Method of comprehensively recovering valuable metals in lead, zinc and silver-containing material
A technology for valuable metals and materials, applied in the field of comprehensive recovery of valuable metals in materials containing lead, zinc and silver, to achieve the effects of clean production, low cost of raw materials, and improved utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
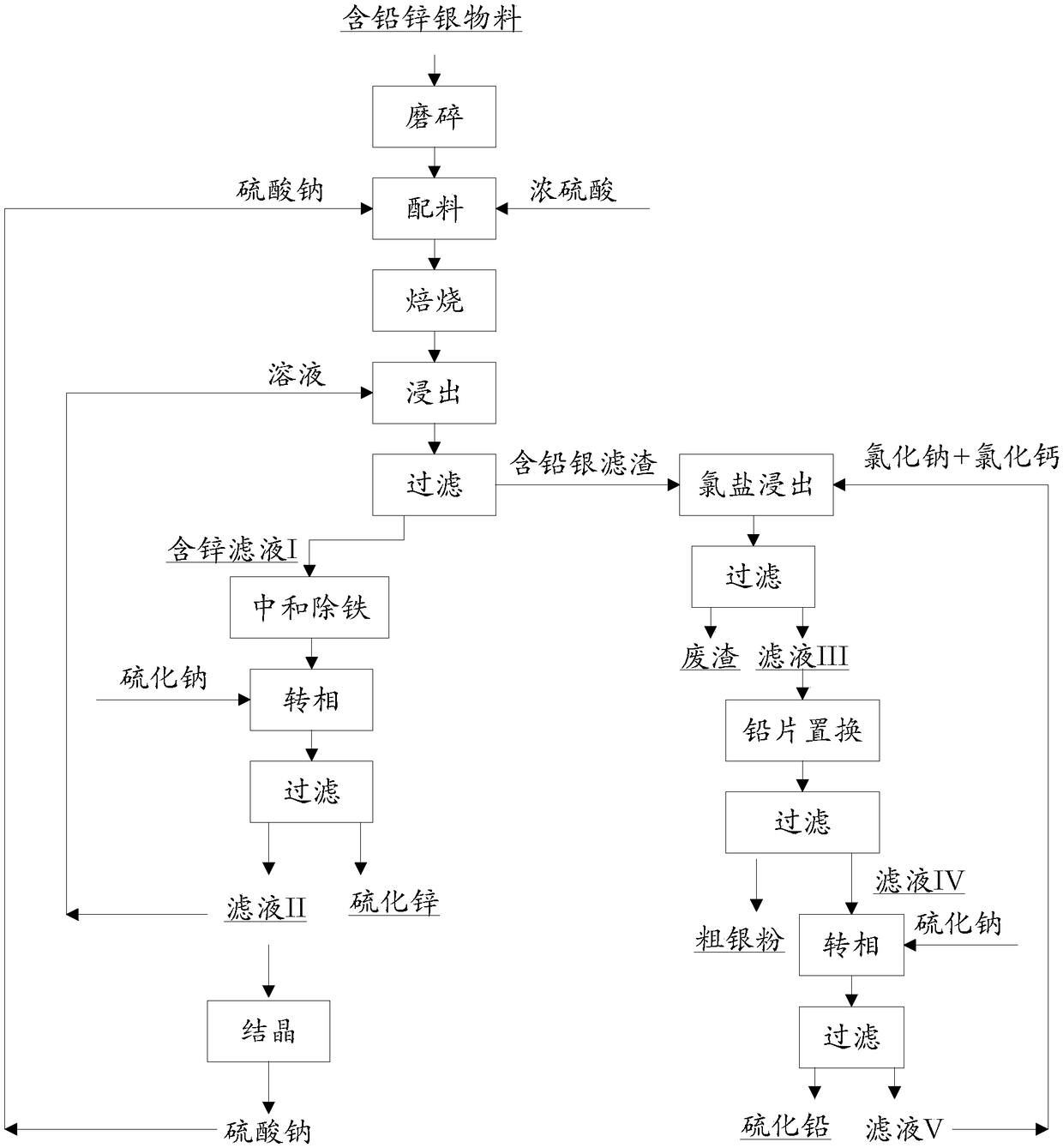
[0034] process such as figure 1 As shown, 100g of lead-zinc-silver material (Zn: 6.21%, Pb: 7.09%; Ag: 324.1g / t) from a lead-zinc smelter in Inner Mongolia was ground to a particle size of -200 mesh to -400 mesh, and concentrated Sulfuric acid (content 98%) 60g, sodium sulfate 60g carry out batching and mix evenly, put into muffle furnace and roast, control roasting temperature to be 250 ℃, roasting time is 2h. After roasting, the obtained material was added to sulfuric acid solution (concentration ~ 2wt%), the solid-to-liquid ratio (g / mL) was 1:5, stirred at 90°C for 1 hour and then filtered to obtain filtrate I containing zinc and Filter residue of lead and silver. Then add sodium carbonate to the zinc-containing filtrate I, adjust its pH to 3.5, and react at 50° C. for 1 hour to neutralize and remove iron. Then add sodium sulfide (excess coefficient: 0.9) to the zinc-containing filtrate I after iron removal, and react at a temperature of 50° C. and a reaction time of 1 h ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] process such as figure 1 As shown, 100g of lead-zinc-silver material (Zn: 6.21%, Pb: 7.09%, Ag: 324.1g / t) from a lead-zinc smelter in Inner Mongolia was ground to a particle size of -200 mesh to -400 mesh, and concentrated Sulfuric acid (content 98%) 70g, sodium sulfate 70g carry out batching and mix evenly, put into muffle furnace and roast, control roasting temperature to be 300 ℃, roasting time is 3h. After roasting, the obtained material was added to sulfuric acid solution (concentration ~ 3wt%), the solid-to-liquid ratio (g / mL) was 1:5, stirred at 90°C for 1.5h, and then filtered to obtain filtrate I containing zinc and Filter residue containing lead and silver. Then add sodium carbonate to the zinc-containing filtrate I, adjust its pH to 4.0, and react at 70° C. for 1 hour to neutralize and remove iron. Then add sodium sulfide (excess coefficient: 0.9) to the zinc-containing filtrate I after iron removal, and react at a temperature of 70° C. and a reaction time ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] process such as figure 1 As shown, 100g of lead-zinc-silver material (Zn: 6.21%, Pb: 7.09%, Ag: 324.1g / t) from a lead-zinc smelter in Inner Mongolia was ground to a particle size of -200 mesh to -400 mesh, and concentrated Sulfuric acid (content 98%) 90g, sodium sulfate 90g carry out batching and mix evenly, put into muffle furnace and roast, control roasting temperature to be 350 ℃, roasting time is 4h. After roasting, the obtained material was added to sulfuric acid solution (concentration ~ 3wt%), the solid-to-liquid ratio (g / mL) was 1:5, stirred at 95°C for 2h and then filtered to obtain filtrate I containing zinc and Filter residue of lead and silver. Then add sodium carbonate to the zinc-containing filtrate I, adjust its pH to 3.6, and react at 90° C. for 2 hours to neutralize and remove iron. Then add sodium sulfide (excess coefficient: 0.9) to the zinc-containing filtrate I after iron removal, and react at a temperature of 90° C. and a reaction time of 2 hours...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com