Method for reducing emission factor of fine particulate matters in biomass fuel
A biomass fuel, emission factor technology, applied in the direction of biofuel, waste fuel, fuel, etc., can solve the problem of high fixed asset investment and operating costs, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
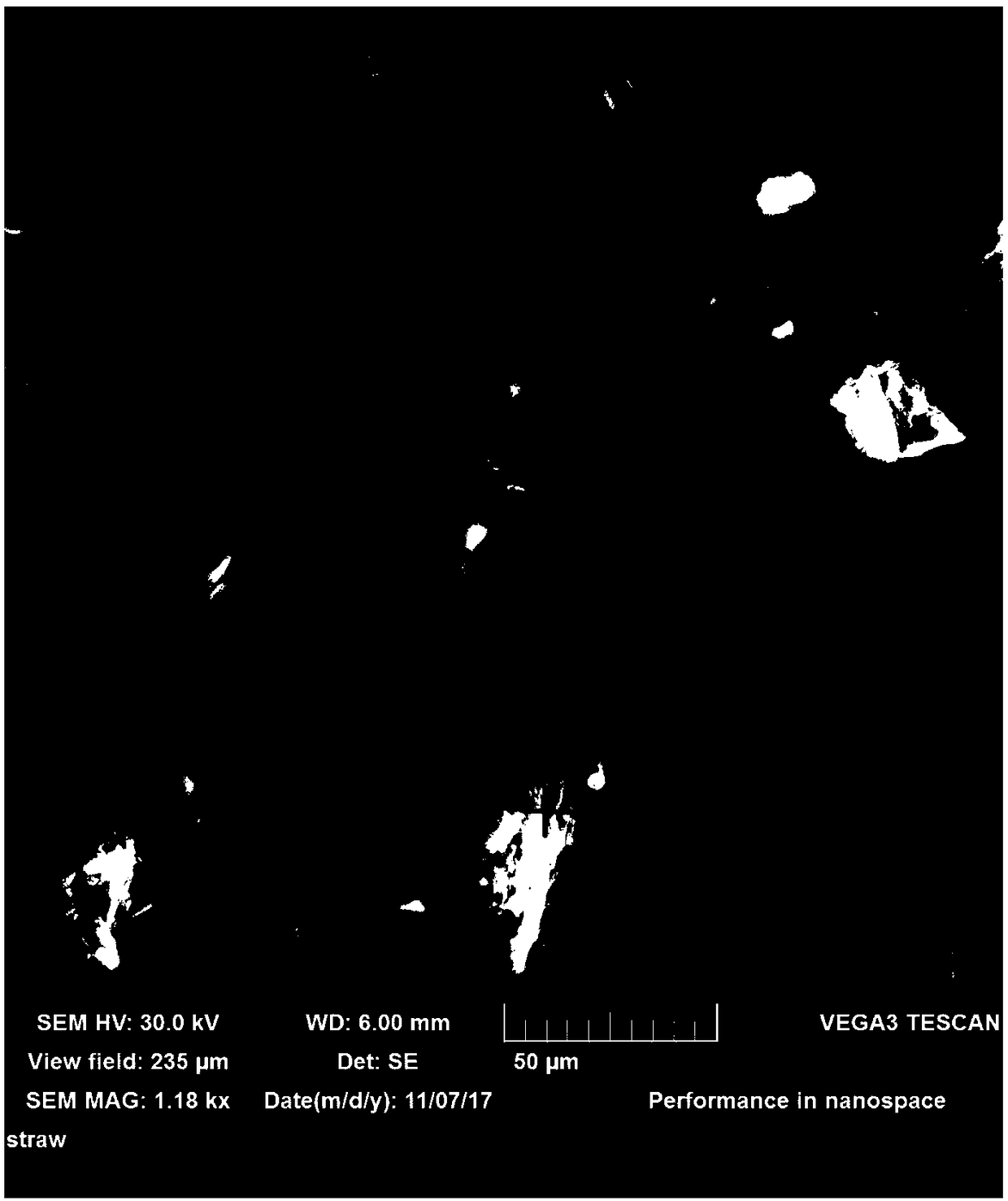
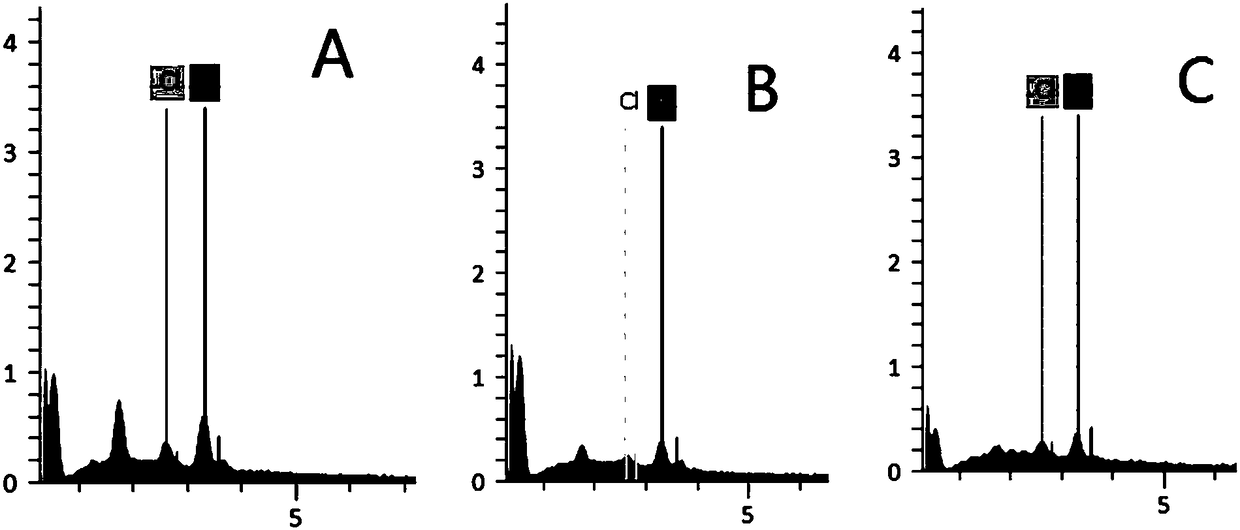
[0027] Example 1: The biomass fuel in this example is rice straw; after crushing, pass through a 200-mesh sieve, take 50g of powder under the sieve as a sample, put the sample in a ceramic boat and put it in a tube furnace for combustion in a stacked manner, In the experiment, the tube furnace was placed in a closed room of 4m*3m*3m, and the PM2.5 detection used a large flow sampler (TH-1000, flow rate 1.05m3 min-1, Wuhan Tianhong) equipped with a PM2. cutting head, and the combustion The generated soot particles were collected on the quartz filter membrane (Pallflex 2500QAT-UP, 8X10inch); the sampling pump was turned on at the beginning of the combustion, and the sampling was continued for 40 minutes until the raw material was taken out to cool down to collect the emitted soot particles as much as possible; before each combustion experiment, Pump air for 30 minutes to reduce laboratory background interference; after the filter membrane is dried in an incubator, weigh the net m...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: The biomass fuel of this embodiment is corn cob, PM2.5 emission factor is bigger (1090.2 ± 605.5mg / kg), pyrolysis gas output is smaller, biomass carbon content is larger, suitable as smoldering fuel ; The milling, sampling, heating and cooling method of the present embodiment are identical with the embodiment;
[0046] A method for reducing particulate matter (PM2.5) emission factors in biomass fuels, the specific steps are as follows:
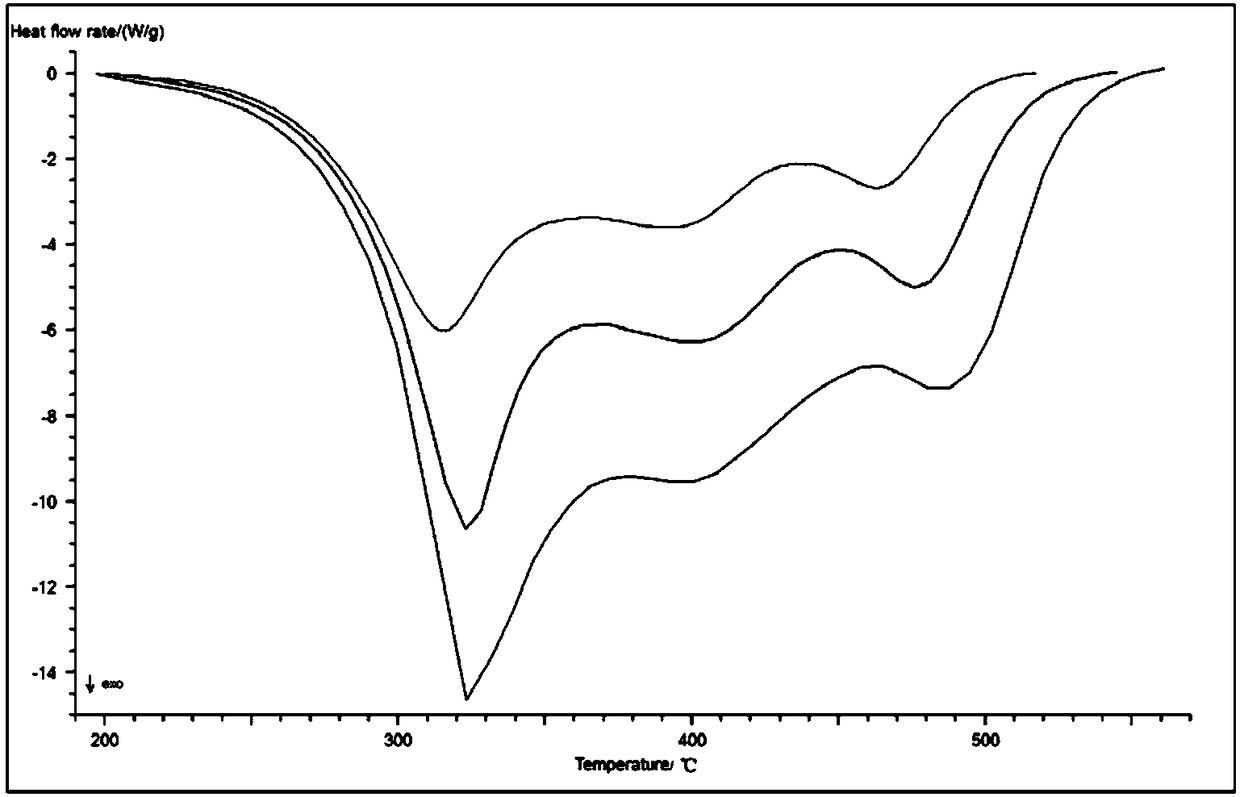
[0047] (1) According to the thermodynamic analysis data of biomass fuel combustion, that is, the differential scanning calorimetry data, the Ozawa-Flynn-Wall kinetic analysis method is used to calculate the Arrhenius formula at the temperature from 200 ° C to the combustion temperature Activation energy value;
[0048] Ozawa-Flynn-Wall kinetic analysis method for reaction process α t The initial value is 0, and the reaction is 1 when the reaction is completed. At any time in the reaction, t is calculated according to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com