High-yield linear-chain glucan strain and glucan fermentation and production method thereof
A production method and dextran technology, applied in the field of high-yielding straight-chain glucan strains and their glucan fermentation production, can solve the problems of low yield and achieve high sugar yield, high solubility, and short sugar production cycle Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Isolation and screening of a high-production exopolysaccharide strain
[0037] (1) culture medium
[0038] MRS basal medium: glucose 20g, tryptone 10g, beef extract 10g, yeast extract 5g, ammonium citrate 2g, K 2 HPO 4 2g, CH 3 COONa 5g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.58g, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 0.25g, Tween 80 1mL, distilled water 1000mL, pH 6.5, sterilized at 115°C for 20min.
[0039] MRS sugar production fermentation medium: 50g sucrose, 10g tryptone, 10g beef extract, 5g yeast extract, K 2 HPO 4 2g, CH 3 COONa 5g, ammonium citrate 2g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.58g, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 0.25g, Tween 80 1mL, distilled water 1000mL, pH 6.5, sterilized at 115°C for 20min.
[0040] (2) Sample pretreatment
[0041] Weigh 1g of milk tofu and add it into 9mL sterile saline to make 10 -1 Concentration of the sample solution, after shaking and mixing, gradually dilute to the appropriate concentration, and set aside for later use.
[0042] (3) Primary screening of slime-producing coloni...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Identification of a high-production exopolysaccharide strain
[0047] (1) Morphological identification
[0048] Inoculate the strain N21 on the MRS agar plate with a three-section line, and after culturing at 30°C for 24-48 hours, observe and record the single colony characteristics of the strain on the plate. Use an inoculation needle to pick a small amount of fresh bacteria and spread it on a clean glass slide for Gram staining, and then observe the individual shape and arrangement of the cells under a microscope.
[0049] (2) Physiological and biochemical identification
[0050] ① Contact enzyme test: Select the strains with positive Gram staining results for contact enzyme test.
[0051] ②Glucose acid and gas production test: Add 1.6% bromocresol violet 2mL / L and inverted Duchenne tubules to ordinary MRS liquid medium. The color of the indicator in the medium changes from purple to yellow, indicating acid production, and if it is still purple, it indic...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3: A fermentation process for producing exopolysaccharides by fermentation of a high-yield exopolysaccharide strain
[0067] In this embodiment, a fermentation process for producing exopolysaccharide by fermentation of a high-yield exopolysaccharide strain is carried out according to the following steps:
[0068] (1) Preparation of seed solution
[0069] Leuconostoc citreum N21 was inoculated in the basic MRS medium, so that the initial cell concentration in the medium was 1.0×10 8 unit / mL is the seed solution.
[0070] (2) Fermentation conditions for sugar production
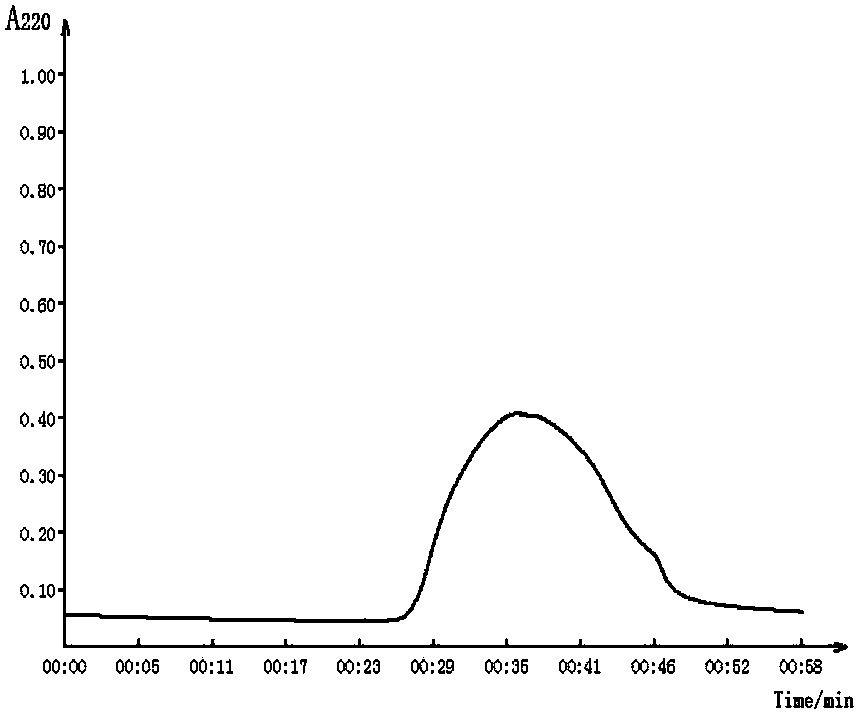
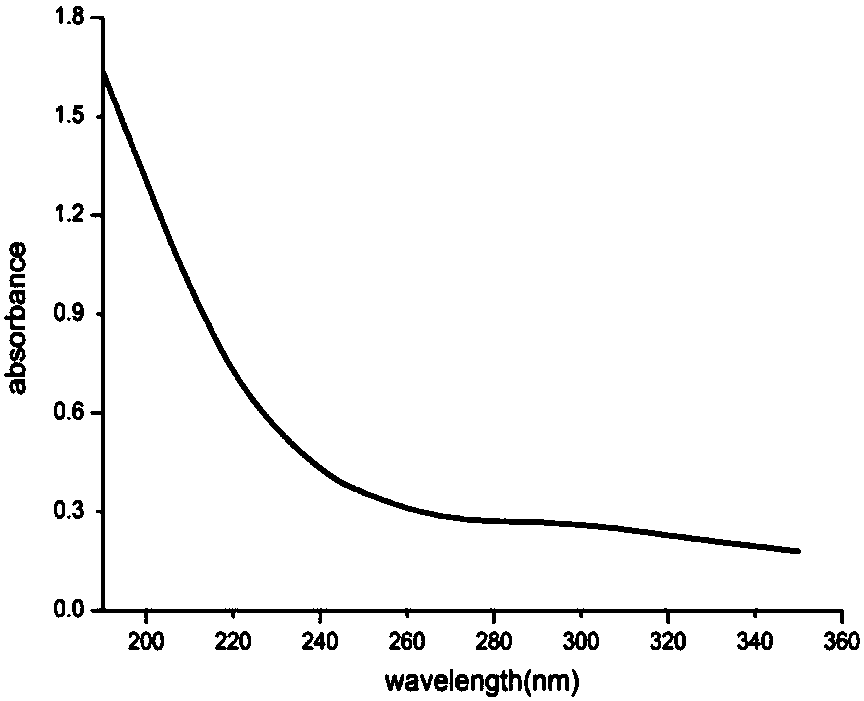
[0071] Inoculate Leuconostoc citreum N21 with an inoculation amount of 2.0% (V / V) in a 100 / 250mL medium with an initial pH value of 6-8, and culture it with constant temperature shaking at a temperature of 25-37°C 36-72h, use the phenol-sulfuric acid method to measure the polysaccharide content of the fermentation supernatant.
[0072] Under the conditions of an initial pH value of 6.5, a tem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com