Preparation method for preparing feed for sheep by using composite strains and disease-resistant Chinese herbal medicines
A technology of compound bacteria and Chinese herbal medicine, applied in the direction of animal feed, animal feed, application, etc., can solve the problems of low disease resistance and poor palatability of feed, and achieve the effect of reducing disease rate, enhancing immunity and improving body immunity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
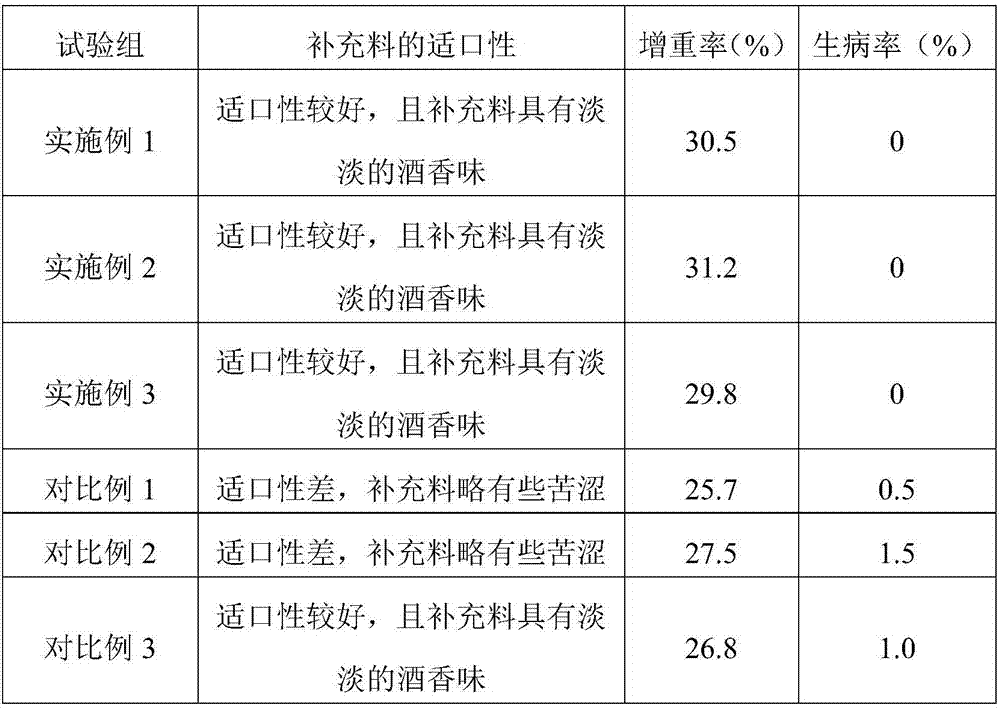
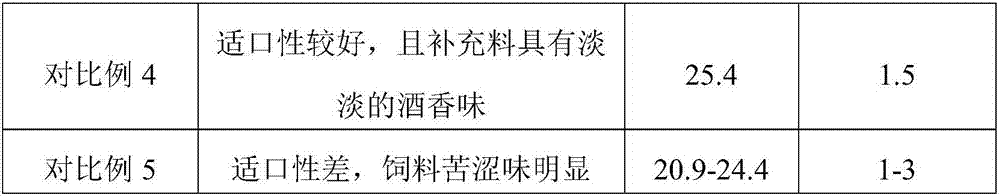
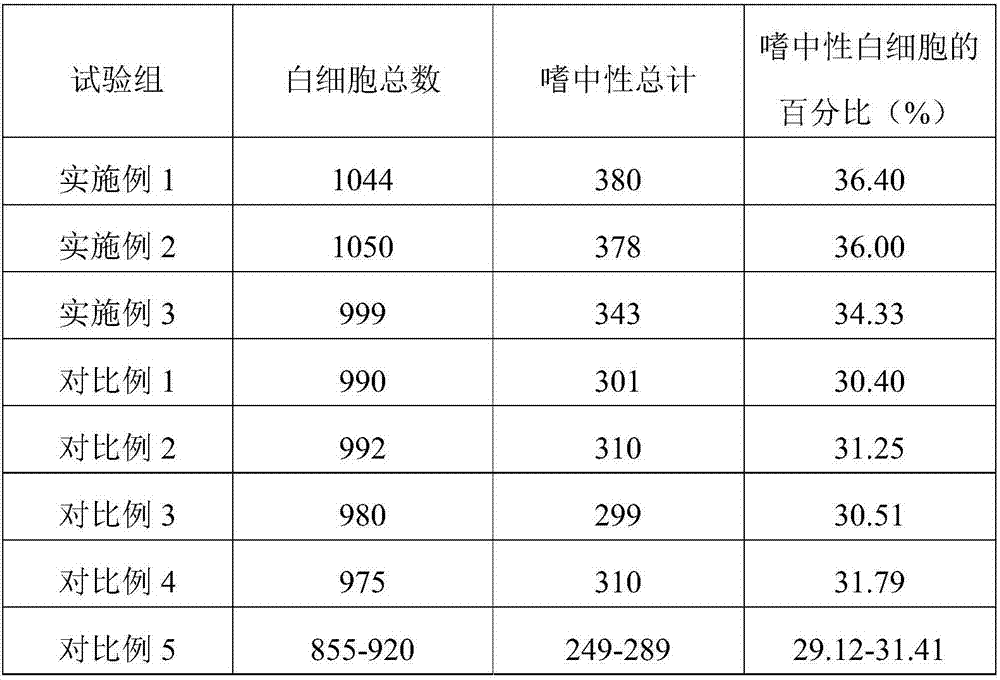
[0036] Sheep feed is based on parts by weight, including the following raw materials: 70 parts of sugarcane tail leaves, 60 parts of peanut straw, 70 parts of wheat bran, 40 parts of soybean meal, 10 parts of compound bacteria, 10 parts of grape pomace, 5 parts of pear pomace, tryptophan 12 parts of acid, 2 parts of iron and zinc, 8 parts of anti-disease Chinese herbal medicine extract;
[0037] The compound bacteria are obtained by the following method:
[0038] T1: Medium: mix broccoli juice 0.5g / l, peptone 2.5g / l, glucose 0.7g / l, sodium chloride 0.4g / l, potassium phosphate 0.8g / l, and sterilize to obtain medium;
[0039] T2: Inoculation: insert the purified Trametes versicolor, microbacteria, and yeast into the medium of step T1, the ratio of each strain is 1:1:0.5, and the inoculum amount is 0.5ml per 100g medium ;
[0040] T3: Preparation of composite bacteria: The culture medium containing Trametes versicolor, microbacteria, and yeast was cultured statically for 6 days at 28°C,...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Sheep feed is based on parts by weight, including the following raw materials: 80 parts of sugarcane tail leaves, 65 parts of peanut straw, 80 parts of wheat bran, 50 parts of soybean meal, 15 parts of compound bacteria, 12 parts of grape pomace, 8 parts of pear residue, threonine 13 parts of acid, 4 parts of zinc and selenium, 10 parts of disease-resistant Chinese herbal medicine extract;
[0054] The compound bacteria are obtained by the following method:
[0055] T1: Medium: mix broccoli juice 0.8g / l, peptone 3.8g / l, glucose 1.0g / l, sodium chloride 0.6g / l, potassium phosphate 1.0g / l, and sterilize to obtain medium;
[0056] T2: Inoculation: insert the purified Trametes versicolor, microbacteria, and yeast into the medium of step T1, the ratio of each strain is 1:1:0.5, and the inoculum amount is 0.8ml per 100g medium ;
[0057] T3: Preparation of composite bacteria: The culture medium containing Trametes versicolor, microbacteria, and yeasts was allowed to stand and cultiva...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Sheep feed is based on parts by weight, including the following raw materials: 90 parts of sugarcane tail leaves, 70 parts of peanut straw, 90 parts of wheat bran, 60 parts of soybean meal, 20 parts of compound bacteria, 14 parts of grape pomace, 10 parts of pear pomace, and lysine 14 parts of acid, 6 parts of iron and manganese elements, 12 parts of disease-resistant Chinese herbal medicine extracts;
[0071] The compound bacteria are obtained by the following method:
[0072] T1: Medium: Mix 1g / l broccoli juice, 5g / l peptone, 1.2g / l glucose, 0.9g / l sodium chloride, and 1.3g / l potassium phosphate, and sterilize to obtain a medium;
[0073] T2: Inoculation: insert the purified Trametes versicolor, microbacteria, and yeast into the medium of step T1, the ratio of each strain is 1:1:0.5, and the amount of inoculation is 1.0ml per 100g medium ;
[0074] T3: Preparation of composite bacteria: The culture medium containing Trametes versicolor, microbacteria, and yeasts is staticall...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com