Method for producing gamma-amino butyric acid through continuous conversion of immobilized enzyme
A technology for immobilizing enzymes and aminobutyric acid, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, immobilized on/in organic carriers, botany equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of complex production process and γ-aminobutyric acid output The difference is large, the reaction efficiency needs to be improved, etc., to achieve the effect of simple separation of enzyme and product, simple and fast immobilization process, and good industrialization prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
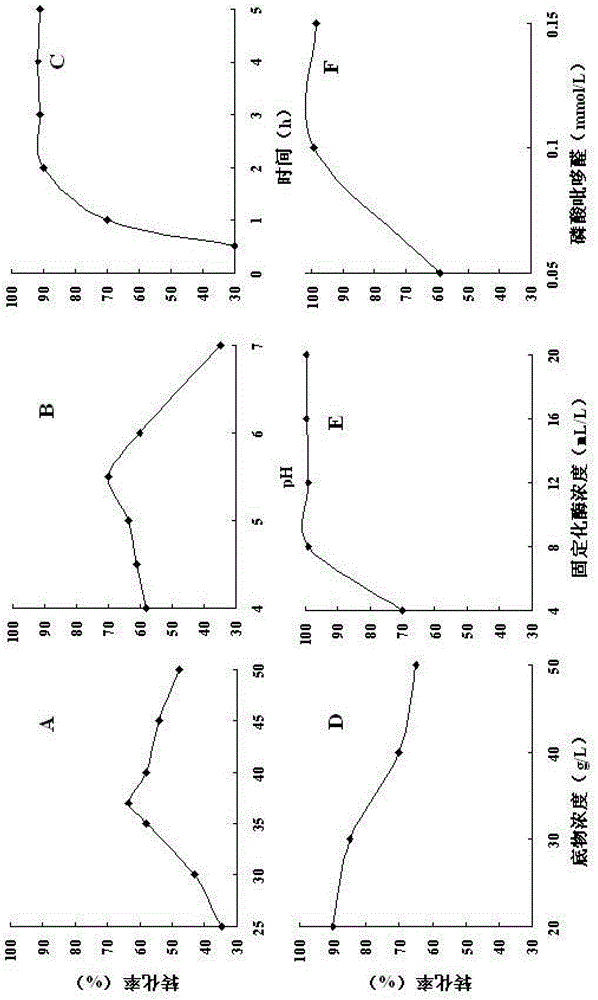
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Cloning and expression of embodiment 1 glutamic acid decarboxylase gene
[0030] According to the glutamic acid decarboxylase gene sequence of Escherichia coli BL21 included in the NCBI database, the upstream primer GAD1: 5'-CGC GGA TCC ATG GAT AAG AAG CAA G-3' and the downstream primer GAD2: 5'CCG CTC GAG CGG TCA GGT were designed ATG TTT AAA G-3'.
[0031] The glutamic acid decarboxylase gene was obtained by PCR amplification using the genome of Escherichia coli BL21 as a template. After the target band was recovered by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, the pET21a(+) vector was connected to construct pET21a(+)-GAD, and transfection Inject BL21(DE3) to obtain genetically engineered bacteria BL21(DE3)-pET21a(+)-GAD.
[0032] Take a single colony of glutamic acid decarboxylase engineered bacteria and inoculate it in LB medium, cultivate overnight at 37°C to obtain a saturated culture, inoculate the saturated culture at 1% in LB medium containing Amp (100 μg / ml), 37 ℃Cont...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The high-performance liquid chromatography detection of embodiment 2γ-aminobutyric acid
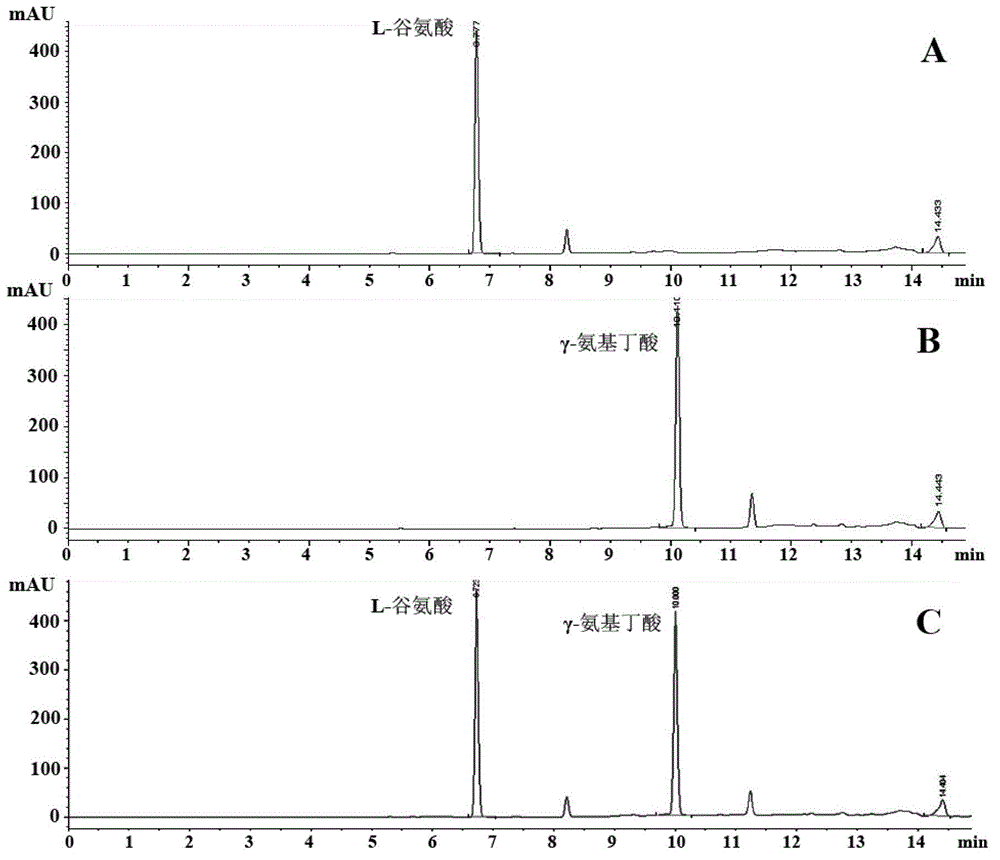
[0035] The content of L-glutamic acid and γ-aminobutyric acid was determined by pre-column derivatization HPLC method, and the derivatization reagent was o-phthalaldehyde reagent. The pre-column derivatization method is as follows: accurately measure 100 μL of sample solution, add 50 μL of derivatization reagent, mix and react for 2 minutes, and take 20 μL of sample for analysis. Column: C 18 Chromatographic column (Inertsil ODS-SP5μ, 4.6×250mm); mobile phase: 0-11min, B phase 8%-100%; room temperature; flow rate 1mL / min; detection wavelength 340nm.
[0036] The reaction solution was centrifuged to get the supernatant, which was derivatized by the above method and then analyzed by HPLC. The results are shown in figure 1 , compared with the γ-aminobutyric acid standard curve to calculate the molar conversion rate of L-sodium glutamate in the substrate solution.
Embodiment 3
[0037] The immobilization of embodiment 3 glutamic acid decarboxylase
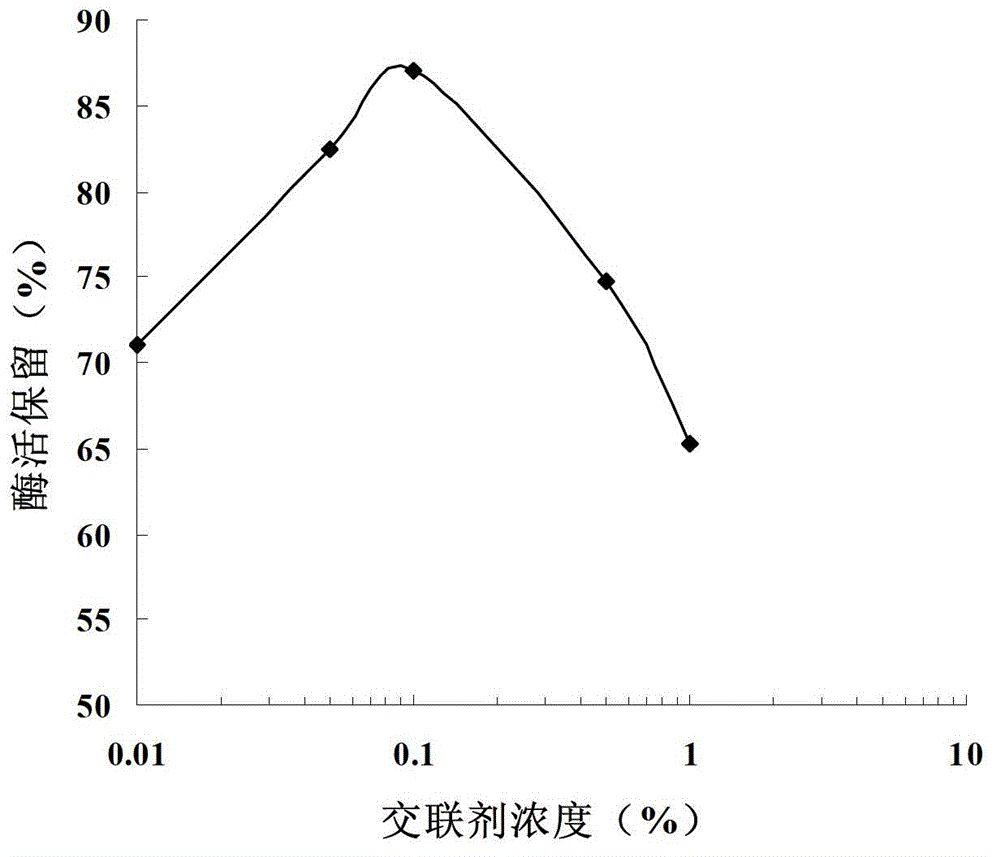
[0038] Take 10 mL of cellulose microspheres (see Chinese Patent, Application No. 200710057042.9) and add them to 50 mL of the cell lysate of the genetically engineered bacteria BL21(DE3)-pET35b-GAD obtained in Example 1, shake overnight at 4°C. After washing with sodium phosphate buffer, add 0.01% to 1% of different concentrations of glutaraldehyde for cross-linking, then block with 1M Gly for 10 h, and wash with sodium phosphate buffer to obtain immobilized glutamic acid decarboxylase, that is, immobilized enzyme. Store at 4°C for later use. Take 1 mL of cellulose microspheres immobilized under different immobilization conditions, add the same dose of L-sodium glutamate to investigate the immobilization efficiency, the results are as follows: figure 2 As shown, the optimal concentration of crosslinker glutaraldehyde is 0.1%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com