Molecular tag connector as well as preparation method and application thereof
A molecular tag and linker technology, applied in molecular tag linkers and their preparation, and in the application field of ultra-low frequency gene mutation detection, can solve the problems of inevitable linker self-connection, reduction of UIDs types, unfavorable data correction, etc. Data correction, improve detection sensitivity, and facilitate the effect of data error correction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Example 1, Preparation of Molecular Tag Adapter
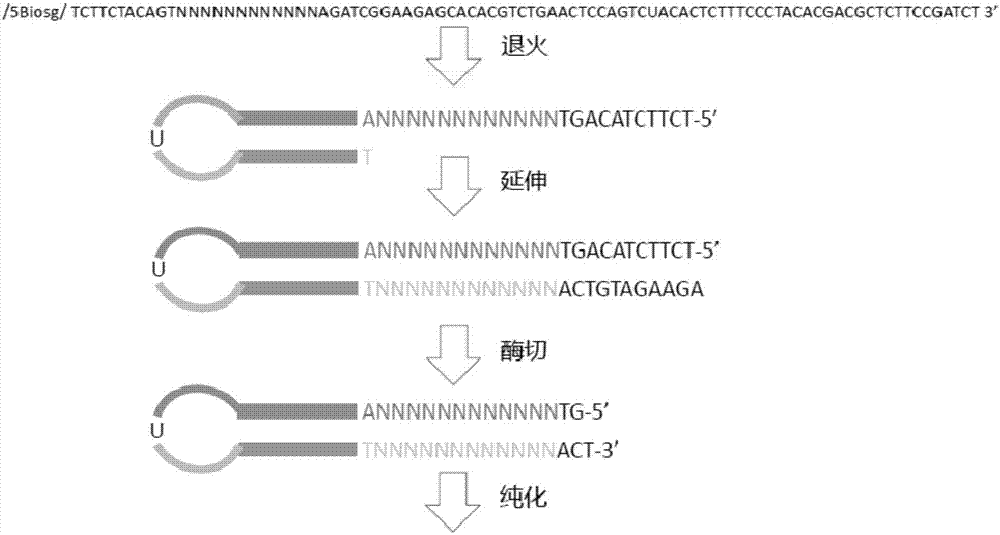
[0070] Taking Molecular Tag Adapter 1 as an example, the flowchart for preparing Molecular Tag Adapter 1 with Adapter Primer 1 is shown in figure 1 .
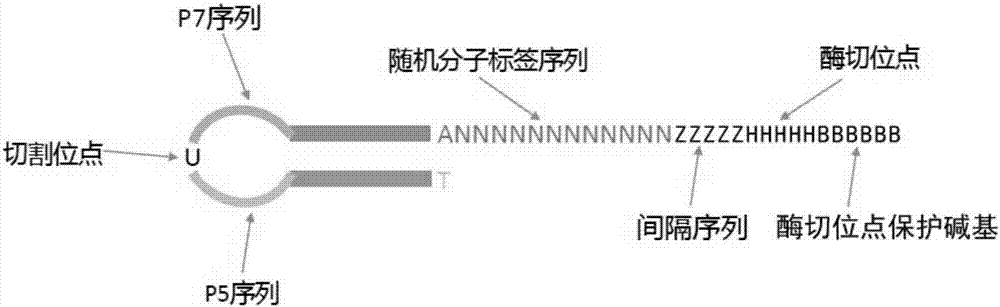
[0071] The schematic diagram of the structure of the linker primer is shown in figure 2 .
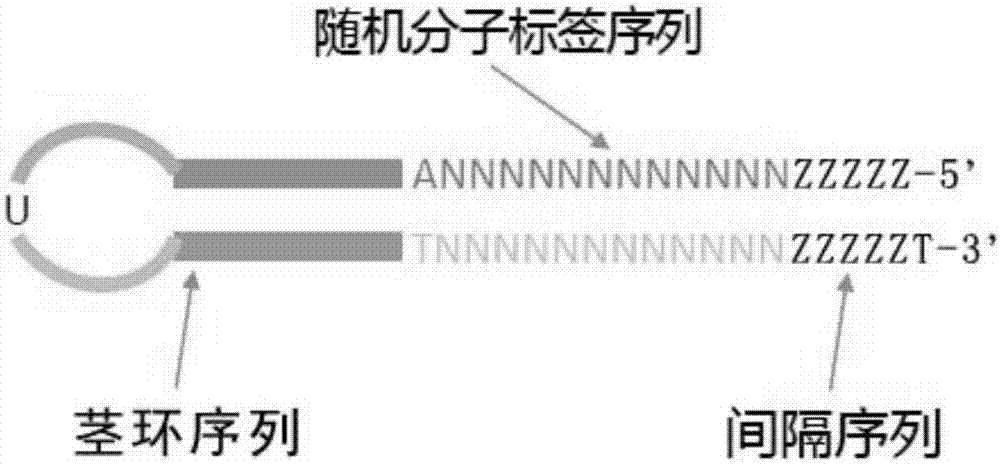
[0072] A schematic diagram of the structure of the molecular tag linker is shown in image 3 .
[0073] Schematic diagrams of molecular tag adapter 1 to molecular tag adapter 4 are shown in Figure 4 .
[0074] 1. Linker primer synthesis
[0075] The nucleotide sequence of the linker primer is as follows:
[0076] Adapter primer 1 (SEQ ID NO: 1 of Sequence Listing):
[0077] Adapter primer 2 (SEQ ID NO: 2 of the Sequence Listing):
[0078] Linker primer 3 (SEQ ID NO: 3 of the Sequence Listing):
[0079] Linker primer 4 (SEQ ID NO: 4 of the Sequence Listing):
[0080] In the linker primer, NNNNNNNNNNNN is a molecular tag sequence consisting of 12 random n...
Embodiment 2
[0122] Example 2. Ultra-low-frequency gene variation detection using molecular label adapters
[0123] See flow chart Image 6 .
[0124] 1. Library Construction
[0125] 1. Prepare a DNA sample, which consists of background DNA and standard DNA.
[0126] The standard DNA was purchased from Horizon, involving 8 mutant forms of four genes (EGFR gene, KRAS gene, NRAS gene and PIK3CA gene), see Table 4 for details.
[0127] Table 4
[0128] chromosome
Entrez ID
mutation type
HGVS
amino acid changes
7p12
EGFR
1956
SNVs
c.2573T>G
L858R
7p12
EGFR
1956
Deletion
c.2236_2250del15
ΔE746-A750
7p12
EGFR
1956
SNVs
c.2369C>T
T790M
7p12
EGFR
1956
c.2300_2308dupCCAGCGTGG
V769-D770insASV
12p12.1
3845
SNVs
c.35G>A
G12D
1p13.2
NRAS
4893
SNVs
c.181C>A
Q61K
1p13.2
NRAS
4893
SNVs
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com