Method for detecting content of microplastics in water body
A technology for microplastics, water bodies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
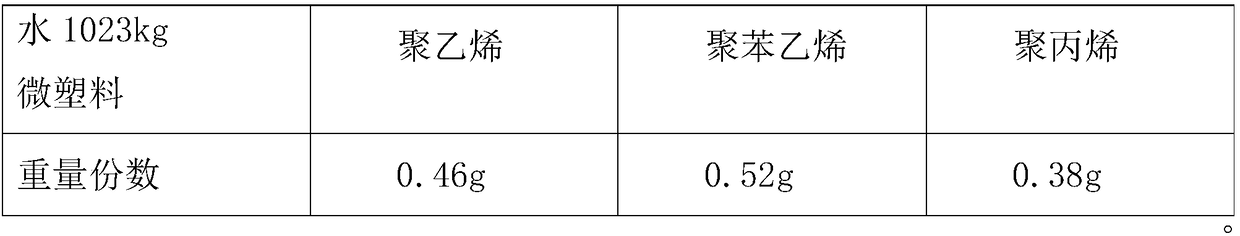
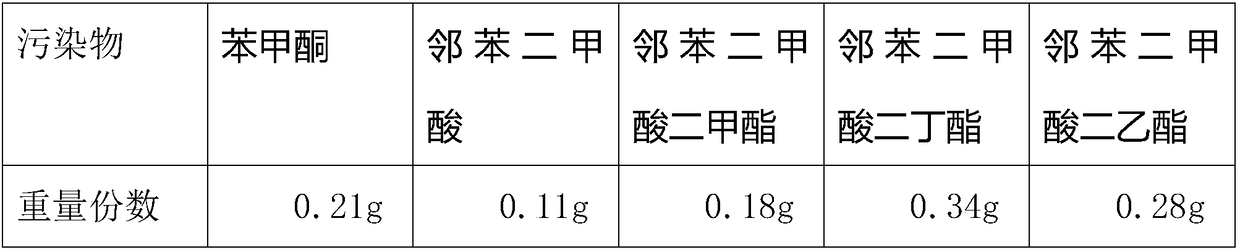
[0034] Example 1 Sampling by direct selection method, collecting 1000ml of water
[0035] First of all, use a binocular microscope to remove impurities from the sampled water body. If the observed fibers are linear without bending or entanglement, they may be biological fibers and should be removed. The particle boundaries must be clear and the overall color uniform. If the particles are white or transparent, use greater magnification or use a fluorescent labeling microscope;
[0036] Then, process the silver filter foil and bend it into a cylindrical shape, select the stirring rod made of glass, and then adhere the filter foil to the stirring rod completely seamlessly by means of magnetron sputtering with activated carbon powder material;
[0037] Secondly, configure the precipitation catalytic reaction solution, and then pour the configured purification solution into the solvent bottle to be detected, the pouring ratio is 0.34:1 by volume, and then connect the stirrer proces...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com