Coding sequence of paddy rice indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase gene OsGH3.6 and applications thereof
A nucleotide sequence, rice technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as affecting the initiation of main root growth, crown root initiation, blocking auxin signaling pathway, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1, rice gene OsGH3.6 clone
[0047] 1. Rice variety Nipponbare ( Oryza sativa Japonica ) were cultured in an incubator (SPX-250-GB, Shanghai, China): the growth conditions were photoperiod 16h / 8h (L / D), 28°C;
[0048] 2. RNA extraction. Take about 100 mg of fresh rice plant tissue material and grind it fully with liquid nitrogen. Add 1 ml Trizol reagent, vortex for 15 s, and place at room temperature for 5 min. Add 0.2 ml chloroform, remove protein, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10min, transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of isopropanol, mix thoroughly, place at room temperature for 10min, centrifuge at 12k rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant, and treat with DEPC Wash the precipitate with 1 ml of 75% ethanol prepared in water, and repeat once. Dry at room temperature for 5-10 min, dissolve in 20 μl DEPC water, measure OD value, and detect by electrophoresis;
[0049] 3. Cloning of genes. Using the first strand of reve...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2, rice OsGH3.6 Gene organ expression pattern analysis
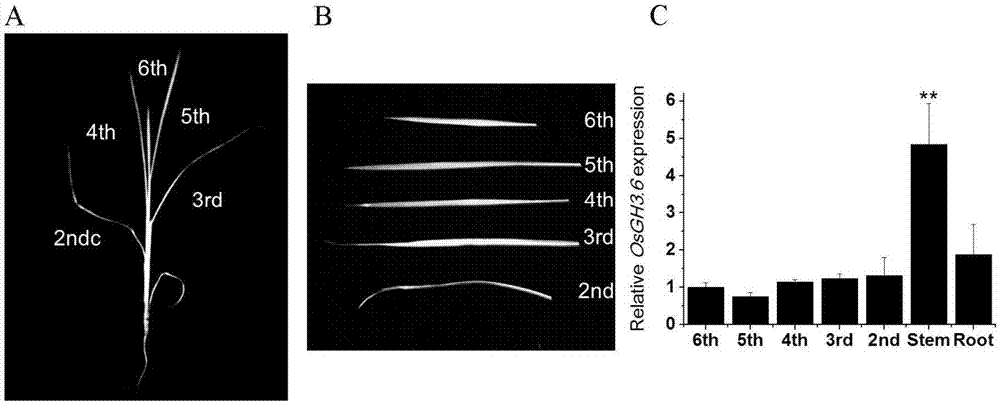
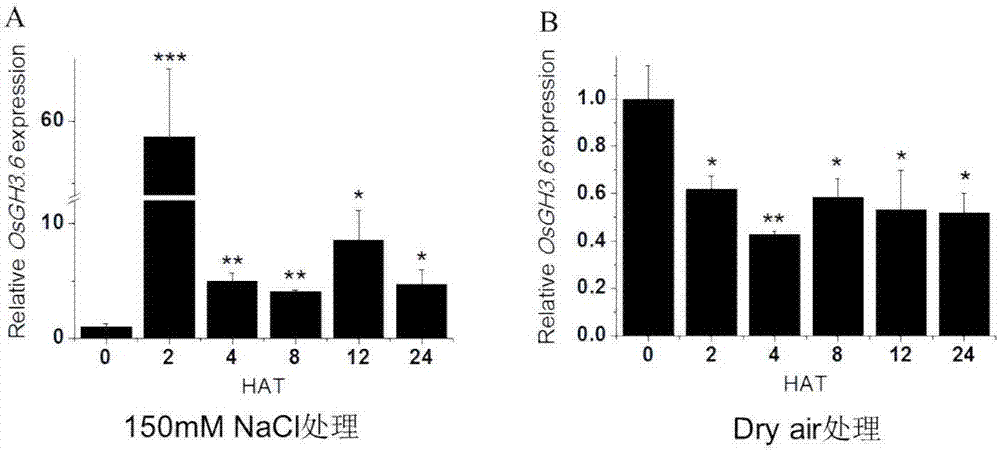
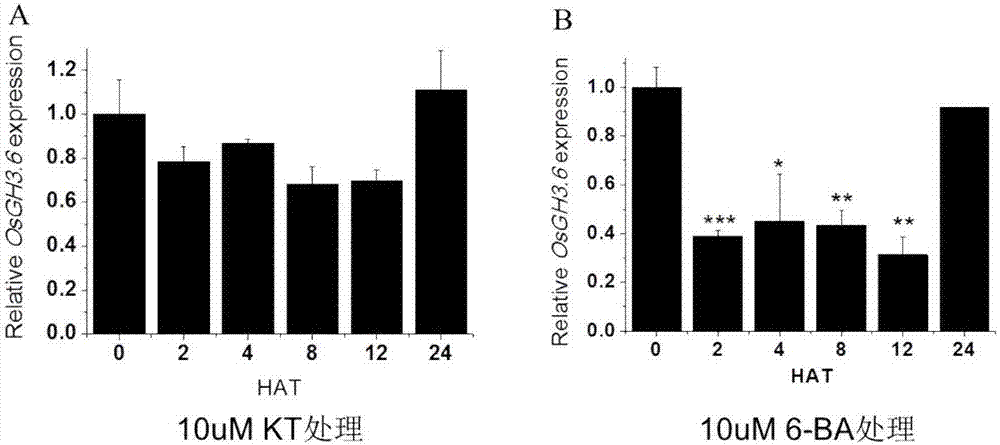
[0051] Extract total RNA from rice stems, young leaves, old leaves, roots, etc., use a reverse transcription kit to reverse transcribe the total RNA into cDNA, and use primers SEQ ID NO.5 and SEQ ID NO.6 for real-time fluorescence Quantitative PCR detection ( figure 1 ). The results show, OsGH3.6 The gene was constitutively expressed in various organs, but there was no significant difference in the expression of leaves and roots in different parts, and the expression level in stems was significantly increased.
Embodiment 4
[0054] Example 4, OsGH3.6 Molecular characterization of tilling mutants
[0055] The total DNA in the mutant and the wild-type control group was extracted respectively, and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection and sequencing were performed using primers SEQ ID NO.7 and SEQ ID NO.8 ( Figure 5 ). according to osgh3-6 mutant g19 with g20 respectively with WT's GH3.6 DNA sequences were compared and it was found that: g19 At 452bp, G is mutated to A;g20 At 452bp, G was mutated to A ( Figure 5 A, B). All of the above are in OsGH3-6 A mutation occurred in the coding region, which is a sense mutation. OsGH3-6 two mutants of g19 with g20 with WT GH4 protein ( Figure 5 C, D) Comparison found that the histidine (H) at position 87 was mutated to arginine (R).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com