Inserted-intron-modified soy amino acid transport protein fusion gene and application thereof
A technology of fusion gene and transporter, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of excessive nitrogen fertilizer application, low nitrogen use efficiency of crops, etc., to achieve enhanced absorption, crop yield and quality improvement, low nitrogen tolerance and nitrogen The effect of improving the efficiency of nutrient utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1: Creation of soybean amino acid transporter fusion gene NKNUE1 modified by inserting an intron
[0053] Using soybean genomic DNA as a template, fragment A of the NKNUE1 fusion gene was amplified by PCR; using soybean cDNA as a template, fragment B of the NKNUE1 fusion gene was amplified by PCR; after fusion PCR, the amplified product was recovered and TA cloned. Specific steps are as follows:
[0054] (1) PCR amplification of the target fragment
[0055] ①PCR amplification of target gene composition fragment A
[0056] According to the soybean genome sequence, specific primer 1 and primer 2 were designed, the sequences of which were shown in SEQ ID No.2 and SEQ ID No.3, and an Apa I restriction site was introduced into primer 1.
[0057] The fragment A of the NKNUE1 fusion gene was prepared by using the CTAB method to extract soybean genome DNA as a template, and carrying out PCR amplification using the above primers.
[0058] PCR reaction system:
[0059...
Embodiment 2
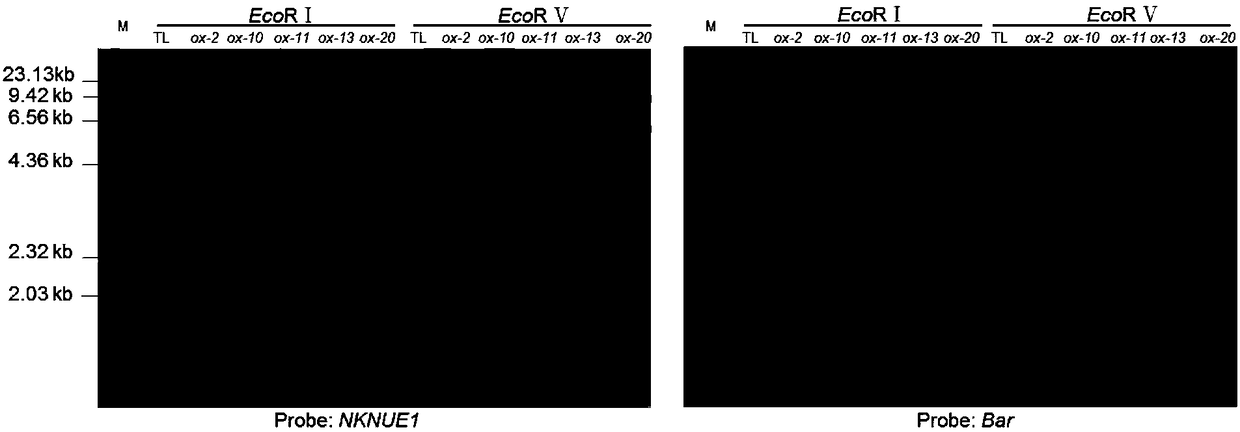
[0093]Example 2: The pCAMBIA 1301 vector (containing the CaMV 35S promoter) was used to construct a binary expression vector driven by the CaMV 35S promoter to express the fusion gene NKNUE1.
[0094] (1) First obtain the intermediate carrier
[0095] Design specific primer 5 and primer 6 according to the sequence of known eYFP, as shown in SEQ ID No.6 and SEQ ID No.7, introduce Apa I restriction site, Nco I restriction site and SpeI in primer 5 Restriction site, primer 6 introduces BstP I restriction site.
[0096] The vector pSAT6-eYFP-N1 plasmid was extracted from Escherichia coli, and the plasmid was used as a template to perform PCR amplification with the above primers to prepare the eYFP gene fragment.
[0097] PCR reaction system:
[0098]
[0099] PCR reaction program:
[0100] 94°C for 5 minutes;
[0101] 94°C for 30 seconds, 58°C for 30 seconds, 72°C for 1 minute, 30 cycles;
[0102] 72°C for 10 minutes;
[0103] After the PCR reaction, the target gene was r...
Embodiment 3
[0120] Embodiment 3: Preparation of transgenic Arabidopsis
[0121] (1) Transform Arabidopsis thaliana with the binary expression vector constructed in Example 2 driven by the CaMV 35S promoter to express the fusion gene NKNUE1. The specific transformation method adopts the bud soaking method mediated by Agrobacterium (Clough and Bent, 1998), to obtain The seeds were screened for resistance to 30mg / L hygromycin, and the plants that grew normally were transferred to soil for culture.
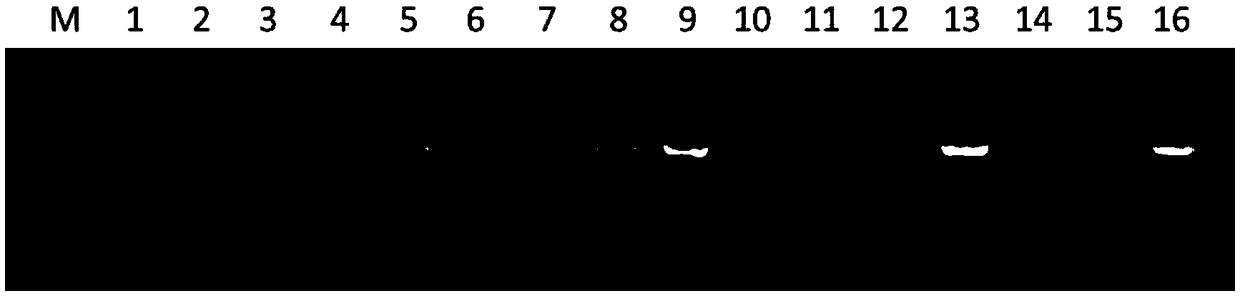
[0122] (2) PCR detection of transgenic plants: cut the leaves of transgenic plants and wild-type plants respectively, and extract genomic DNA from leaves with reference to the method of "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide (Third Edition)" (Huang Peitang et al., 2002), and use primer 1 (SEQ ID No.2) and primer 4 (SEQ ID No.5) were used for PCR reaction, and the reaction system was the same as in Example 1.
[0123] The PCR product was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis, and the NKNUE1 gene ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com