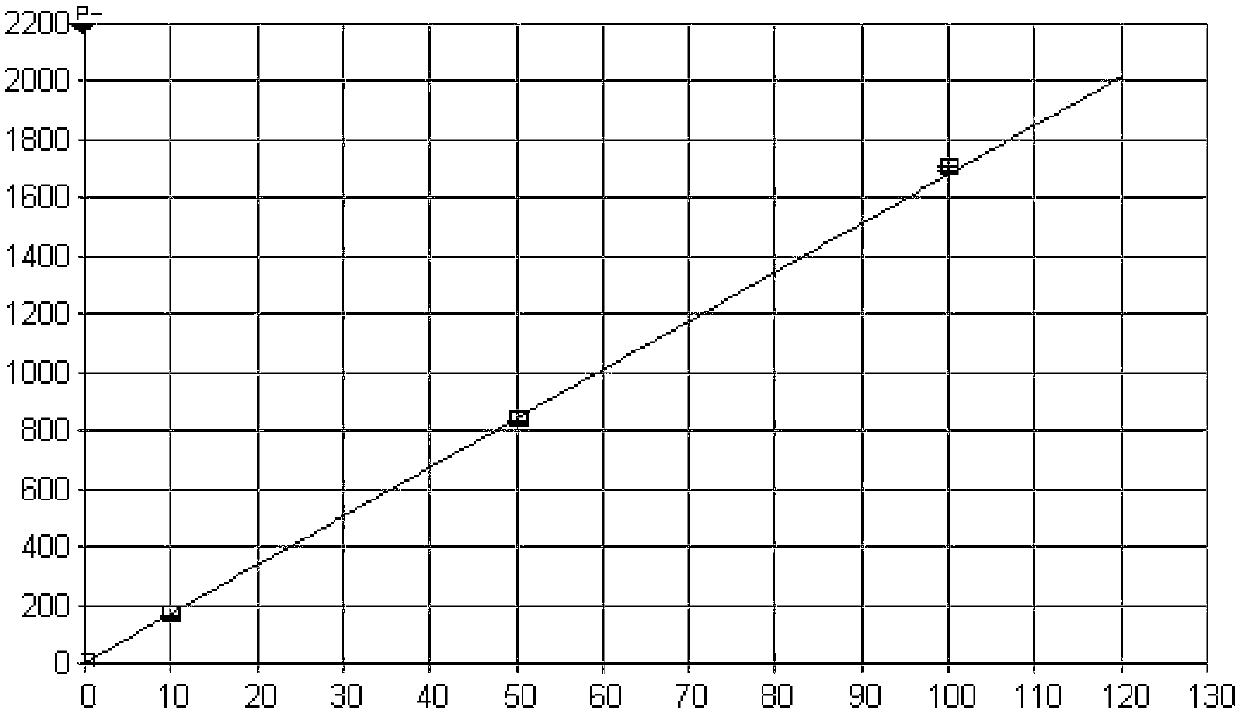
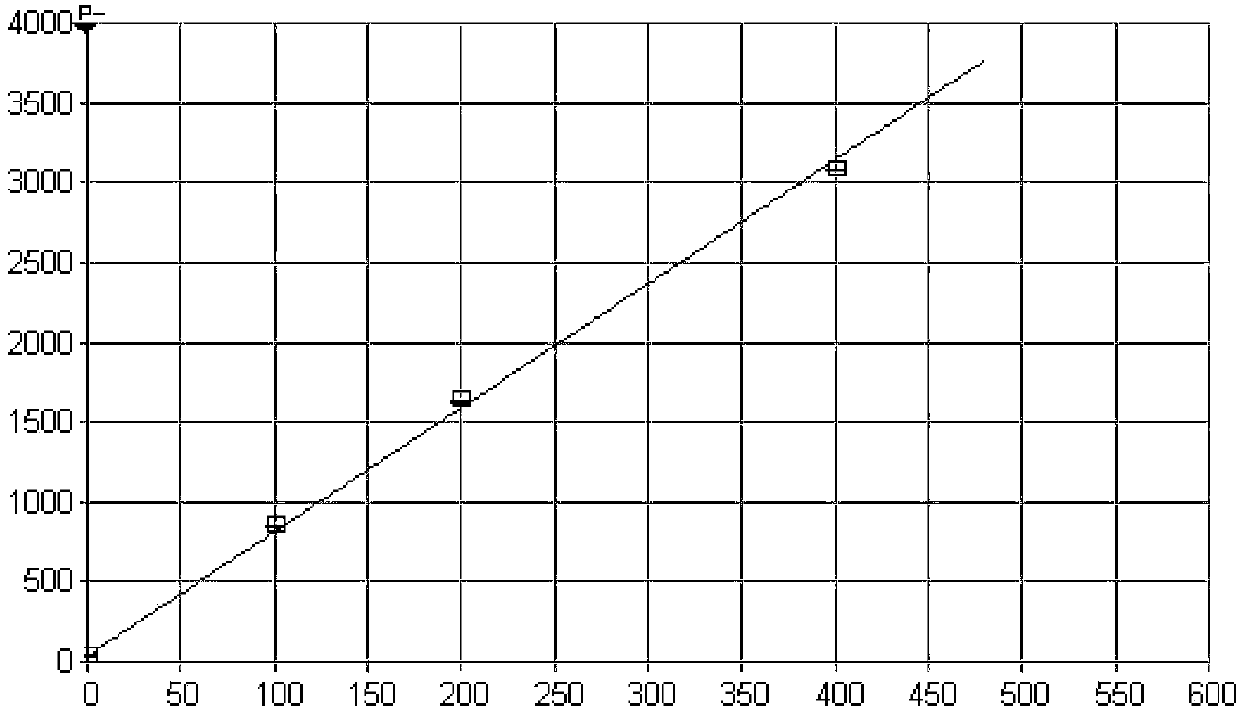
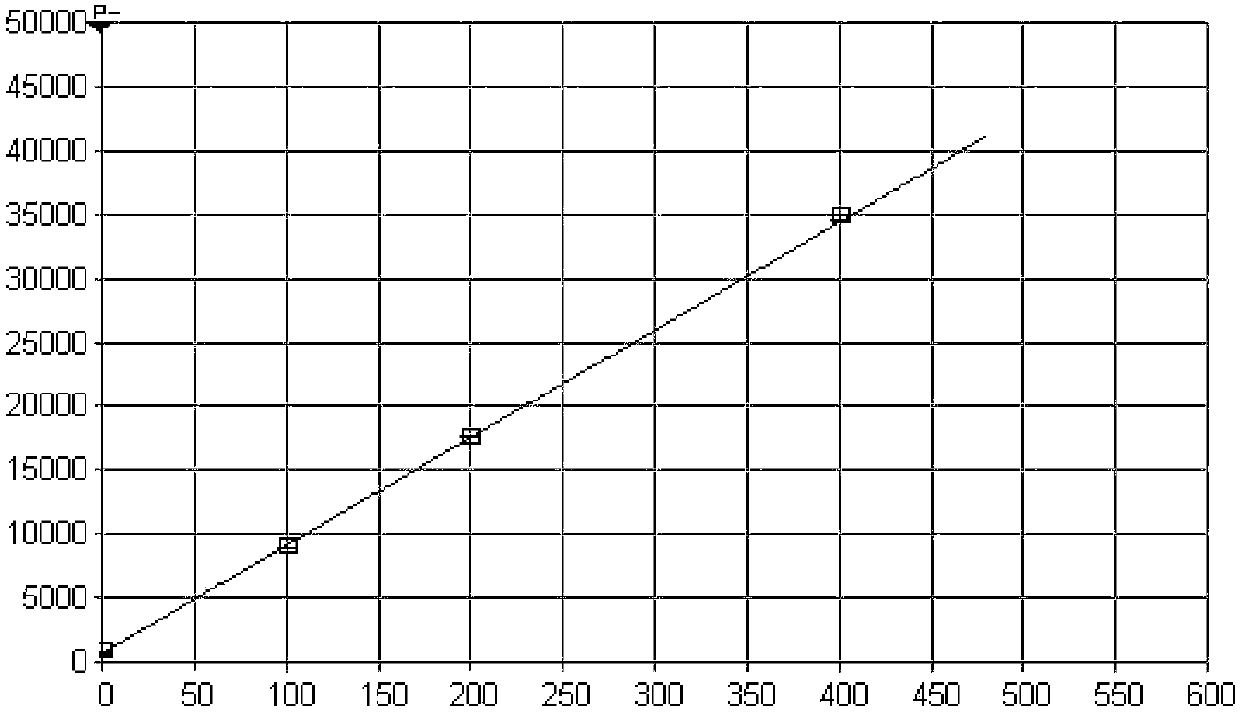
Method for detecting microelements in chromium powder
A technology for medium and trace elements and trace elements, which is applied in the field of quantitative analysis of analytical chemistry, can solve problems such as no reports in literature or patents, and achieve the effect of saving test costs, eliminating influence, and fast and efficient analysis methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] The method for detecting nickel, manganese, iron, zinc, calcium, magnesium, aluminum, titanium, vanadium, and cobalt in No. 1 chromium powder sample, the detection wavelength of the trace elements to be measured, the detection limit of the method, and the lower detection limit of the sample.
[0082] S1: draw the standard working curve
[0083] S11: Preparation of chromium matrix standard series solutions
[0084] Weigh four parts of 0.1000g high-purity chromium powder matrix in parallel, place them in four 200mL quartz beakers respectively, add 20mL hydrochloric acid, cover with a quartz watch glass, dissolve on a 250°C electric heating plate, the sample is completely dissolved, remove it, and use a small amount of Rinse the cup wall and the inner wall of the watch glass with water, dilute to about 30mL, cover the watch glass, heat and boil on a 250°C electric heating plate for 1min, remove and cool, transfer the test solution into four 100mL volumetric flasks, and the...
Embodiment 2
[0110] The method for detecting nickel, manganese, iron, zinc, calcium, magnesium, aluminum, titanium, vanadium, and cobalt in No. 1 chromium powder sample, the detection wavelength of the trace elements to be measured, the detection limit of the method, and the lower detection limit of the sample.
[0111] S1: draw the standard working curve
[0112] S11: Preparation of chromium matrix standard series solutions
[0113] Weigh four parts of 0.2000g high-purity chromium powder matrix in parallel, place them in four 200mL quartz beakers respectively, add 30mL hydrochloric acid, cover with a quartz watch glass, dissolve on a 300°C electric heating plate, the sample is completely dissolved, remove it, and use a small amount of Rinse the cup wall and the inner wall of the watch glass with water, dilute to about 30mL, cover the watch glass, heat and boil on a 300°C electric heating plate for 1min, remove and cool, transfer the test solution into four 100mL volumetric flasks, and the...
Embodiment 3
[0139] The method for detecting nickel, manganese, iron, zinc, calcium, magnesium, aluminum, titanium, vanadium, and cobalt in No. 1 chromium powder sample, the detection wavelength of the trace elements to be measured, the detection limit of the method, and the lower detection limit of the sample.
[0140] S1: draw the standard working curve
[0141] S11: Preparation of chromium matrix standard series solutions
[0142] Weigh four parts of 0.4000g high-purity chromium powder matrix in parallel, place them in four 200mL quartz beakers respectively, add 40mL hydrochloric acid, cover with a quartz watch glass, dissolve on a 300°C electric heating plate, the sample is completely dissolved, remove it, and use a small amount of Rinse the cup wall and the inner wall of the watch glass with water, dilute to about 30mL, cover the watch glass, heat and boil on a 300°C electric heating plate for 1min, remove and cool, transfer the test solution into four 100mL volumetric flasks, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com