Two attenuated lipid A producing Cronobacter mutant strains and application thereof
A technology of ATCC51329, strain, applied in the field of two Cronobacter mutant strains producing attenuated lipid A, to achieve the effects of reducing infection level, improving permeability and weakening cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Construction of mutant C. sakazakii BAA894△lpxM and ATCC 51329△lpxM
[0024] 1. Obtaining the knockout fragment of lpxM gene
[0025] The knockout fragment of the lpxM gene was obtained by chemical total synthesis or step-by-step PCR amplification. The two ends of the gene were the upstream and downstream homology arms, and the middle was the kan fragment with the LoxP site. C. sakazakii BAA894 and ATCC 51329 The nucleotide sequences of the lpxM gene fragments are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The lpxM gene knockout fragment was cloned into pBlueScript II SK(+) to obtain the recombinant plasmid pBlueScript II SK(+)-lpxMU-Lkan-lpxMD. Using the plasmid as a template, the knockout fragment lpxMU-Lkan-lpxMD can be amplified.
[0026] 2. Preparation and electrotransformation of knockout competent cells
[0027] C.sakazakii BAA894( LuLiu, Xiaoyuan Wang, Yanyan Li, Wen Guo. A phosphoethanolamine transferasespecific for the 4′-phosphate residu...
Embodiment 2
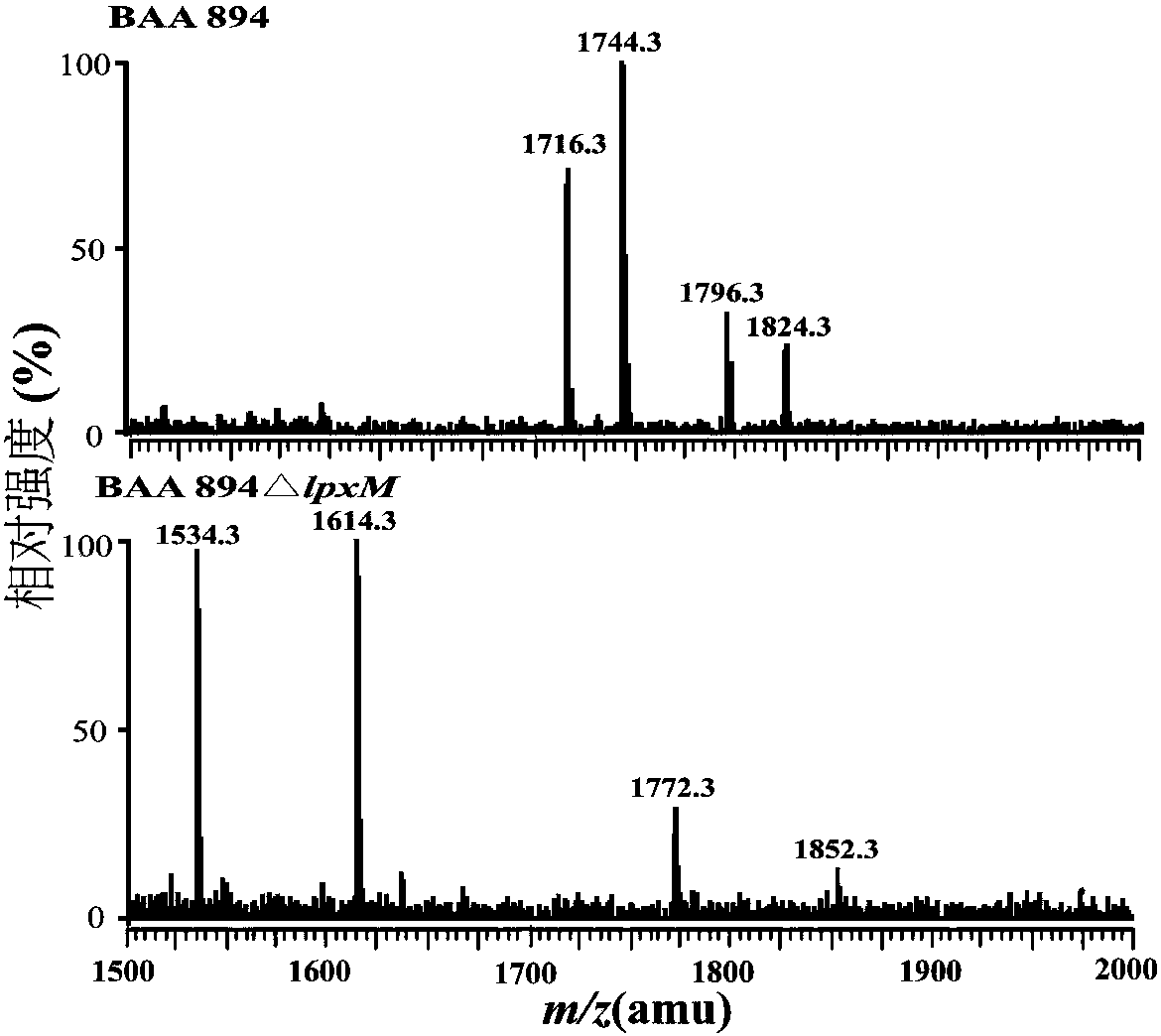
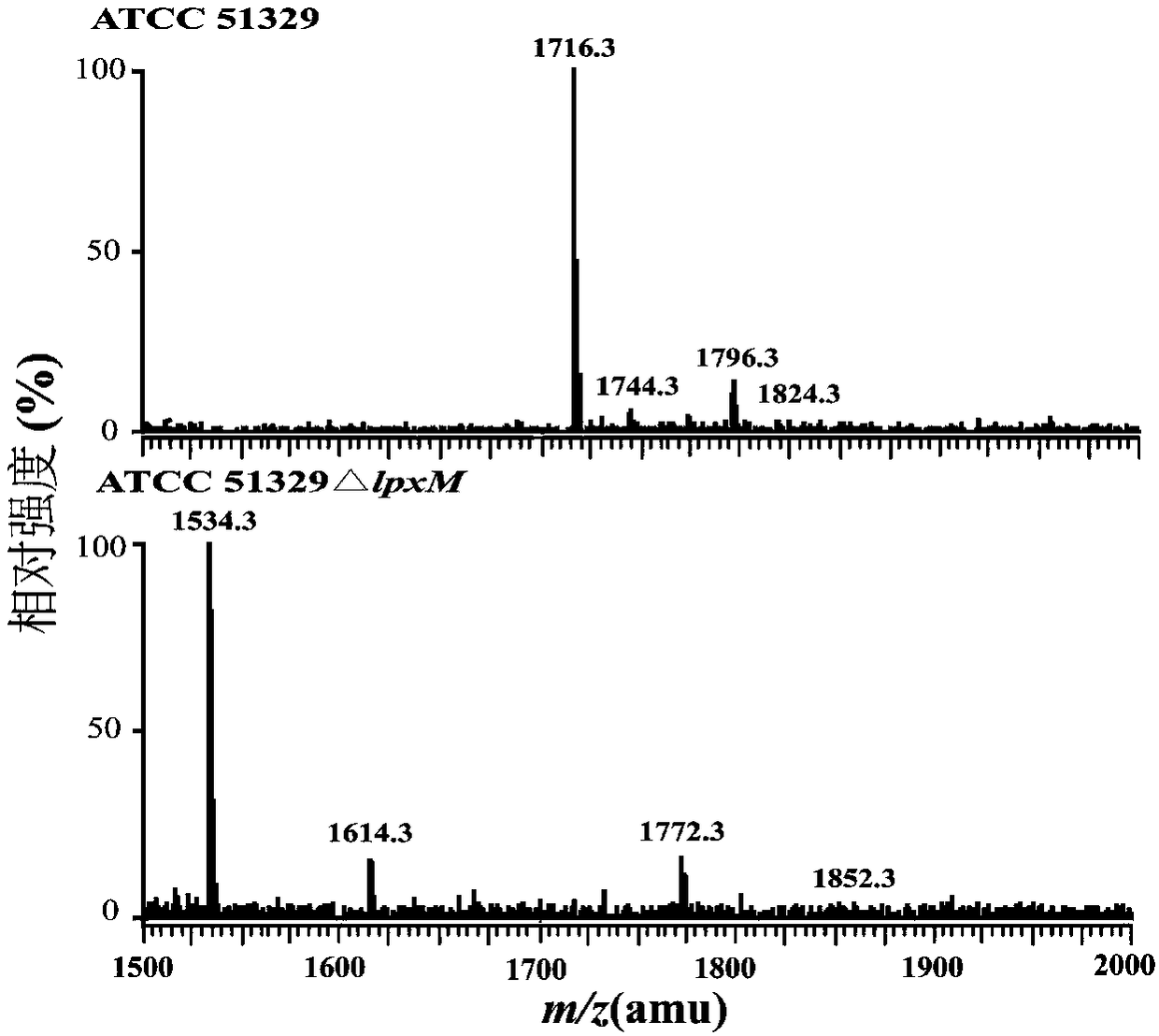
[0031] Lipid A structure ESI / MS analysis of embodiment 2C.sakazakii BAA894 and ATCC 51329 and its lpxM deletion mutant strain
[0032] Lipid A was extracted using chloroform / methanol / H 2 O solution mixed phase extraction. The overnight cultured bacterial solution was divided into initial OD 600 =0.02 transferred to 200mL LB liquid medium, cultivated at 37°C to the late logarithmic phase of the bacteria, centrifuged at 4000rpm for 30min to collect the bacteria, ddH 2 After washing the cells once, use Bligh-Dyer one-phase system (chloroform / methanol / water solution, 1:2:0.8, v / v / v) to suspend the cells in 76mL, magnetically stir for 1h, and centrifuge at 2000rpm for 30min to separate the phases. The system washes the cell fragments 2-3 times; add 27mL of 12.5mM sodium acetate (pH 4.5) solution, ultrasonically shake for 2min, and cleavage the sugar chains in a water bath at 100°C for 30min. After cooling to room temperature, add 30mL chloroform and 30mL methanol to form a Bligh-D...
Embodiment 3
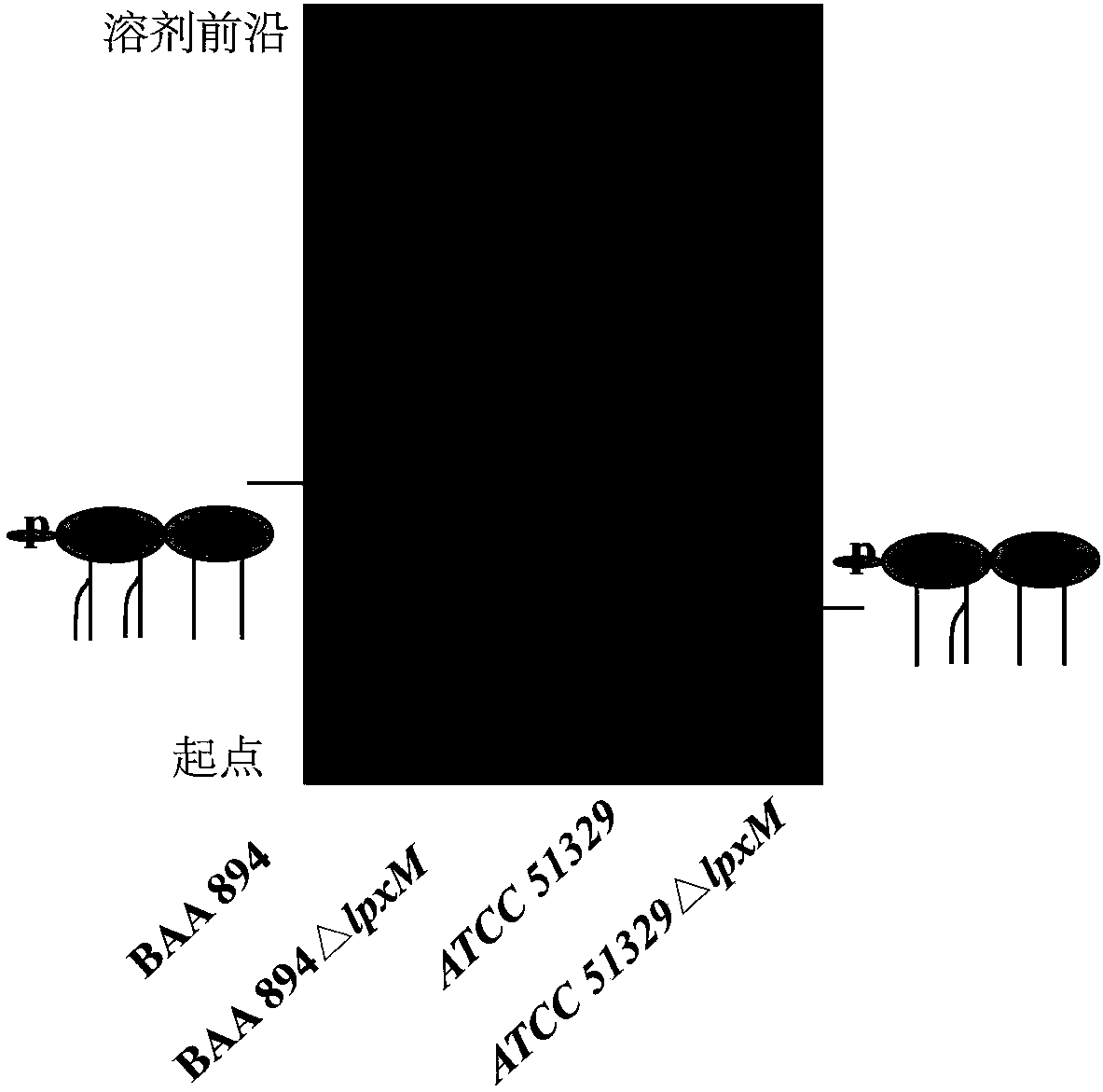
[0036] Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) detection of embodiment 3C.sakazakii BAA894, ATCC 51329 wild type and lpxM deletion mutant strain
[0037] Carry out TLC of lipid A, spot the sample on Gel 60TLC plate, developing agent is chloroform / methanol / water / ammonia (25:15:4:2, v / v / v / v). After the end of the chromatography, dry the developing agent remaining on the plate, carbonize it with 10% sulfuric acid dissolved in ethanol, and place it on a heating plate for color development (the results are as follows: image 3 ).
[0038] TLC results show that this method extracts lipid A from C. sakazakii BAA894, ATCC 51329, and lpxM deletion mutant strains. On the TLC plate, the more fatty acid chains of lipid A, the greater the hydrophobicity and the greater the migration rate. The migration rate of the lipid A strain was lower than that of the wild strain, which indicated that the main structure of the mutant strain lipid A lacked a fatty acid chain.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com