Preparation method of protein-modified phytosterol liposome powder
A phytosterol lipid and protein modification technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of protein-modified phytosterol liposome powder, can solve the problems of low solubility and reduced embedding rate, achieve good solubility, improve stability, and improve redispersibility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
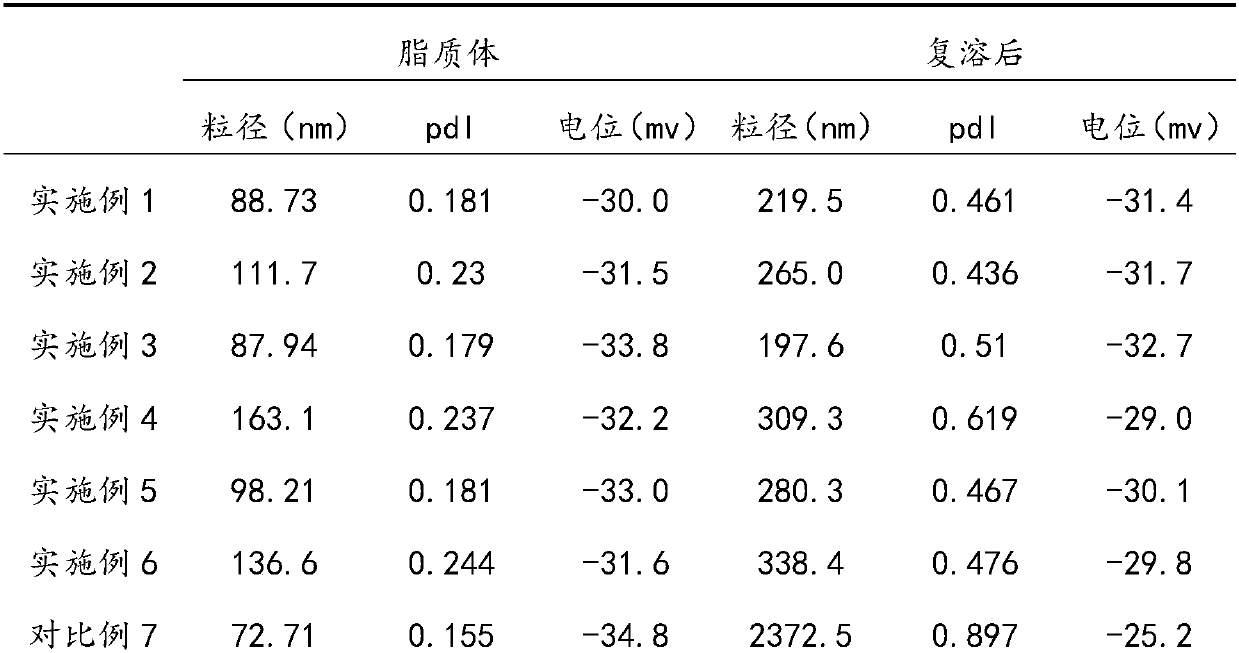
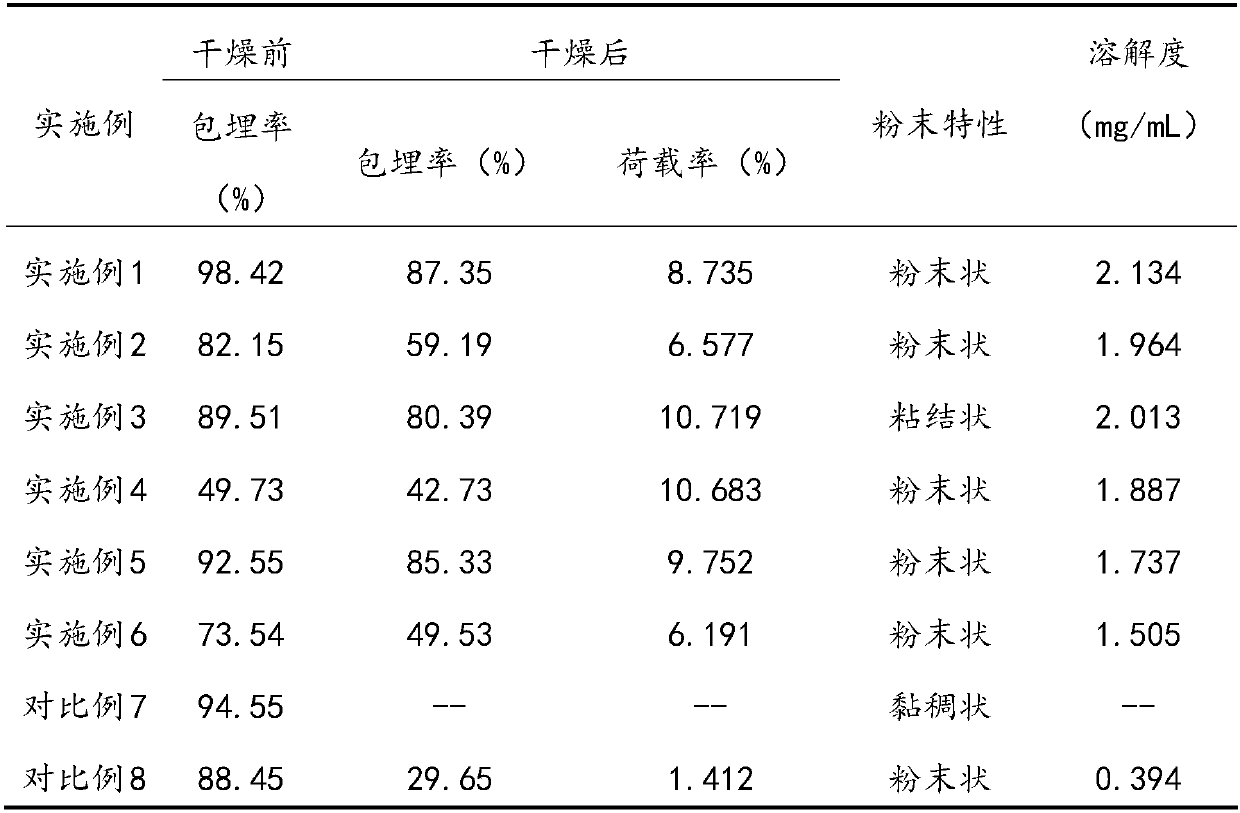
[0024] (1) Lecithin and phytosterol are added to absolute ethanol at a ratio of 4:1 (w / w), so that the concentration of phytosterol is 1% (w / v), and stirred at room temperature to dissolve;
[0025] (2) Add soybean protein isolate to deionized water at a ratio of 1% (w / v), stir and dissolve at room temperature, adjust pH to 7.0, and hydrate overnight at 4°C;
[0026] (3) Slowly inject the phytosterol-lecithin ethanol solution obtained in step (1) into the protein solution obtained in step (2) according to the volume ratio of 1:4, and disperse at a high speed of 10000r / min for 5min; then under 80MPa High-pressure homogenization 8 times to obtain protein-modified phytosterol liposomes;
[0027] (4) The phytosterol liposomes obtained in the step (3) were subjected to rotary evaporation at 40°C under a vacuum of 0.11 MPa to remove ethanol, and freeze-dried to obtain a freeze-dried powder.
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) Lecithin and phytosterol are added to absolute ethanol at a ratio of 3:1 (w / w), so that the concentration of phytosterol is 2% (w / v), and stirred at room temperature to dissolve;
[0030] (2) Add soybean protein isolate to deionized water at a ratio of 1% (w / v), stir and dissolve at room temperature, adjust pH to 7.0, and hydrate overnight at 4°C;
[0031] (3) Slowly inject the phytosterol-lecithin ethanol solution obtained in step (1) into the protein solution obtained in step (2) according to the volume ratio of 1:4, and disperse at a high speed of 10000r / min for 3min; then under 90MPa High-pressure homogenization 4 times to obtain protein-modified phytosterol liposomes;
[0032] (4) The phytosterol liposomes obtained in the step (3) were subjected to rotary evaporation at 40°C under a vacuum of 0.13 MPa to remove ethanol, and freeze-dried to obtain a freeze-dried powder.
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) Lecithin and phytosterol are added to absolute ethanol at a ratio of 4:1 (w / w), so that the concentration of phytosterol is 4% (w / v), and stirred at room temperature to dissolve;
[0035] (2) Add soybean protein isolate to deionized water at a ratio of 0.5% (w / v), stir and dissolve at room temperature, adjust pH to 7.0, and hydrate overnight at 4°C;
[0036] (3) Slowly inject the phytosterol-lecithin ethanol solution obtained in step (1) into the protein solution obtained in step (2) according to the volume ratio of 1:4, and disperse at a high speed of 8000r / min for 5min; then under 80MPa High-pressure homogenization 4 times to obtain protein-modified phytosterol liposomes;
[0037] (4) The phytosterol liposomes obtained in the step (3) were subjected to rotary evaporation at 45° C. to remove ethanol under a vacuum of 0.11 MPa, and freeze-dried to obtain freeze-dried powder.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com