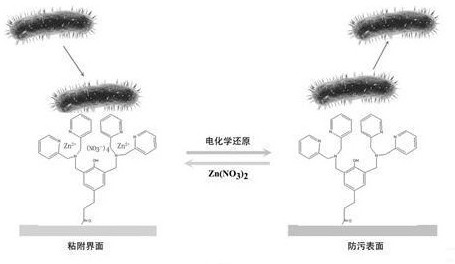
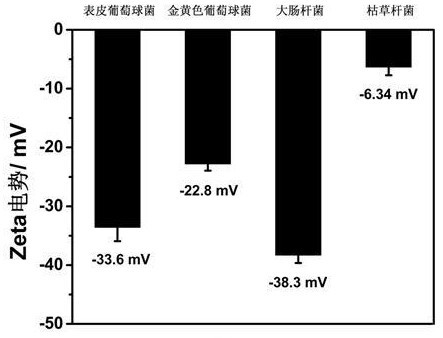
Construction and application of electrochemically controllable bacterial adhesion interface
A technology of bacterial adhesion and construction method, which is applied in the field of nanobiomedicine, can solve the problems of accelerating the aging process of underwater sensors, failure of medical operation operations, increasing fuel consumption of ships, etc., to achieve clinical application, shorten incubation time, interfere with small effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for constructing an electrochemically controllable bacterial adhesion interface, comprising the following steps:
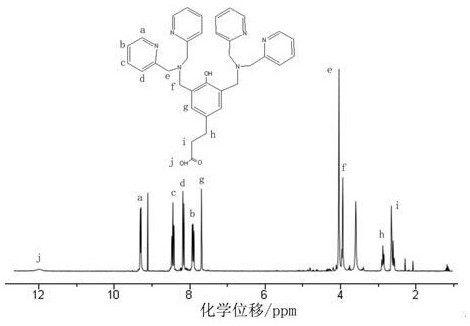
[0025] 1) Preparation of 3,5-bis(bis(pyridine-2-methyl)-aminomethyl)-4-hydroxyphenylpropanoic acid: put 550 mg paraformaldehyde and 2.8 g lutamine in 250 mL In a round bottom flask, add 15 mL of ethanol and 45 mL of water, then add 1.0 g of methyl p-hydroxyphenylpropionate and 1.4 mL of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid, and reflux for 24 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and washed with saturated Na 2 CO 3 Neutralize to neutral, then extract the solution with excess chloroform. Na for organic phase 2 SO 4 After drying, chloroform was evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by silica gel column chromatography (methanol:chloroform=5:95, v:v) to obtain a light yellow oily substance which was 3,5-bis(bis(pyridine-2-methyl)-aminomethyl)-4 -Hydroxyphenylpropionic acid. Its structure can be given by figure 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] A method for constructing an electrochemically controllable bacterial adhesion interface, comprising the following steps:
[0032] 1) Preparation of 3,5-bis(bis(pyridine-2-methyl)-aminomethyl)-4-hydroxyphenylpropanoic acid: put 400 mg paraformaldehyde and 2.8 g lutamine in 250 mL In a round bottom flask, add 15 mL of ethanol and 45 mL of water, then add 1.0 g of methyl p-hydroxyphenylpropionate and 1.4 mL of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid, and reflux for 24 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and washed with saturated Na 2 CO 3 Neutralize to neutral, then extract the solution with excess chloroform. Na for organic phase 2 SO 4 After drying, chloroform was evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by silica gel column chromatography (methanol:chloroform=5:95, v:v) to obtain a light yellow oily substance which was 3,5-bis(bis(pyridine-2-methyl)-aminomethyl)-4 -Hydroxyphenylpropionic acid. Its structure can be given by figure 2 ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] A method for constructing an electrochemically controllable bacterial adhesion interface, comprising the following steps:
[0039] 1) Preparation of 3,5-bis(bis(pyridine-2-methyl)-aminomethyl)-4-hydroxyphenylpropanoic acid: put 600 mg paraformaldehyde and 2.8 g lutamine in 250 mL In a round bottom flask, add 15 mL of ethanol and 45 mL of water, then add 1.0 g of methyl p-hydroxyphenylpropionate and 1.4 mL of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid, and reflux for 24 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and washed with saturated Na 2 CO 3 Neutralize to neutral, then extract the solution with excess chloroform. Na for organic phase 2 SO 4 After drying, chloroform was evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by silica gel column chromatography (methanol:chloroform=5:95, v:v) to obtain a light yellow oily substance which was 3,5-bis(bis(pyridine-2-methyl)-aminomethyl)-4 -Hydroxyphenylpropionic acid. Its structure can be given by figure 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com