Method for detecting dioxin and dioxin polychlorinated biphenyl in poultry eggs
A technology of dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls, which is applied in measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of interference, cumbersome pretreatment purification methods, complex substrates, etc., and achieves the effect of safe and environmentally friendly extraction of solvents.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
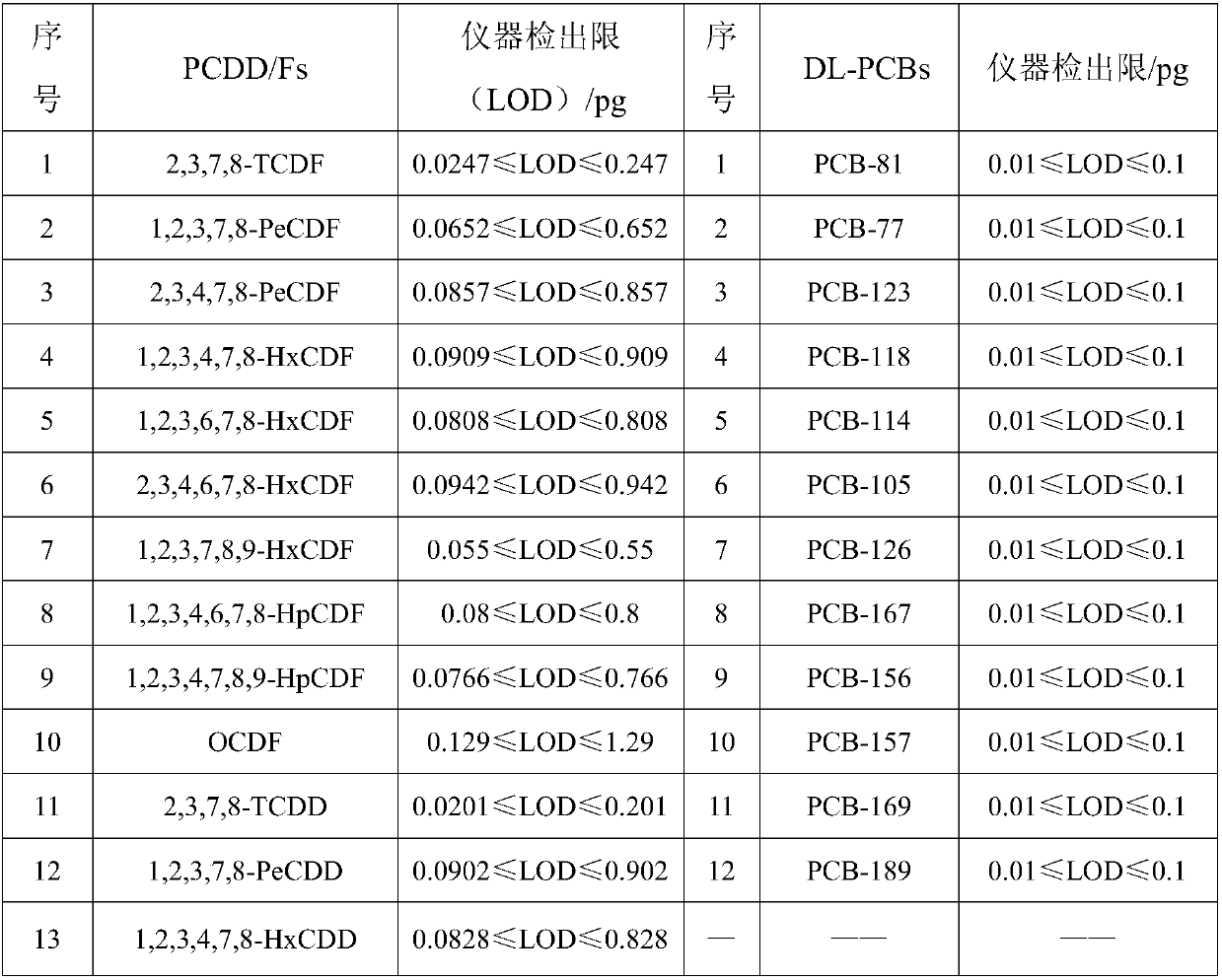
[0045] The method for detecting dioxins and dioxins-like polychlorinated biphenyls in poultry eggs provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0046] (1) Sample preparation
[0047] Collect egg samples (including eggs, duck eggs, goose eggs, pigeon eggs, quail eggs and snake eggs), and mark and number them. The samples collected on site are packed with light-proof materials such as aluminum foil, and are transported to the experiment in a small freezer Store at room temperature.
[0048] Place the sample in an oven at 90-100°C, wait for the egg whites to solidify, remove the shell with tweezers, place it on tin foil, and bake it in an oven at 90-100°C for 21 to 33 hours. Use a meat grinder to crush the shelled samples, mix them, and store them in a dry box.
[0049] The best oven temperature is 90~100℃. If the temperature is lower than 90℃, it will take a long time to dry the samples. If the temperature is higher than 100℃, the eggs will burst and splash. The baking t...
Embodiment 2
[0114] The difference from Example 1 is that when preparing the sample in step (1), place the sample in an infrared desiccator at 90-100°C. After the egg whites are solidified, use tweezers to remove the shells and place them on tin foil. Bake in an infrared dryer at 90~100℃ for 21~33h. The test results are shown in Table 8 and Table 9. Compared with Example 1, the relative error is less than 10%.
[0115] Table 8 Comparison of the total dioxin toxicity equivalent of Example 2 and Example 1
[0116]
[0117]
[0118] Table 9 Comparison of the total toxicity equivalent of dioxin-like PCBs in Example 2 and Example 1
[0119]
Embodiment 3
[0121] The difference from Example 1 is that when preparing the test substance in step (2), the rapid extraction apparatus is used to extract the test substance in the test sample.
[0122] Test conditions of fast extraction instrument:
[0123] Apparatus: Fast solvent extraction instrument, 34ml stainless steel extraction cell; extraction collection bottle (40mL; 60mL)
[0124] Solvent: n-hexane (pesticide grade), methylene chloride (pesticide residue grade).
[0125] Extraction conditions: pressure 1500-2000psi; temperature 80℃~150℃; heating time 5min~20min; static time 5min~15min; solvent, n-hexane: dichloromethane (ratio range 1:0.5~1.5); washing volume 45%~ 75% (volume of extraction tank);
[0126] The range of N2 purge time is 60s~150s; the static cycle is 2~6 times; the total extraction time is 17min~45min for each sample.
[0127] Sample Preparation:
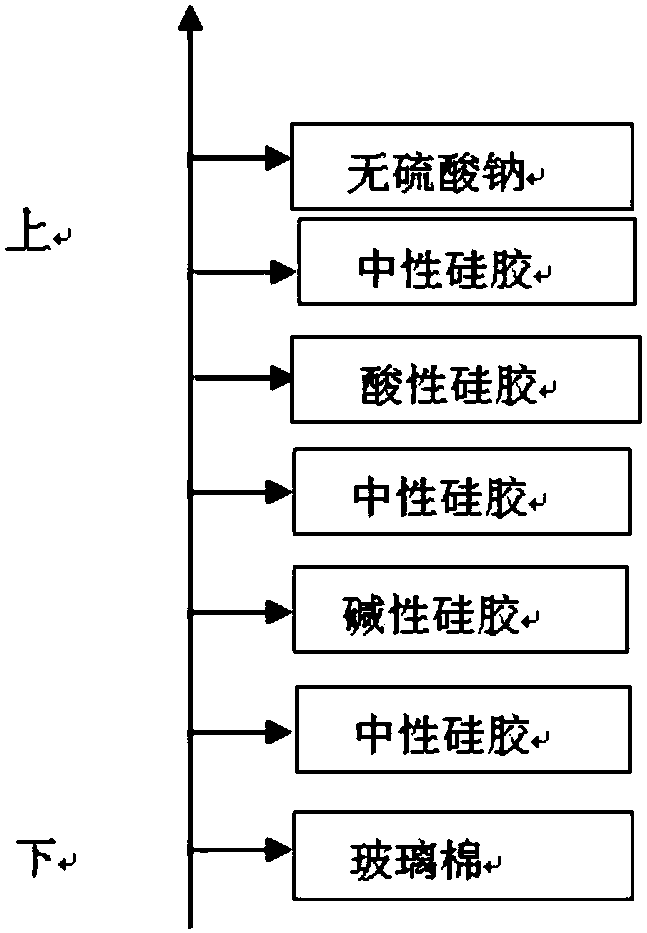
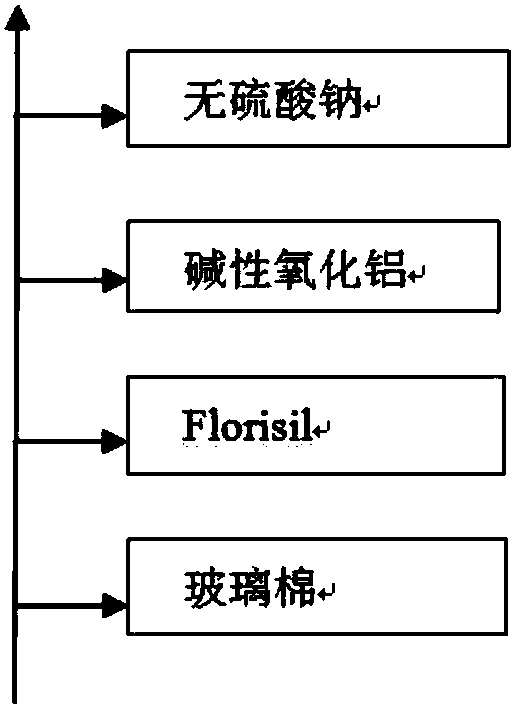
[0128] 10g of the sample is uniformly mixed with 5-10g of sodium sulfate, then ground and dried. Fill 5g alumina through the fib...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com