Processing technology and formula of lactic acid bacteria steamed buns
A processing technology and technology of lactic acid bacteria, applied in food science, food preservation, application, etc., can solve problems such as high water activity, high cost, poor product stability, etc., and achieve the goal of improving fermentation activity, reducing production time, and shortening fermentation time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
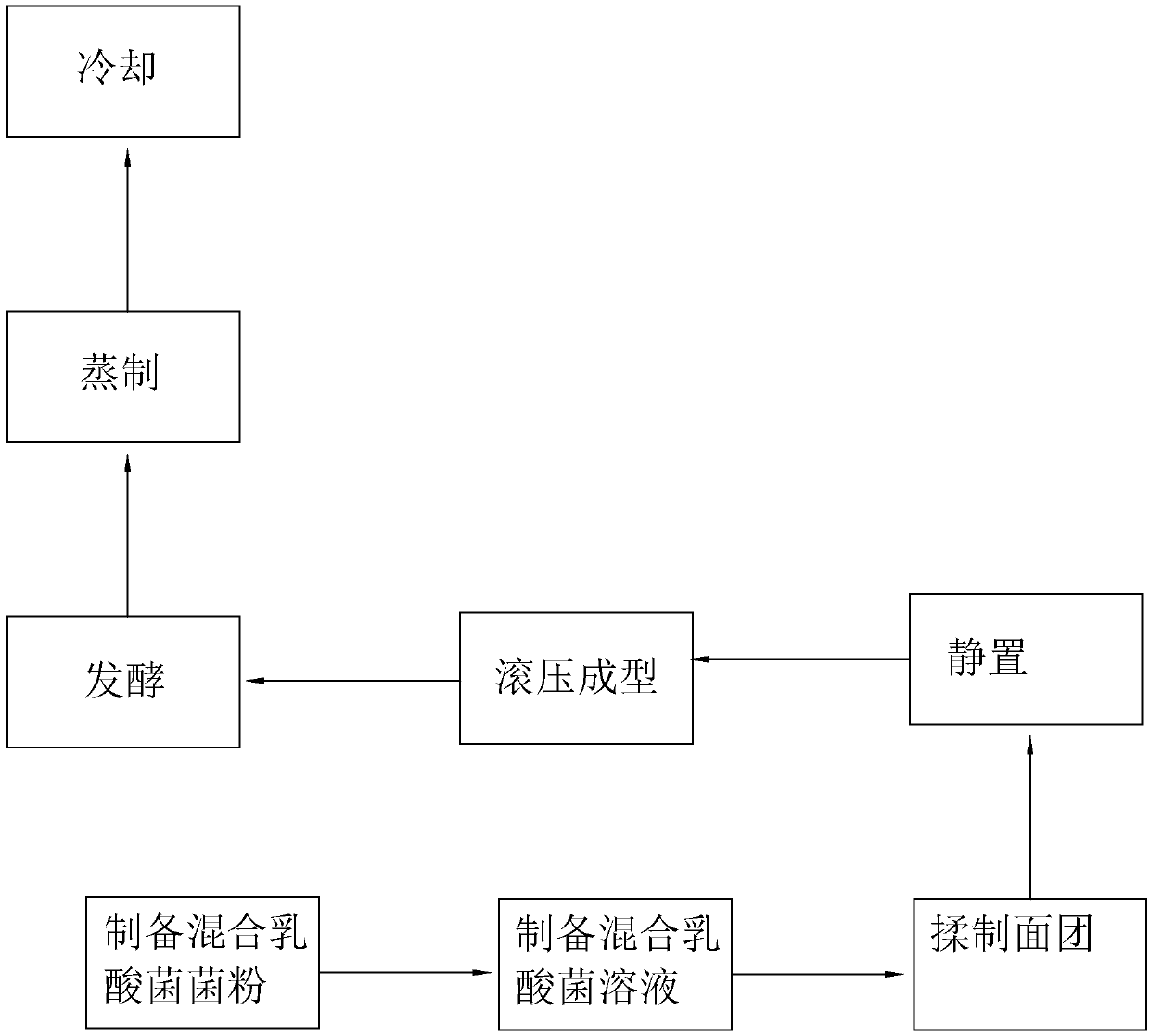
[0037] A kind of lactic acid bacteria steamed bread processing technology, such as figure 1 As shown, it mainly includes the following steps:
[0038] Preparation of mixed lactic acid bacteria powder → preparation of mixed lactic acid bacteria solution → kneading fermented sourdough → fermenting → kneading dough → standing → rolling forming → fermenting → steaming → cooling.
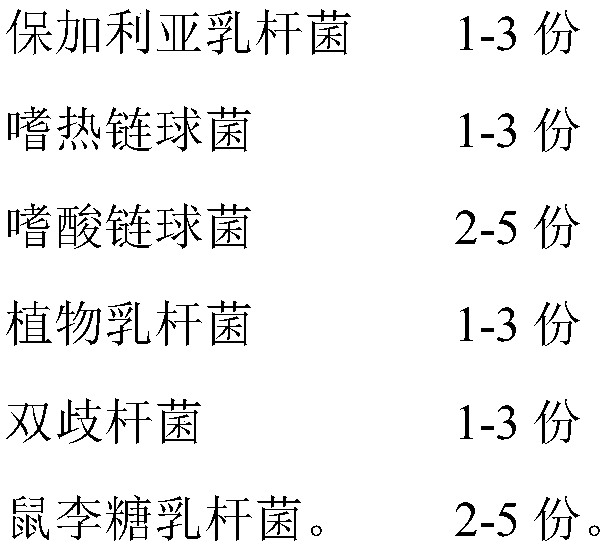
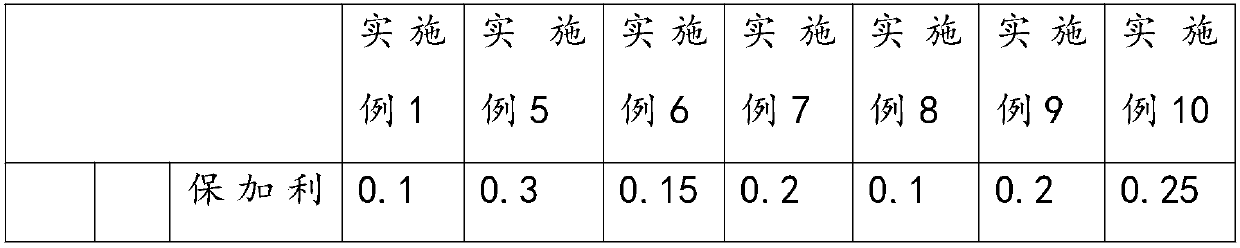
[0039] Take a clean container A, add 90 parts of flour to it, pour 90 parts of water into it and mix evenly, then add 0.1 part of Lactobacillus bulgaricus, 0.1 part of Streptococcus thermophilus, 0.2 parts of Lactobacillus acidophilus, 0.1 part of Lactobacillus plantarum, 0.1 part of Bifidobacterium and 0.2 part of Lactobacillus rhamnosus continue to stir until they are evenly mixed to form a fermented sourdough, and then place the container A together with the fermented sourdough in an environment at 32°C for 8 hours to ferment Sourdough has a pH of 4.2-4.8.
[0040] Pour the mixture of 90 parts of fl...
Embodiment 2
[0047] A kind of lactic acid bacteria steamed bread processing technology, such as figure 1 As shown, it mainly includes the following steps:
[0048] Preparation of mixed lactic acid bacteria powder → preparation of mixed lactic acid bacteria solution → kneading fermented sourdough → fermenting → kneading dough → standing → rolling forming → fermenting → steaming → cooling.
[0049] Take a clean container A, add 90 parts of flour to it, pour 90 parts of water into it and mix evenly, then add 0.1 part of Lactobacillus bulgaricus, 0.1 part of Streptococcus thermophilus, 0.2 parts of Lactobacillus acidophilus, 0.1 part of Lactobacillus plantarum, 0.1 part of Bifidobacterium and 0.2 part of Lactobacillus rhamnosus continue to stir until they are evenly mixed to form a fermented sourdough, and then place the container A together with the fermented sourdough in an environment of 37°C for 10 hours to ferment Sourdough has a pH of 4.2-4.8.
[0050] Pour the mixture of 90 parts of f...
Embodiment 3
[0057] A kind of lactic acid bacteria steamed bread processing technology, such as figure 1 As shown, it mainly includes the following steps:
[0058] Preparation of mixed lactic acid bacteria powder → preparation of mixed lactic acid bacteria solution → kneading fermented sourdough → fermenting → kneading dough → standing → rolling forming → fermenting → steaming → cooling.
[0059] Take a clean container A, add 90 parts of flour to it, pour 90 parts of water into it and mix evenly, then add 0.1 part of Lactobacillus bulgaricus, 0.1 part of Streptococcus thermophilus, 0.2 parts of Lactobacillus acidophilus, 0.1 part of Lactobacillus plantarum, 0.1 part of Bifidobacterium and 0.2 part of Lactobacillus rhamnosus continue to stir until they are evenly mixed to form a fermented sourdough, and then place the container A together with the fermented sourdough in an environment of 35°C for 9 hours to ferment Sourdough has a pH of 4.2-4.8.
[0060] Pour the mixture of 90 parts of fl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com