Preparation method of natural-polymer-based slow-release fertilizer
A natural polymer, slow-release fertilizer technology, applied in the directions of potash fertilizer, phosphate fertilizer, organic fertilizer, etc., can solve the problems of burning seedlings, fertilizers without slow-release properties, improper fertilization, etc., to reduce production costs, improve fruit quality, and promote crops. effect of growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
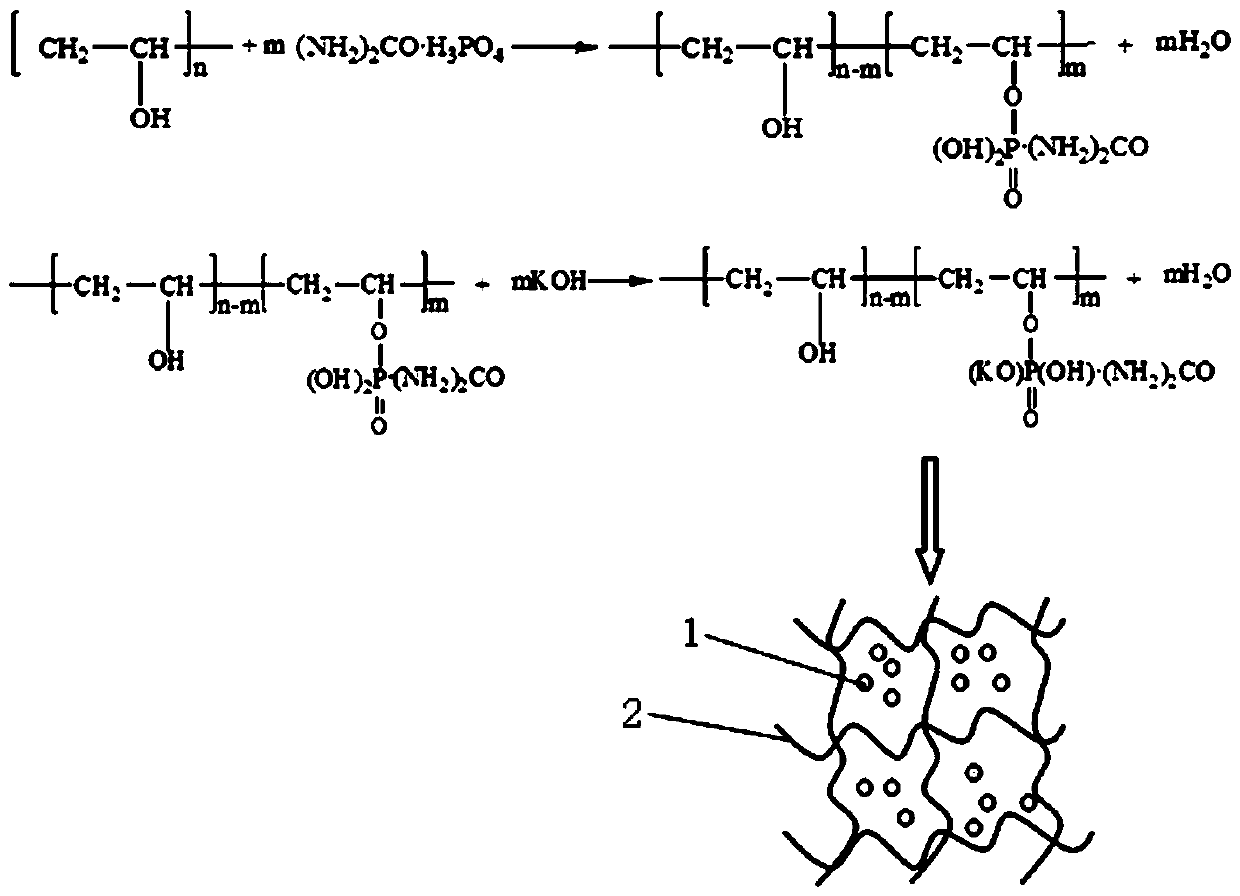
[0029] Example 1, weigh polyvinyl alcohol, urea phosphate and potassium hydroxide according to the mass ratio of 1:21.35:1.25, and the mass ratio of p-toluenesulfonic acid to urea phosphate is 1.5%.
[0030] The first step is to prepare polymer slow-release liquid fertilizer. Weigh polyvinyl alcohol, add it to a flask, then add distilled water, and stir until the polyvinyl alcohol is dissolved at 90°C; and react for 100-150 minutes; then add potassium hydroxide, and react for 80-100 minutes at 90-100°C. After the reaction, polymer slow-release liquid fertilizer is obtained;
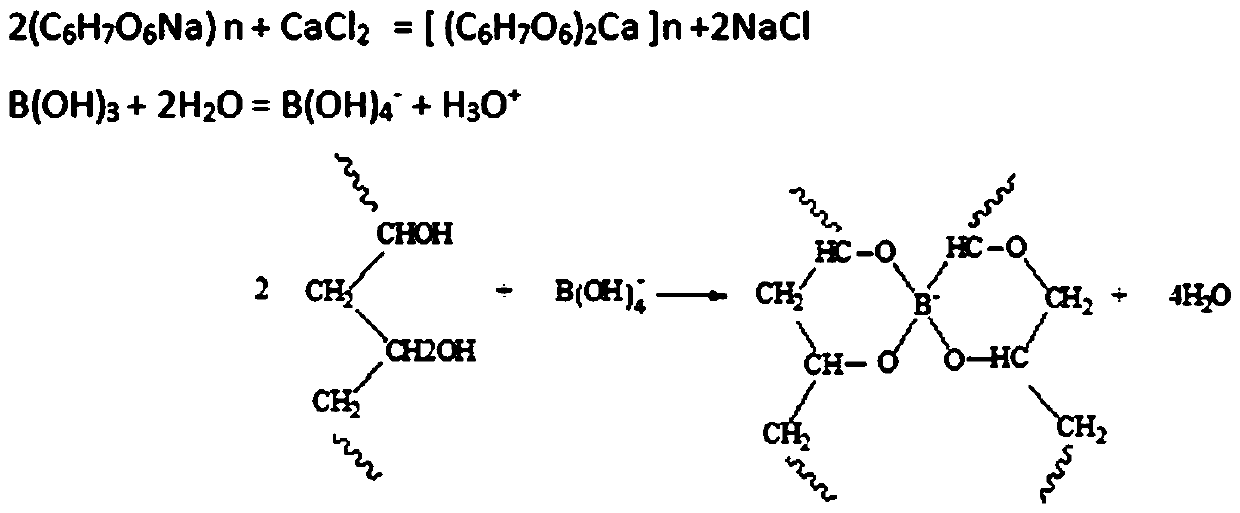
[0031] Second step, prepare 3% borate calcium chloride solution;
[0032] The third step is to mix the polymer slow-release liquid fertilizer and sodium alginate evenly to obtain a mixed solution;
[0033] In the fourth step, the mixed solution obtained in the third step is added dropwise to the 3% calcium chloride borate solution in the second step, and soaked for 30 minutes to obtain a natural polymer-...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2, weigh polyvinyl alcohol, urea phosphate and potassium hydroxide according to the mass ratio of 1:21.35:1.25, and the mass ratio of p-toluenesulfonic acid to urea phosphate is 1.5%.
[0038] The first step is to prepare polymer slow-release liquid fertilizer. Weigh polyvinyl alcohol, add it to a flask, then add distilled water, and stir until the polyvinyl alcohol is dissolved at 90°C; and react for 100-150 minutes; then add potassium hydroxide, and react for 80-100 minutes at 90-100°C. After the reaction, polymer slow-release liquid fertilizer is obtained;
[0039] Second step, prepare 3% borate calcium chloride solution;
[0040] The third step is to mix the polymer slow-release liquid fertilizer and sodium alginate evenly to obtain a mixed solution;
[0041] In the fourth step, the mixed solution obtained in the third step is added dropwise to the 3% calcium chloride borate solution in the second step, and soaked for 40 minutes to obtain a natural polymer-...
Embodiment 3
[0045] In Example 3, polyvinyl alcohol, urea phosphate and potassium hydroxide were weighed according to a mass ratio of 1:21.35:1.25, and the mass ratio of p-toluenesulfonic acid to urea phosphate was 1.5%.
[0046]The first step is to prepare polymer slow-release liquid fertilizer. Weigh polyvinyl alcohol, add it to a flask, then add distilled water, and stir until the polyvinyl alcohol is dissolved at 90°C; and react for 100-150 minutes; then add potassium hydroxide, and react for 80-100 minutes at 90-100°C. After the reaction, polymer slow-release liquid fertilizer is obtained;
[0047] Second step, prepare 3% borate calcium chloride solution;
[0048] The third step is to mix the polymer slow-release liquid fertilizer and sodium alginate evenly to obtain a mixed solution;
[0049] In the fourth step, the mixed solution obtained in the third step is added dropwise to the 3% calcium chloride borate solution in the second step, and soaked for 60 minutes to obtain a natural ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com