Artificial breeding feed for meretrix meretrix linnaeus and method for preparing artificial breeding feed
An artificial clam technology, applied in the field of clam cultivation, can solve problems such as imperfect clam cultivation technology and clam production that cannot fully meet market demand, and achieve the effects of convenient feeding and shortening the growth cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
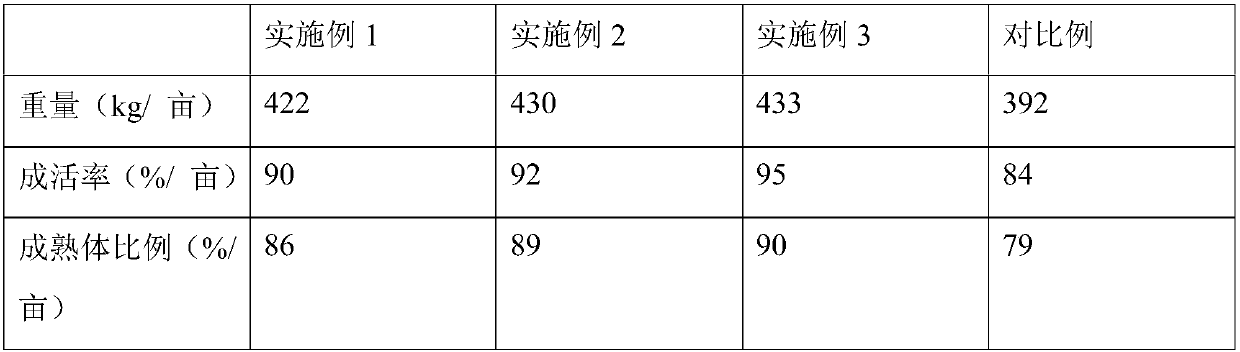
[0020] An artificial breeding feed for clams, comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 21 parts of flour, 10 parts of soybean meal, 7 parts of corn flour, 5 parts of squid powder, 8 parts of silkworm chrysalis powder, 4 parts of shrimp shell powder, 3 parts of liver powder, 25 parts of Parts of Isoflagellates, 17 parts of Chaetoceros, 15 parts of coriander, 2 parts of chicken bone grass, 1 part of small water orchid, 11 parts of calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 7 parts of zeolite powder, 1 part of montmorillonite, 1 Parts of bentonite, 3 parts of choline chloride, 5 parts of betaine, 16 parts of sodium alginate, 6 parts of brassinolide, 7 parts of complex minerals.
[0021] Wherein, each composite mineral contains the following raw materials in weight percentage: 13% copper glycinate, 25% sodium selenite, 17% calcium iodate, 21% manganese methionine, 9% zinc glycinate, 15% cobalt methionine.
[0022] The preparation method of the artificial culture feed of abov...
Embodiment 2
[0027] An artificial breeding feed for clams, comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 25 parts of flour, 13 parts of soybean meal, 9 parts of corn flour, 10 parts of squid powder, 12 parts of silkworm chrysalis powder, 6 parts of shrimp shell powder, 8 parts of liver powder, 28 parts of Parts of Isoflagellates, 22 parts of Chaetoceros, 19 parts of coriander, 9 parts of chicken bone grass, 6 parts of small water orchid, 15 parts of calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 13 parts of zeolite powder, 4 parts of montmorillonite, 4 parts of Parts of bentonite, 6 parts of choline chloride, 7 parts of betaine, 22 parts of sodium alginate, 10 parts of brassin, 9 parts of complex minerals.
[0028] Wherein, each composite mineral contains the following raw materials in weight percentage: 13% copper glycinate, 25% sodium selenite, 17% calcium iodate, 21% manganese methionine, 9% zinc glycinate, 15% cobalt methionine.
[0029] The preparation method of the artificial culture fe...
Embodiment 3
[0034] An artificial breeding feed for clams, comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 23 parts of flour, 12 parts of soybean meal, 8 parts of corn meal, 8 parts of squid meal, 10 parts of silkworm chrysalis meal, 5 parts of shrimp shell meal, 6 parts of liver meal, 27 parts of Parts of Isoflagellates, 20 parts of Chaetoceros, 18 parts of coriander, 4 parts of chicken bone grass, 4 parts of small water orchid, 12 parts of calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 12 parts of zeolite powder, 3 parts of montmorillonite, 3 parts of 1 part bentonite, 5 parts choline chloride, 6 parts betaine, 19 parts sodium alginate, 8 parts brassinolide, 8 parts complex minerals.
[0035] Wherein, each composite mineral contains the following raw materials in weight percentage: 13% copper glycinate, 25% sodium selenite, 17% calcium iodate, 21% manganese methionine, 9% zinc glycinate, 15% cobalt methionine.
[0036] The preparation method of the artificial culture feed of above-mentioned m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com