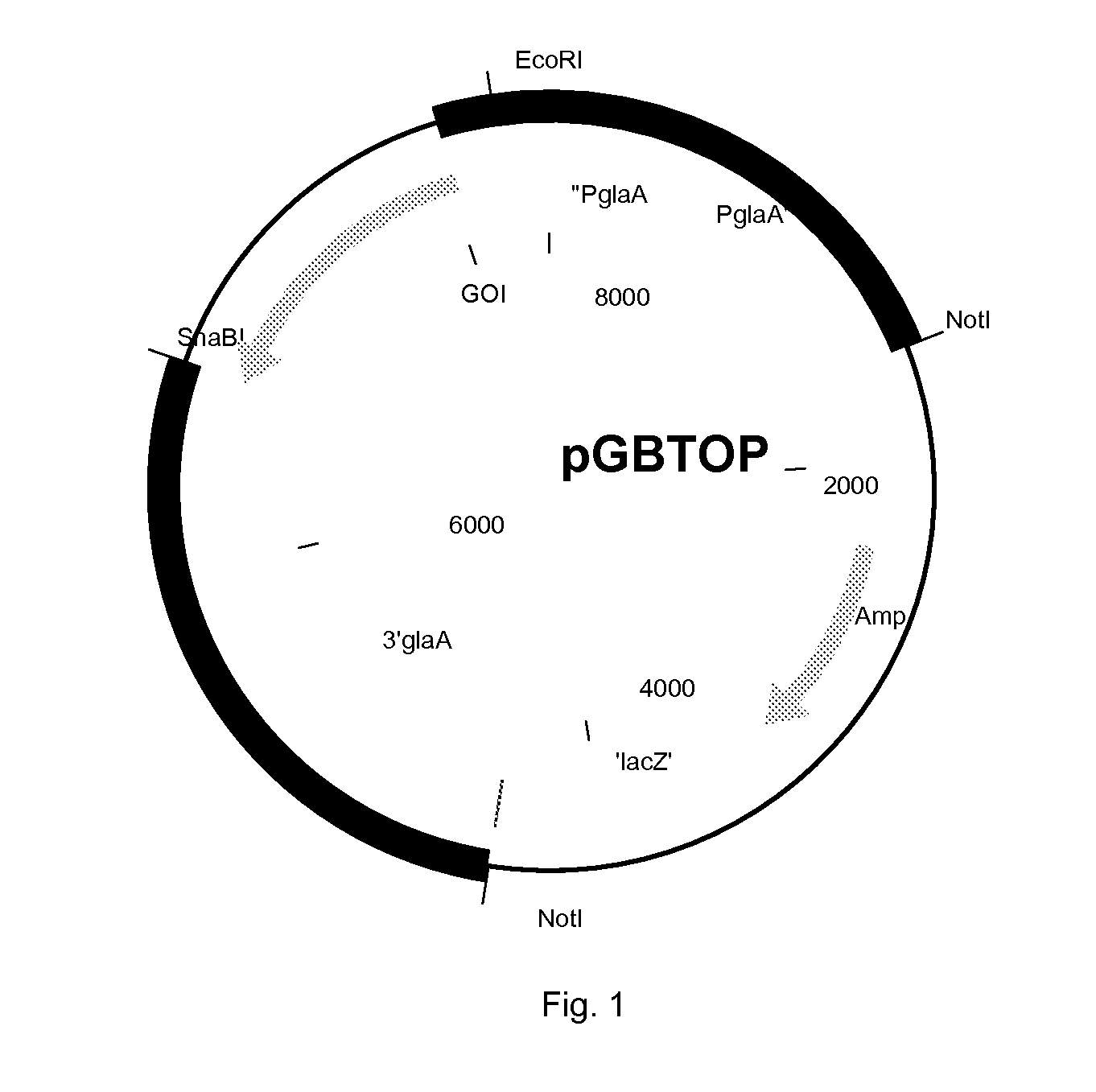
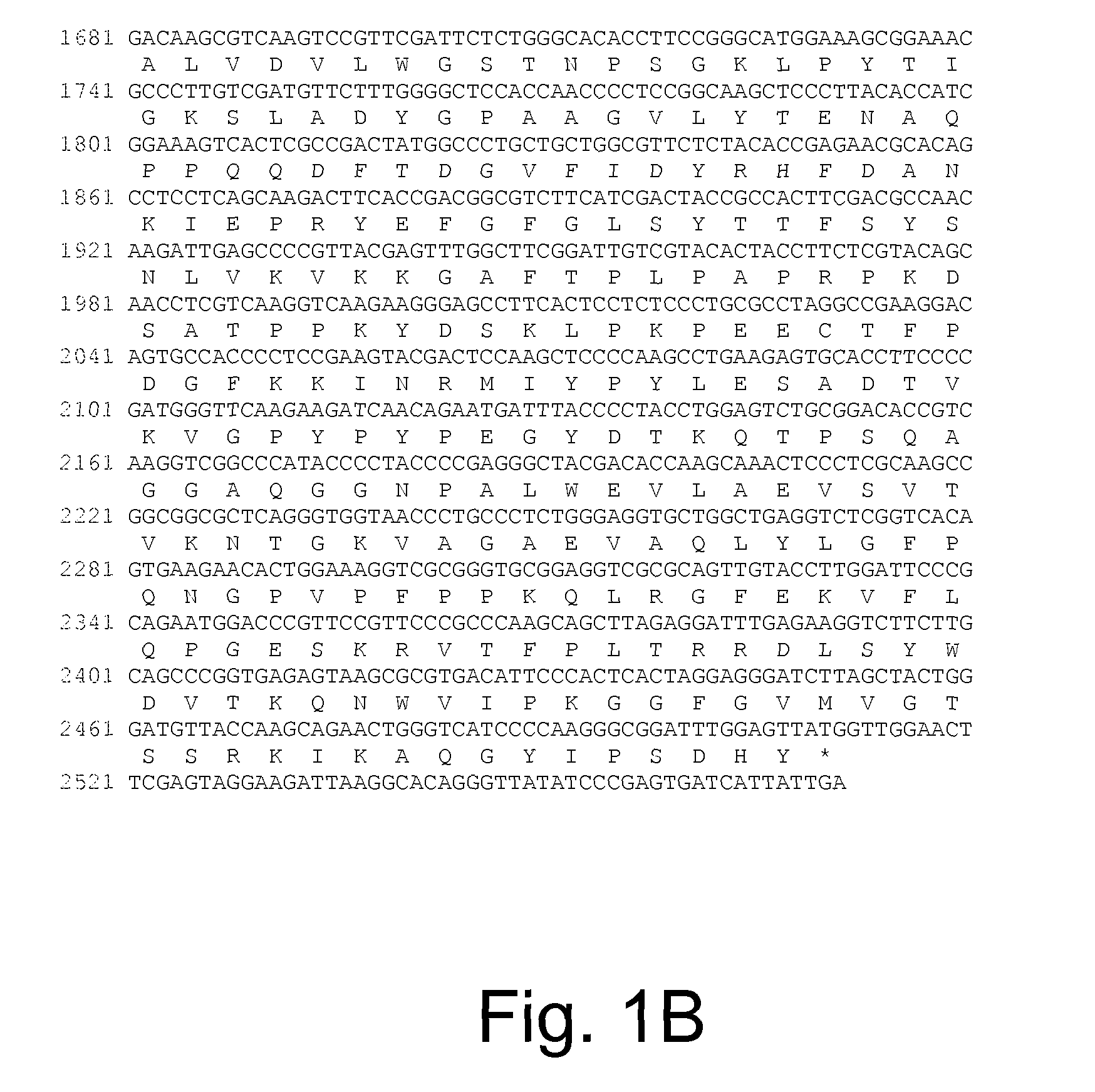
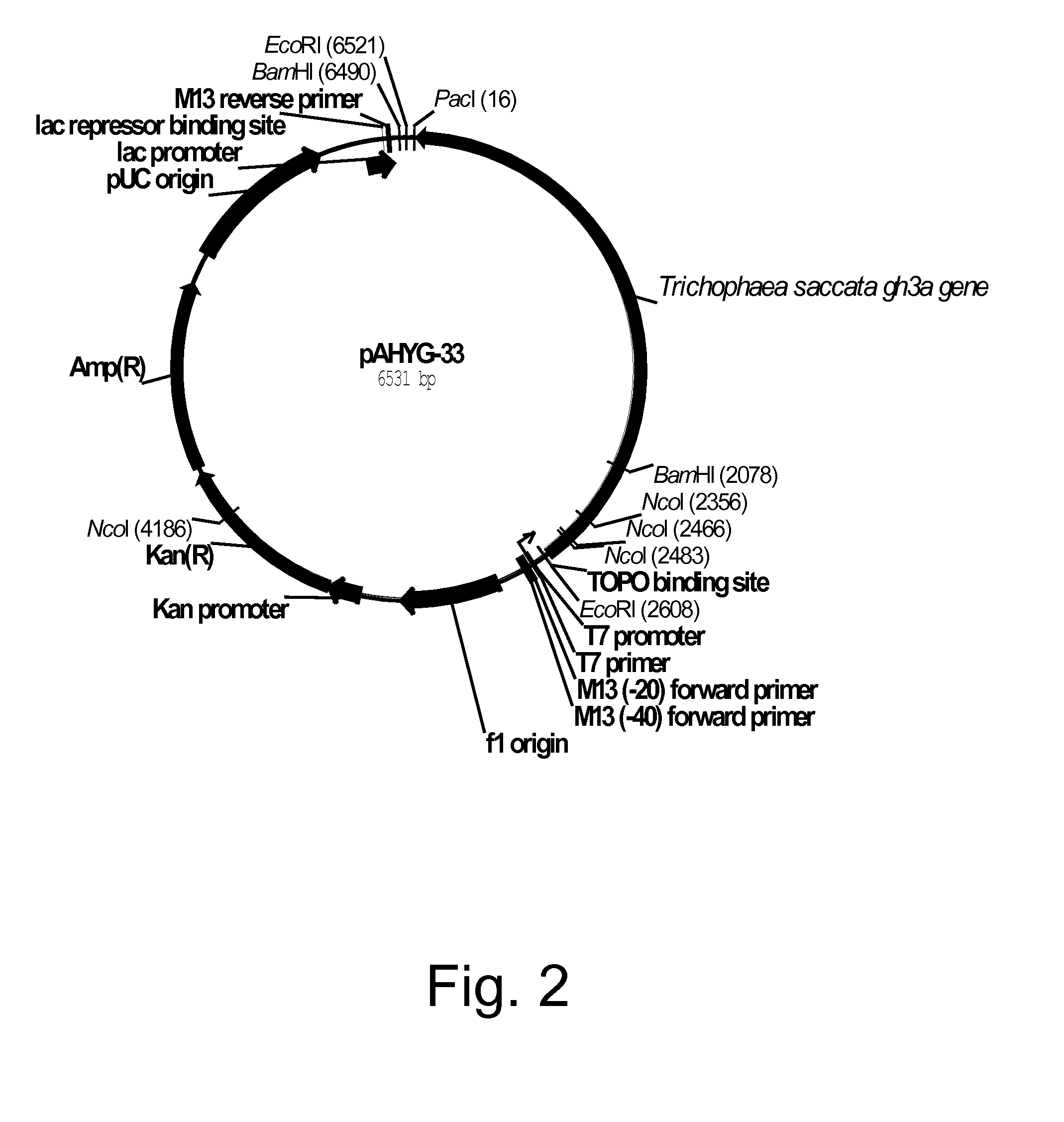
Polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and polynucleotides encoding same
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and isolated polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods for producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVO NORDISKBIOTECH INC
Polypeptides Having Beta-Glucosidase Activity and Polynucleotides Encoding Same
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and isolated polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods for producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
High-activity composite cellulase and preparation thereof, and application method for same in enzymatic saccharification of wood fiber
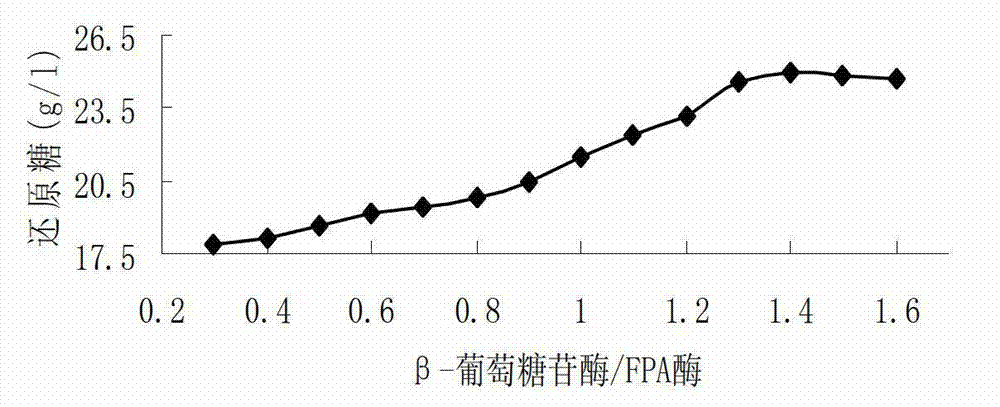
The invention discloses a high-activity composite cellulase and preparation thereof, and an application method for the same in enzymatic saccharification of wood fiber. According to the invention, Eupenicillium javanicum ZN-205 is subjected to shake-flask fermentation so as to produce beta-glucosidase; best enzyme production conditions are that an initial pH value is 6, the concentration of peptone is 0.75%, the concentration of microcrystalline cellulose is 2.5%, the addition amount of tween-80 is 0.05%, culture temperature is 28 DEG C, the volume of liquid filled in a 250 ml triangular flask is 100 ml, a revolving speed of a shaker is 175 r / min, inoculum amount is 5% and the highest activity of beta-glucosidase is 2.312 IU / ml; beta-glucosidase prepared from Eupenicillium javanicum ZN-205 and cellulase prepared from Trichoderma reesei Rut C-30 are compounded, and an obtained optimal ratio of beta-glucosidase activity to filter paper activity of 1.4. Utilization of the compounded enzyme for enzymatic saccharification of wood fiber enables high-efficiency and low-cost enzymatic saccharification effects to be achieved.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Variants of beta-glucosidases
The present invention relates to variants of a parent beta-glucosidase, comprising a substitution at one or more positions corresponding to positions 142, 183, 266, and 703 of amino acids 1 to 842 of SEQ ID NO: 2 or corresponding to positions 142, 183, 266, and 705 of amino acids 1 to 844 of SEQ ID NO: 70, wherein the variant has beta-glucosidase activity. The present invention also relates to nucleotide sequences encoding the variant beta-glucosidases and to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the nucleotide sequences.
Owner:NOVO NORDISKBIOTECH INC
Polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and polynucleotides encoding same
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and isolated polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Variants of Beta-Glucosidase
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Polypeptide having beta-glucosidase activity and uses thereof
ActiveUS9441214B2Few undesirable side activityLow production costSugar derivativesMicroorganismsBiotechnologyBeta-glucosidase activity
The invention relates to a polypeptide comprising the amino acid sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 2 or an amino acid sequence encoded by the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, or a variant polypeptide or variant polynucleotide thereof, wherein the variant polypeptide has at least 96% sequence identity with the sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 2 or the variant polynucleotide encodes a polypeptide that has at least 96% sequence identity with the sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention features the full length coding sequence of the novel gene as well as the amino acid sequence of the full-length functional polypeptide and functional equivalents of the gene or the amino acid sequence. The invention also relates to methods for using the polypeptide in industrial processes. Also included in the invention are cells transformed with a polynucleotide according to the invention suitable for producing these proteins.
Owner:VERSALIS SPA
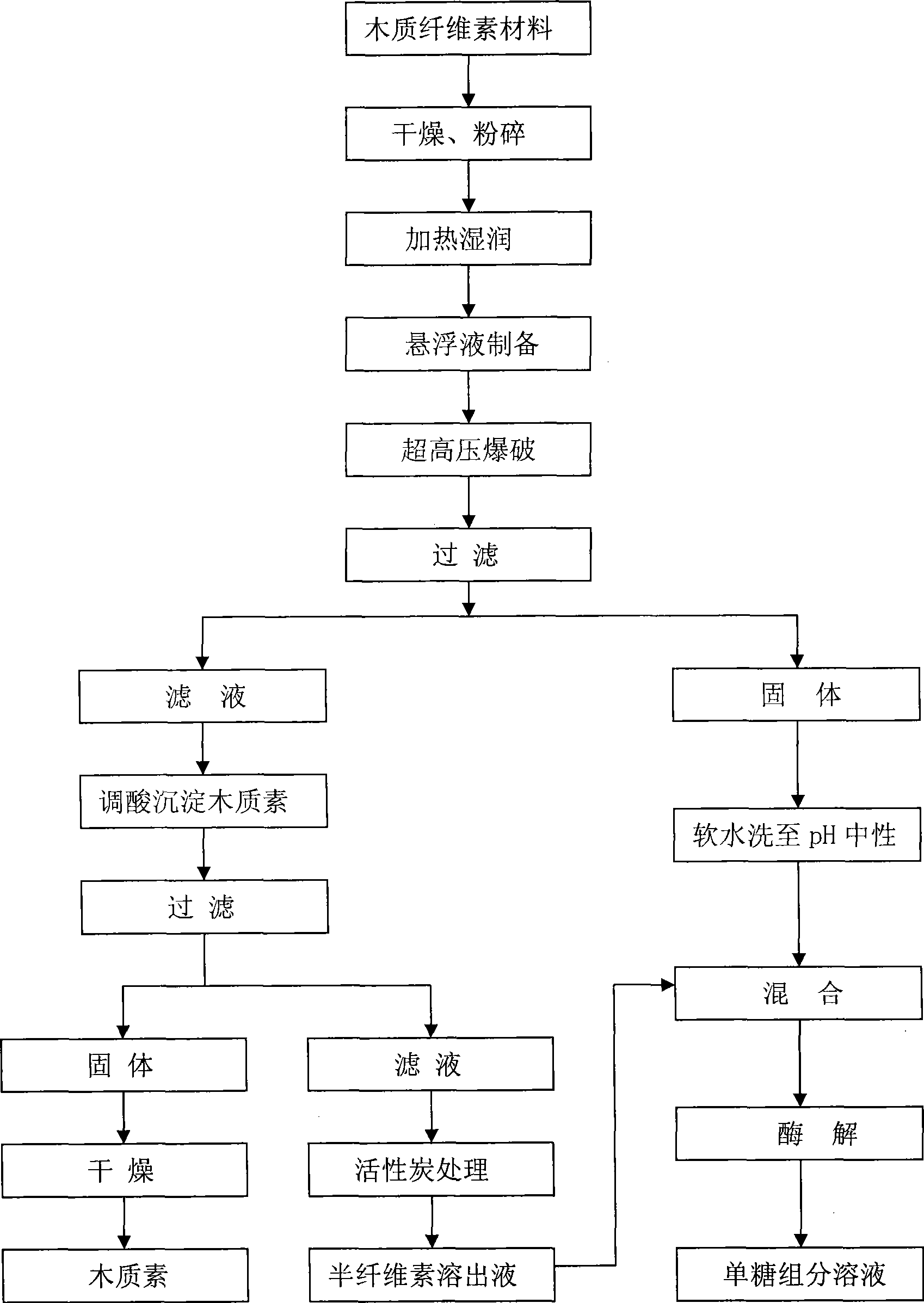
Pretreatment method for ultra-high pressure blasting wood fiber material
InactiveCN101463571AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis rateReduce processing intensityPulping with inorganic basesRaw material divisionCelluloseFiber
The invention discloses a pretreatment method for lignocellulosic materials. The method is as follows: a high-pressure homogenizer which is conventional but is currently only used for processing liquid state materials is taken as the treatment equipment, a stirring device is installed at the feed funnel of the homogenizer, the materials are exploded under ultrahigh pressure by means of transient pressure and pressure elimination in the homogenizing process. The method comprises the steps as follows: the pre-processes like drying, smashing and sieving, etc. of the lignocellulosic materials, the heating and moistening of the materials, the preparation of the suspending liquid, the ultrahigh pressure explosion and the material process after explosion, etc. Compared with various currently disclosed pretreatment methods for lignocellulosic materials, the method not only has the advantages of low requirement for equipment, mild process condition, no harmful substances which inhibit microorganism fermentation and low energy consumption, etc. but also can process the ultramicrostructure which totally changes the lignocellulosic materials and creatively realize the full hydrolyzation of the lignocellulosic materials by making use of the cellulolytic enzyme system of low beta-glucosidase activity.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
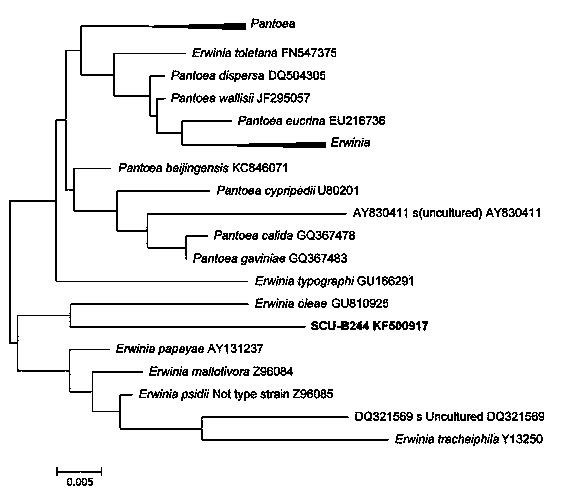
Chlorpyrifos degrading bacteria and application thereof
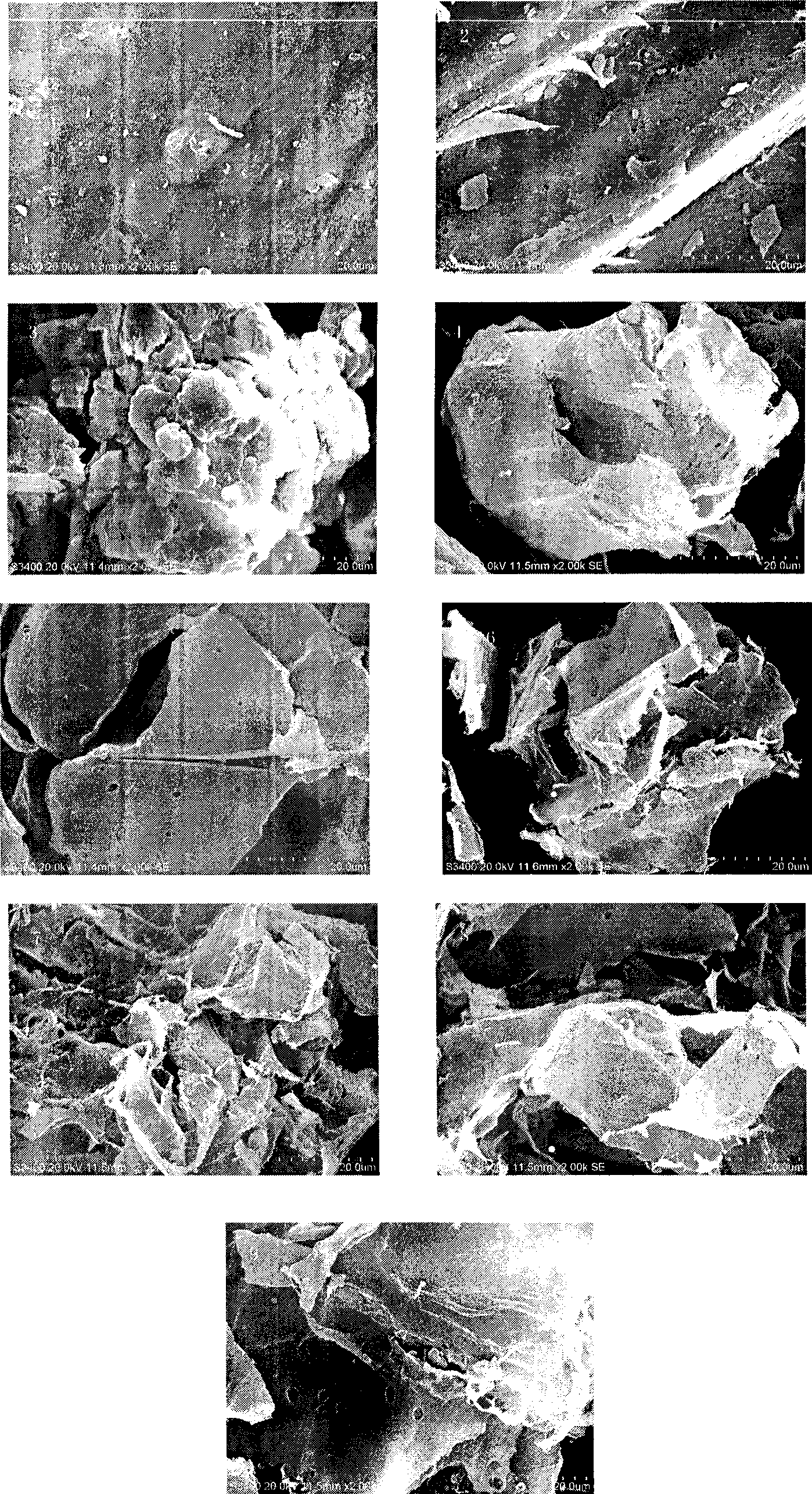
The invention discloses a chlorpyrifos degrading bacteria Erwiniaxishuaiensis SCU-B244<T> = CGMCCNo.1.12772<T> = KCTC42022<T> (Figure) (i). Through the separation from the cricket body surface, screening, physiological and biochemical identification, the bacteria is identified as gram negative and facultative aerobic bacteria, which has cream bacterium colony, and is oxidase negative and catalase positive; the cells mainly comprises fatty acids of C16:0, C16:1delta<9>, C18:1delta<9>, C11:0<3-OH> and C14:0<3-OH>, GC content in cells is 49.3%-49.5%; and the bacteria has alkaline phosphatase, esterase (C4), lipase (C8), acid phosphatase, beta-galactosidase and beta-glucosidase activities. The bacteria has one day degradation rate on chlorpyrifos of 44.64%, and can be widely used in the fields of development of chlopyrifos degrading enzyme and various types of biological engineering enzyme preparations. Figure instructions: the figure is photos of Erwinia xishuaiensis SCU-B244<T> under 30000 times scanning electron microscope.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Polypeptide having beta-glucosidase activity and uses thereof
ActiveUS9121013B2Few undesirable side activityLow production costFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention relates to a polypeptide comprising the amino acid sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 2 or an amino acid sequence encoded by the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, or a variant polypeptide or variant polynucleotide thereof, wherein the variant polypeptide has at least 70% sequence identity with the sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 2 or the variant polynucleotide encodes a polypeptide that has at least 70% sequence identity with the sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention features the full length coding sequence of the novel gene as well as the amino acid sequence of the full-length functional polypeptide and functional equivalents of the gene or the amino acid sequence. The invention also relates to methods for using the polypeptide in industrial processes. Also included in the invention are cells transformed with a polynucleotide according to the invention suitable for producing these proteins.
Owner:VERSALIS SPA
Polypeptide having beta-glucosidase activity and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130095531A1Maintain good propertiesBroad specificitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsBiotechnologyBeta-glucosidase activity
The invention relates to a polypeptide comprising the amino acid sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 2 or an amino acid sequence encoded by the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, or a variant polypeptide or variant polynucleotide thereof, wherein the variant polypeptide has at least 70% sequence identity with the sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 2 or the variant polynucleotide encodes a polypeptide that has at least 70% sequence identity with the sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention features the full length coding sequence of the novel gene as well as the amino acid sequence of the full-length functional polypeptide and functional equivalents of the gene or the amino acid sequence. The invention also relates to methods for using the polypeptide in industrial processes. Also included in the invention are cells transformed with a polynucleotide according to the invention suitable for producing these proteins.
Owner:VERSALIS SPA
Polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and polynucleotides encoding same
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and isolated polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC +1
Penicillium oxalicum capable of degrading 2-phenethyl alcohol produced from rice straw and application thereof
ActiveCN110484452APromote degradationStrong endoglucosidase activityFungiMicroorganism based processesPhenethyl alcoholPenicillium oxalicum
The invention provides penicillium oxalicum capable of degrading 2-phenethyl alcohol produced from rice straw and application thereof. The penicillium oxalicum is penicillium oxalicum T1, and was preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection. The preservation number is CCTCC M 2019608. The penicillium oxalicum T1 provided by the invention has good cellulose degradation ability, can produce cellulase, and has strong endoglucosidase activity, filter paper enzyme activity, exonuclease activity and beta-glucosidase activity; and the penicillium oxalate T1 can degrade 2-phenethyl alcohol produced by degradation of rice straw. The fermentation broth that degrades rice straw can inhibit Phomopsis sp., Magnaporthe grisea and Fusarium oxysporum.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
Beta-glucosidase variant enzymes and related polynucleotides
The invention provides variants of the Thermoanaerobacter brockii CglT beta-glucosidase that have improve beta-glucosidase activity compared to the wild type enzyme. The invention also provides polynucleotides that encode the variants, as well as methods of producing the variants, enzyme compositions comprising the variants, and methods for using the variants in industrial applications.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Bacillus subtilis for inhibiting phomopsis and application thereof
ActiveCN109929782APromote degradationStrong endoglucosidase activityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsKiwi fruitStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a bacillus subtilis for inhibiting phomopsis which is bacillus subtilis T8 deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 5, 2018 with the preservation numberof CCTCC NO: M 2018860. The bacillus subtilis T8 has good cellulose degradation capability, can produce cellulase, and has strong endoglucanase activity, filter paper enzymatic activity, exonucleaseactivity and beta-glucosidase activity. The bacillus subtilis T8 can inhibit phomopsis, and an ethanol supernatant and a protein have inhibitory effects on the phomopsis. In addition, the bacillus subtilis T8 can inhibit the growth of escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, candida albicans, shigella dysenteriae and enterobacter faecalis, and has a development and utilization value in inhibitinghuman pathogenic bacteria. The invention also provides application of the bacillus subtilis T8 in producing cellulase and preventing kiwi fruit soft rot.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
6-phosphoric acid-beta-glucosidase and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a 6-phosphoric acid-beta-glucosidase Pbgl and a coding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the 6-phosphoric acid-beta-glucosidase is shown in SEQ ID NO.2,or, amino acid residue in the amino acid sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO.2 is subjected to any one or more modification of substitution, deletion and addition to obtain amino acid sequence with 6-phosphoric acid-beta-glucosidase activity. According to the 6-phosphoric acid-beta-glucosidase Pbgl and the coding gene and application thereof, clone is carried out on bacillus thermophilus CCTCC No: M2011468 to obtain a new 6-phosphoric acid-beta-glucosidase gene pbgl, the new 6-phosphoric acid-beta-glucosidase gene pbgl can be expressed in host cells to produce the 6-phosphoric acid-beta-glucosidase for degradation of cellulose.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Polypeptides having Beta-glucosidase Activity and Polynucleotides Encoding Same
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and isolated polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC +1
Beta-glucosidase variant enzymes and related polynucleotides
The invention provides variants of the Thermoanaerobacter brockii CglT beta-glucosidase that have improve beta-glucosidase activity compared to the wild type enzyme. The invention also provides polynucleotides that encode the variants, as well as methods of producing the variants, enzyme compositions comprising the variants, and methods for using the variants in industrial applications.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and polynucleotides encoding same
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and isolated polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method for producing xylo-oligosaccharide
Disclosed is a method for producing a xylo-oligosaccharide from a biomass containing xylan and cellulose, wherein the method is simple and a high xylo-oligosaccharide yield is achieved by suppressingxylo-oligosaccharide from being broken down to xylose. According to the method for producing xylo-oligosaccharide, a biomass containing xylan and cellulose is hydrolyzed by a cellulase composition that, at the time of hydrolysis, at least exhibits xylanase, cellobiohydrolase, and beta-glucosidase activities, but does not substantially exhibit beta-xylosidase activity.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Novel glycosyl hydrolase with beta-xylosidase and beta-glucosidase activities and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130130330A1Improve propertiesMass productionDough treatmentBacteriaSilane compoundsBeta-glucosidase activity
A novel glycosyl hydrolase with activities of beta-xylosidase and beta-glucosidase is provided. Said glycosyl hydrolase can convert 7-xylosyltaxane compounds to 7-hydroxyltaxane compounds.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and polynucleotides encoding same
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC +1
Use of a sugar tolerant beta-glucosidase
InactiveUS20190330607A1Efficient hydrolysisHigh activityBiofuelsAlcoholic beverage preparationCelluloseAlglucerase
A method of providing a polypeptide having sugar-tolerant beta-glucosidase activity for hydrolysis of a lignocellulosic substrate to yield glucose and / or other sugars. Also provided is a host cell comprising and / or secreting said polypeptide and a kit-of-parts comprising said polypeptide and one or more other cellulases for hydrolyzing a lignocellulosic substrate in a sugar-tolerant manner.
Owner:UNIV LIEGE
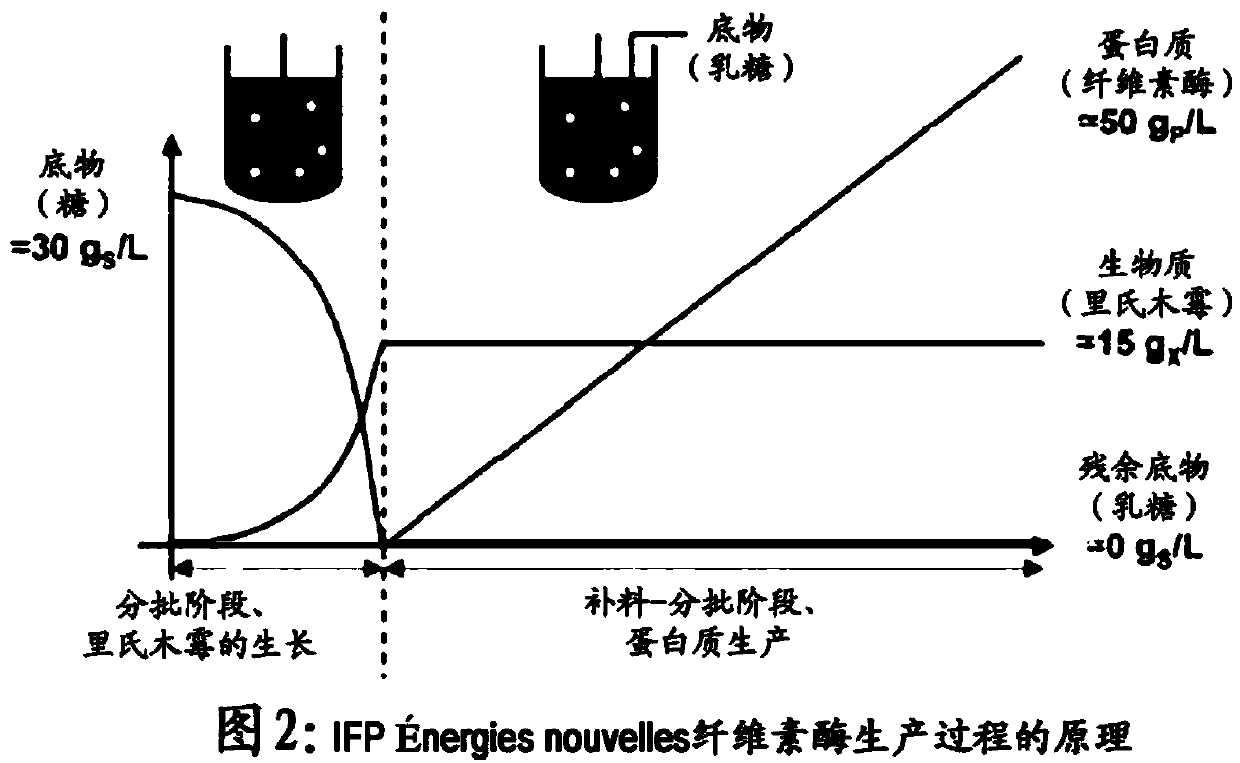
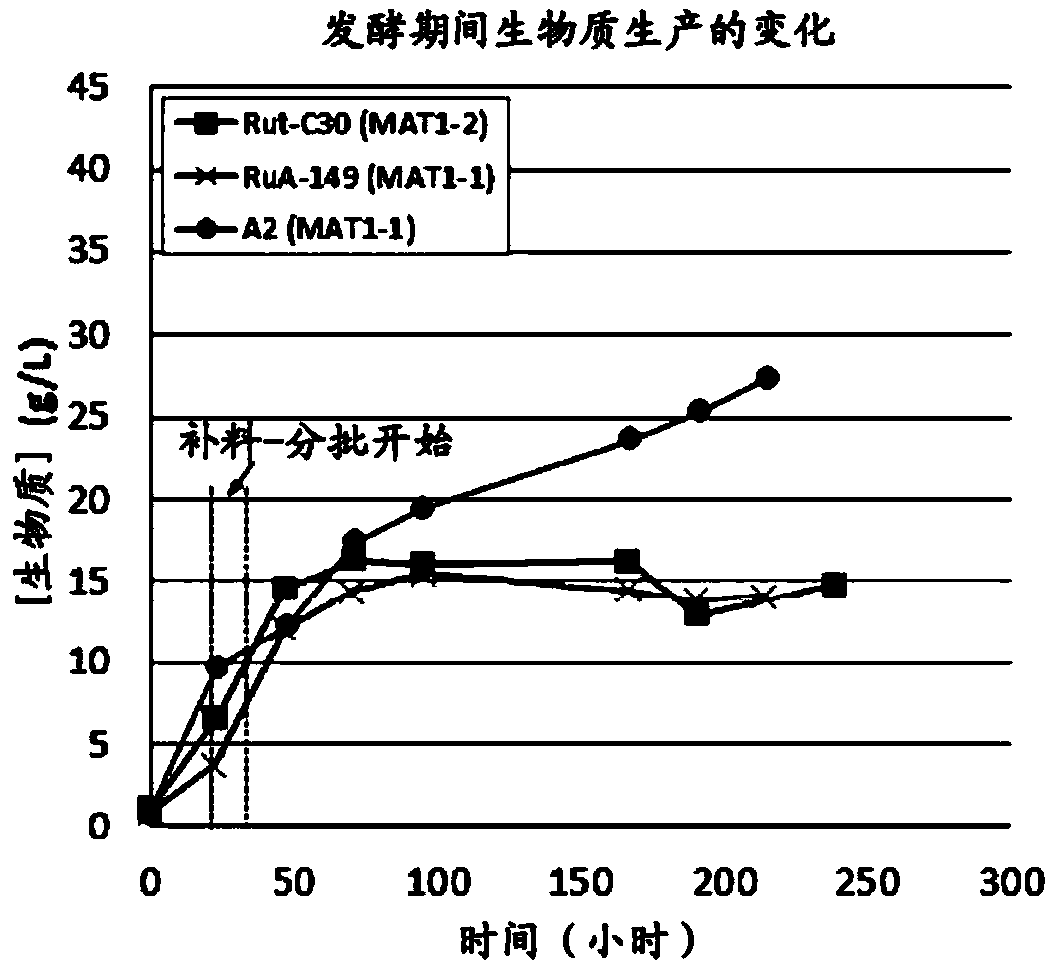
Hyperproductive trichoderma reesei strain featuring improved beta-glucosidase activity
The present invention relates to a Trichoderma reesei strain which is hyper-producing and which has enhanced beta-glucosidase activity, as well as the use of said strain.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and polynucleotides encoding same
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having beta-glucosidase activity and isolated polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Pseudomonas protegens inhibiting phomopsis and application of pseudomonas protegens
ActiveCN110004087APromote degradationStrong endoglucosidase activityBiocideBacteriaStaphylococcus aureusActinia
The invention provides pseudomonas protegens inhibiting phomopsis. The pseudomonas protegens is pseudomonas protegens 13, and is preserved in the Chinese typical culture preservation center on December 5, 2018, wherein the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2018861. The pseudomonas protegens 13 has a good cellulose degradation ability, can produce cellulase, has stronger incision glucosidase activity, filter paper enzyme activity, excision enzyme activity and beta-glucosidase activity, and has application value in the production of the cellulase. The pseudomonas protegens 13 can inhibit the phomopsis. In addition, the pseudomonas protegens 13 can inhibit the growth of escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, candida albicans, shigella dysenteriae and enterobacter faecalis, and has development and utilization value in inhibiting human pathogenic bacteria. The invention also provides the application of the pseudomonas protegens 13 in producing cellulase and controlling kiwi soft rot.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
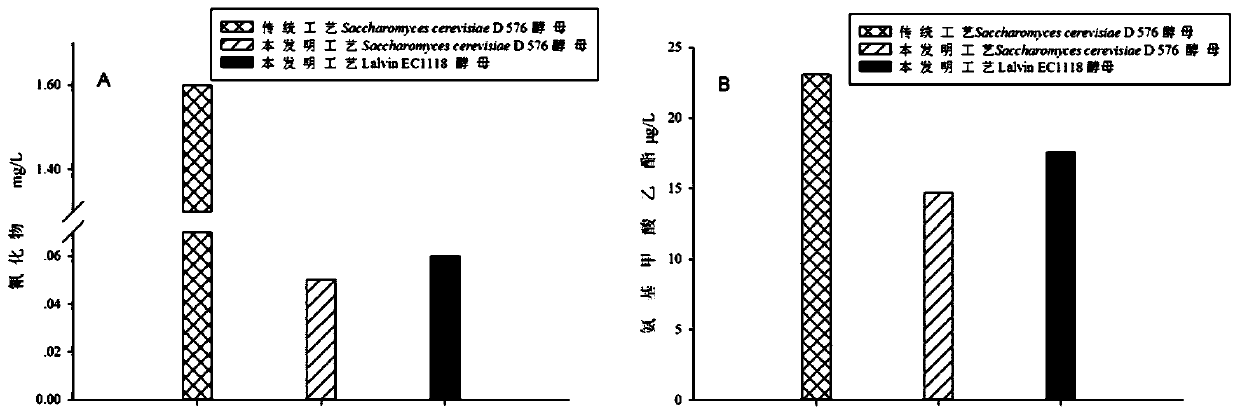
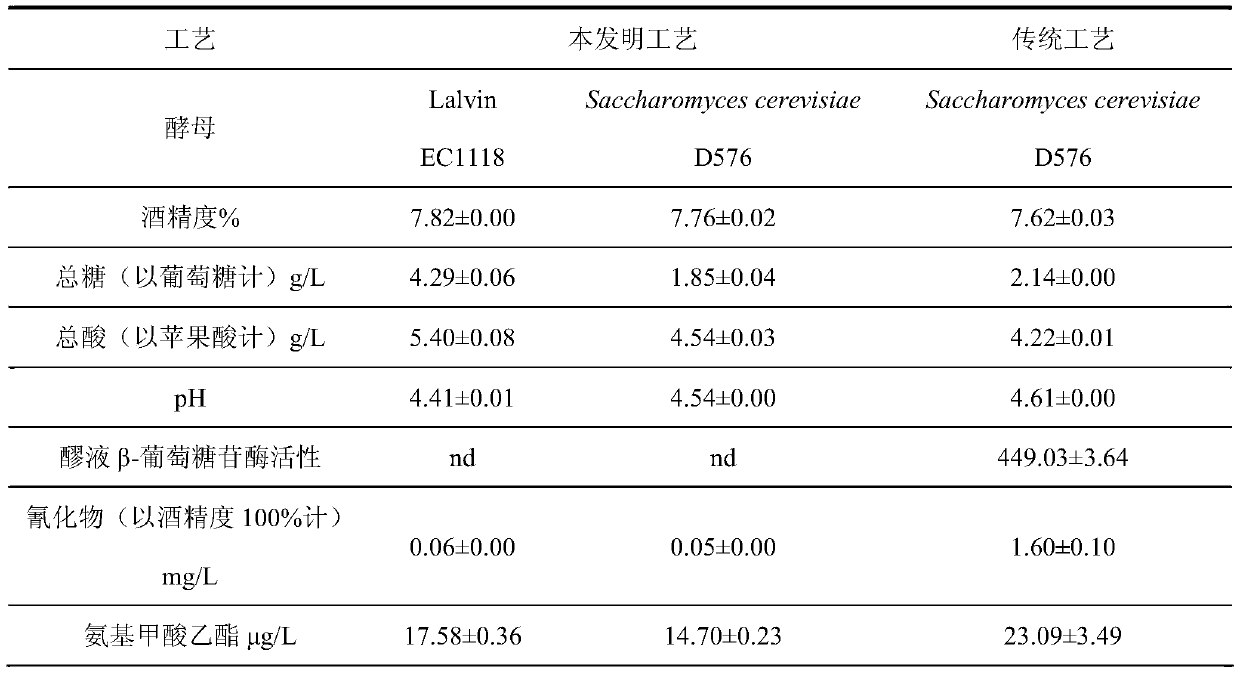
Method for simultaneously reducing cyanide and ethyl carbamate in cherry wine
ActiveCN110484409AReduce contentBright colorMicroorganism based processesAlcoholic beverage preparationBeta-GlucosidasesPhotochemistry
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously reducing cyanide and ethyl carbamate in cherry wine. Healthy cherries are used as raw materials, cherry mash obtained by breaking the cherries is boiled at 100 DEG C for 5 min, it is avoided that cyanide is produced by amygdalin due to the function of beta-glucosidase in microorganisms and the cherry raw materials, and then production of ethyl carbamate is reduced. By adopting special fruit wine yeast with low beta-glucosidase activity, the content of cyanide and ethyl carbamate in the cherry wine can be further reduced. By means of the method, the content of cyanide and ethyl carbamate in the cherry wine can be effectively reduced, and the quality of the fermented cherry wine is improved; the cherry wine prepared by the method is orangered, bright in color, and clear, transparent and glossy in liquor, and the content of cyanide and ethyl carbamate is significantly lower than that of a traditional technology.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain FM-S-4 capable of improving color and luster stability of fruit wine and application
ActiveCN107746814ASecurity resourcesReliable resourceFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationFruit wineFlocculation
The invention relates to a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain FM-S-4 capable of improving the color and luster stability of fruit wine and application and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. A novel saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with low beta-glucosidase activity, strong flocculation capability and good fermentation performance is screened from a traditional fermented food, namely Kefir grains, is named as FM-S-4 and is identified to saccharomyces cerevisiae. The FM-S-4 is used as a fruit wine fermentation agent of berries including blackberries, blueberries and the like and the reduction of content of phenol substances and anthocyanin substances in fruit wine fermentation and ageing processes can be effectively alleviated; the color and luster stability of the fruit wine is easy to improve; the fermentation and clarification time is shortened and the flavor of the fruit wine is improved, so that the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain FM-S-4 has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
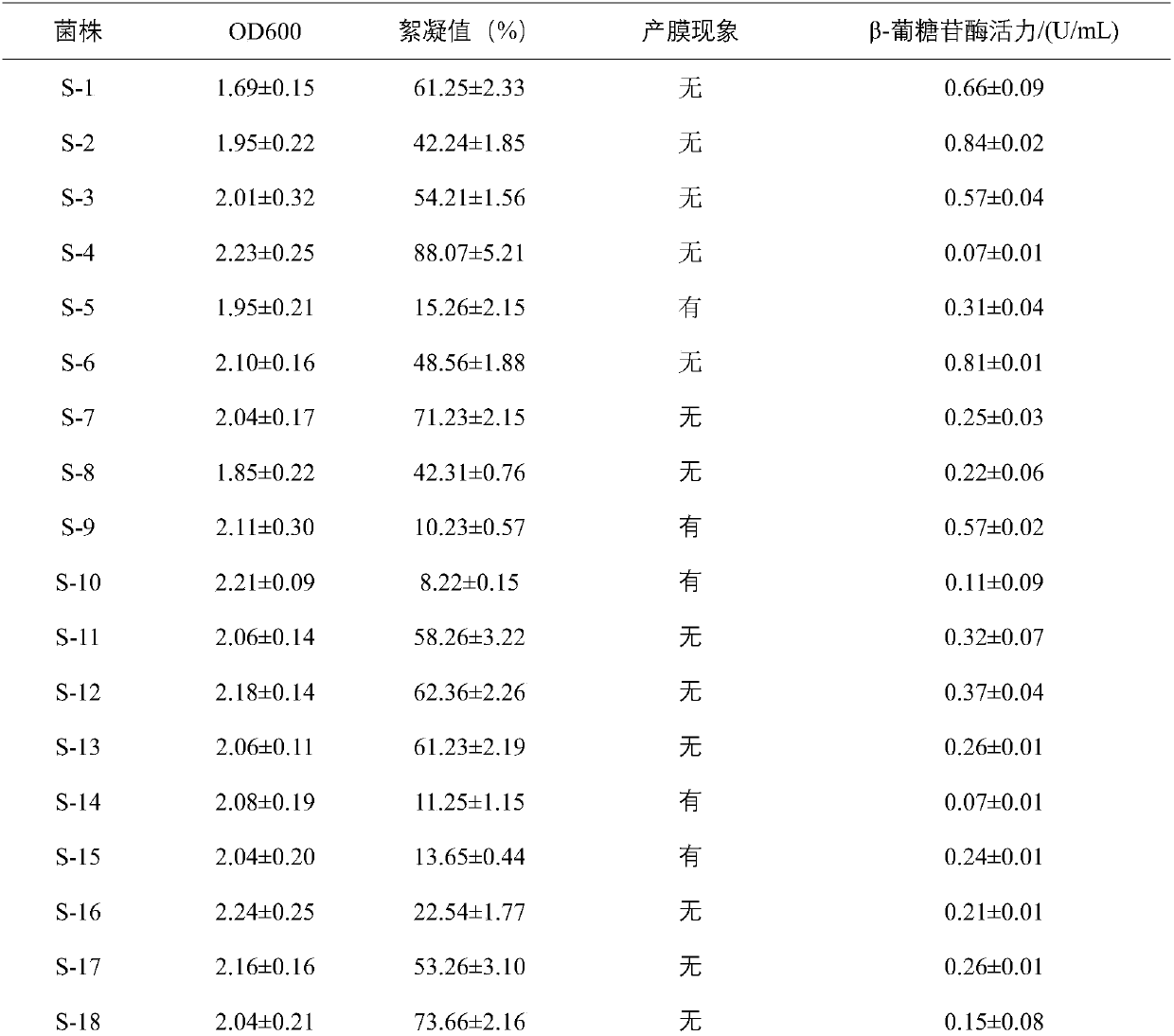
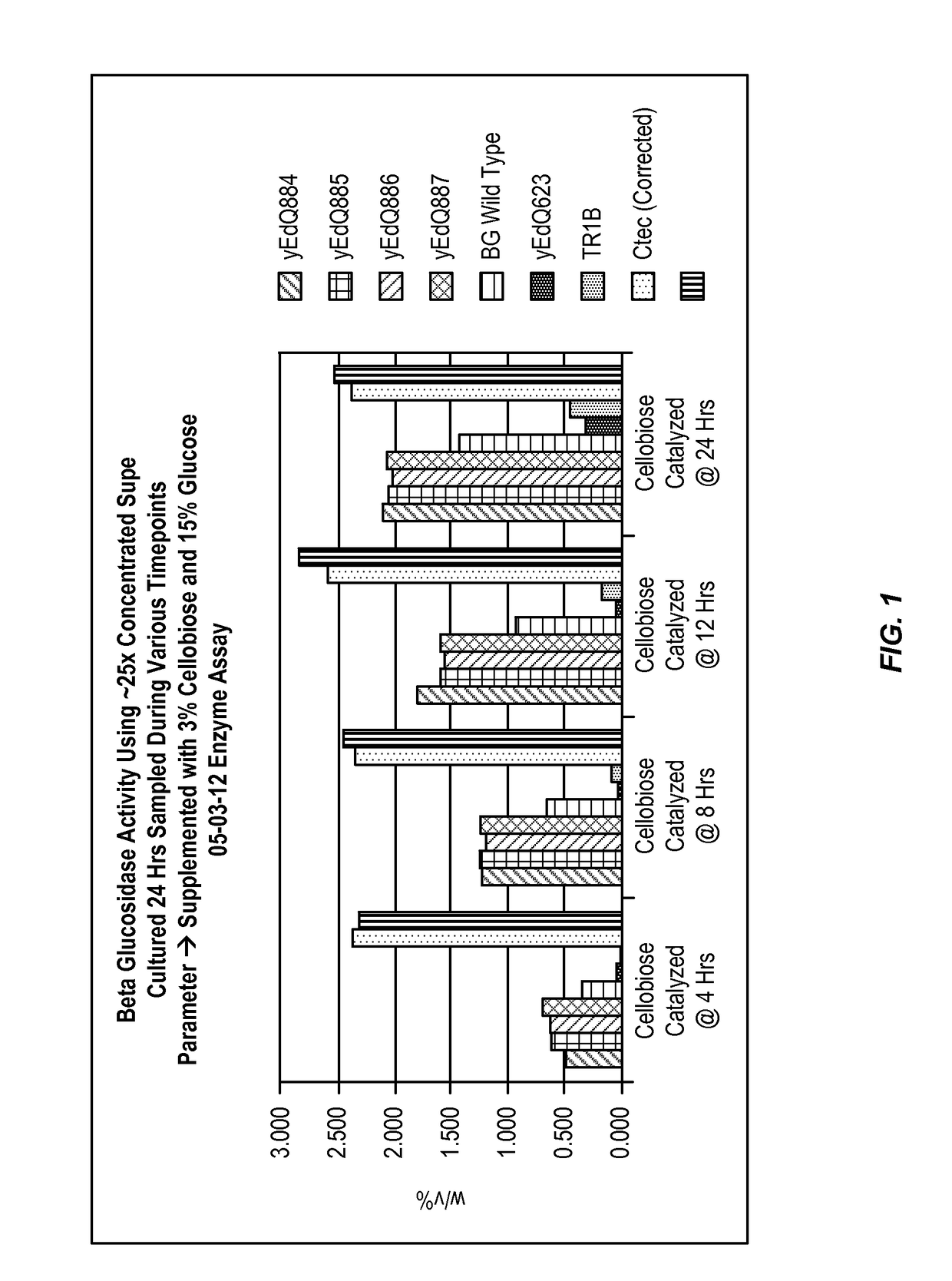
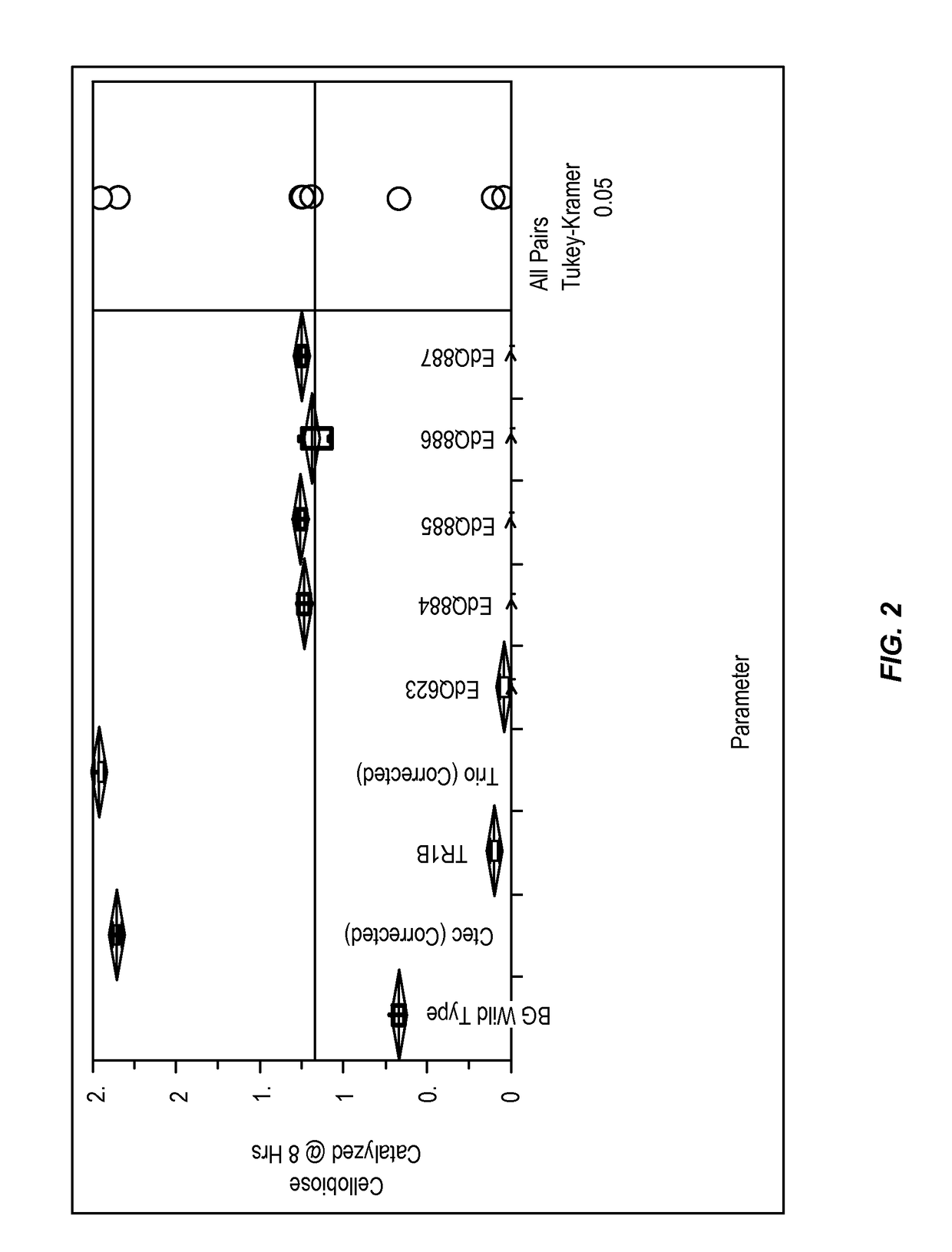
Beta-glucosidase enzymes for increased biomass saccharification
Described herein are beta-glucosidase enzymes that have improved beta-glucosidase activity compared to a control beta-glucosidase enzyme. The improved beta-glucosidase enzymes are useful for converting a cellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars such as glucose. Also described are isolated polynucleotides that encode polypeptides having improved beta-glucosidase activity, expression cassettes for expressing the improved beta-glucosidase polypeptides, and cells, such as yeast cells, transformed with the expression cassettes.
Owner:EDENIQ INC
Methods and compositions for stimulating tissue growth and epithelial moisturization
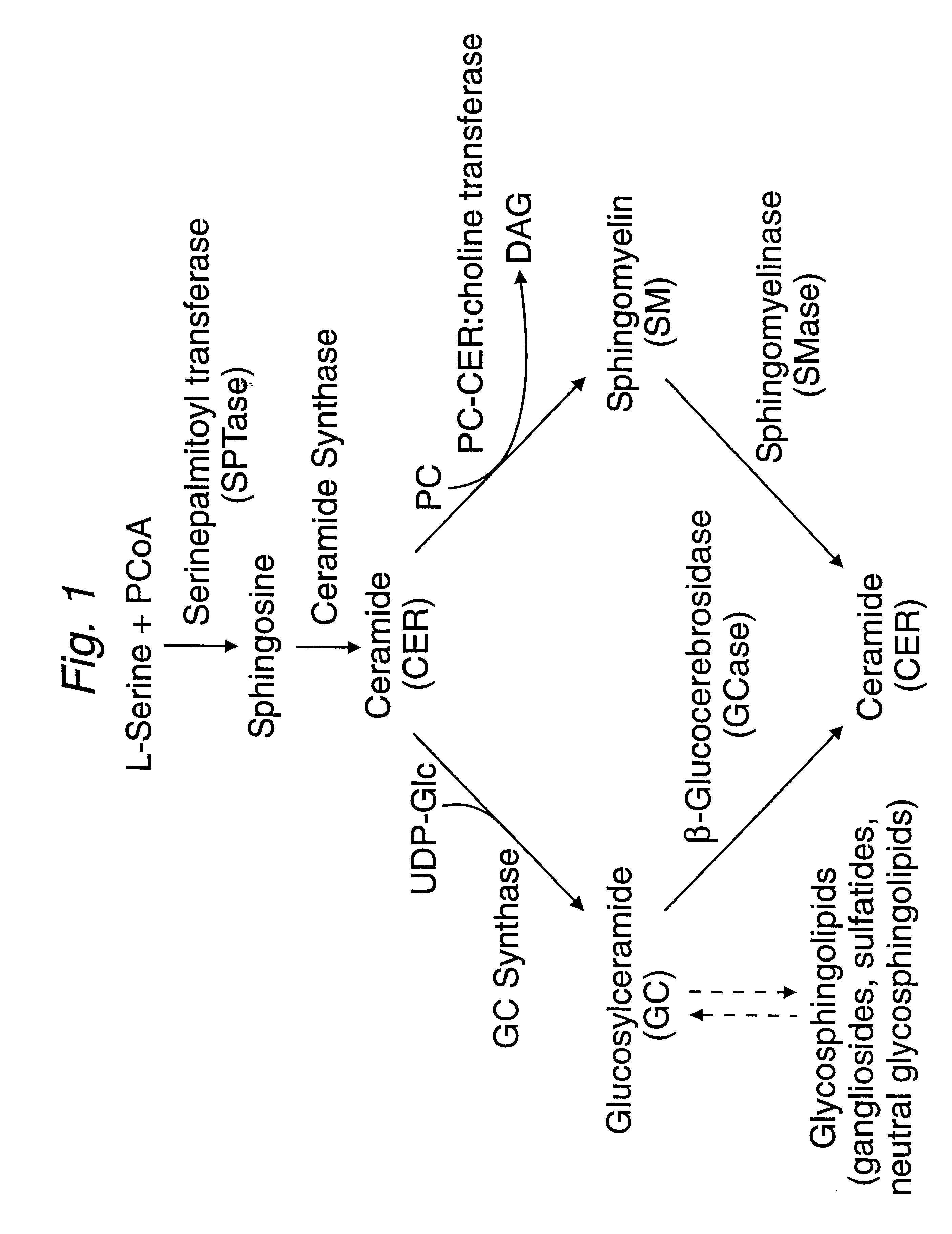
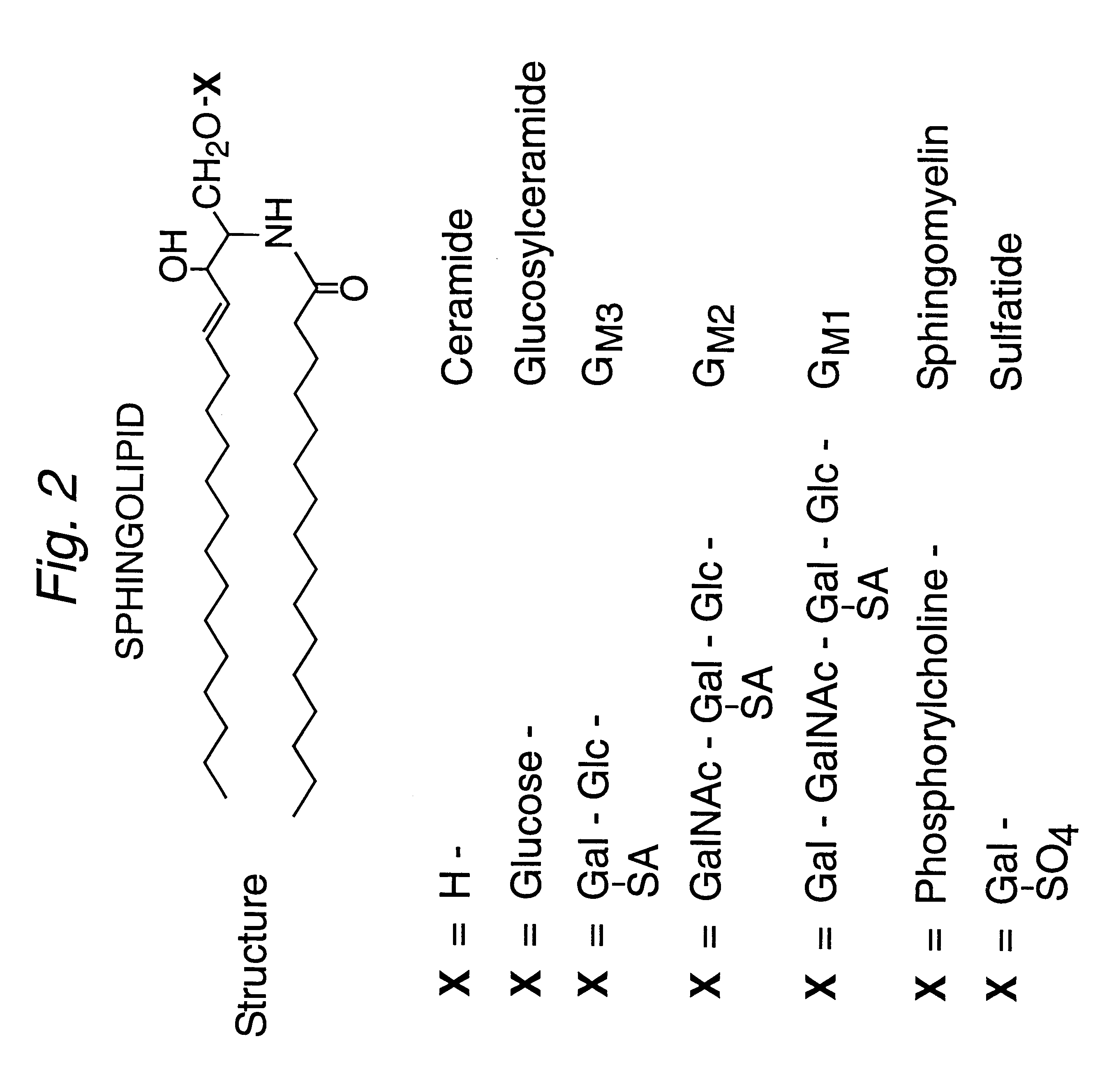
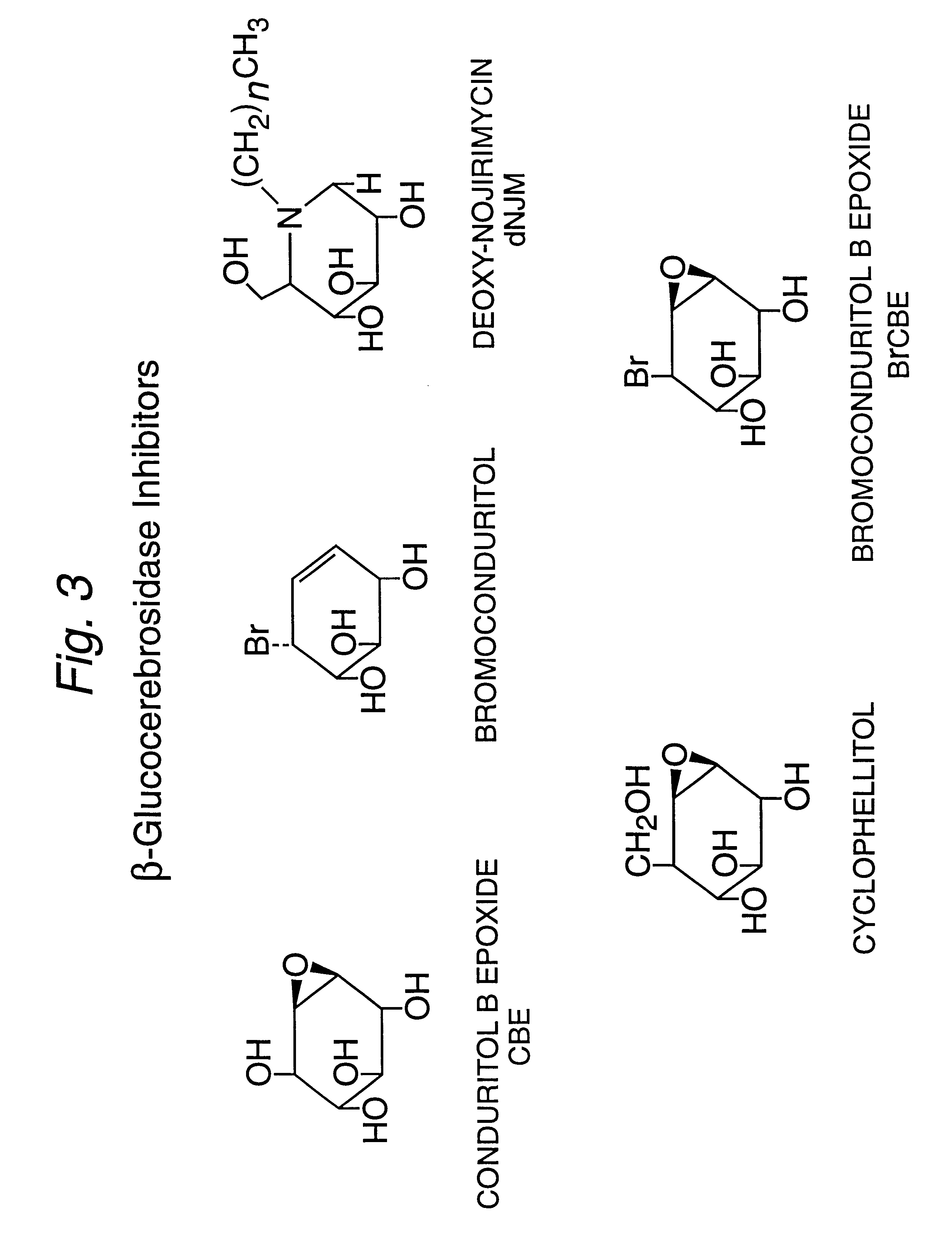
The invention herein encompasses methods effective to stimulate epithelial cell proliferation and / or enhance epithelial moisturization and lubrication in a mammalian subject utilizing a composition comprising one or more inhibitors of beta-glucosidase activity or beta-glucocerebrosidase activity. The composition of the method may alternatively comprise a glycosphingolipid, particularly glucocerebroside, or a combination of the above inhibitor(s) and a glycosphingolipid. The method is effective to enhance the cosmetic appearance of skin and promote healing of skin and mucous membranes damaged or deficient from aging, traumatic wounds, photo-aging and a variety of atrophic conditions.The method may be applied to cells in culture. Also included in the invention is a composition comprising one or more inhibitors of beta-glucosidase and a glycosphingolipid useful to stimulate cell proliferation and enhance tissue moisturization and lubrication.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com