Method for evaluating self-discharge of lithium ion battery
A technology of lithium ion battery and evaluation method, applied in the field of lithium ion power battery, can solve the problems of accelerating the dissolution of metal elements and shortening the evaluation period, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
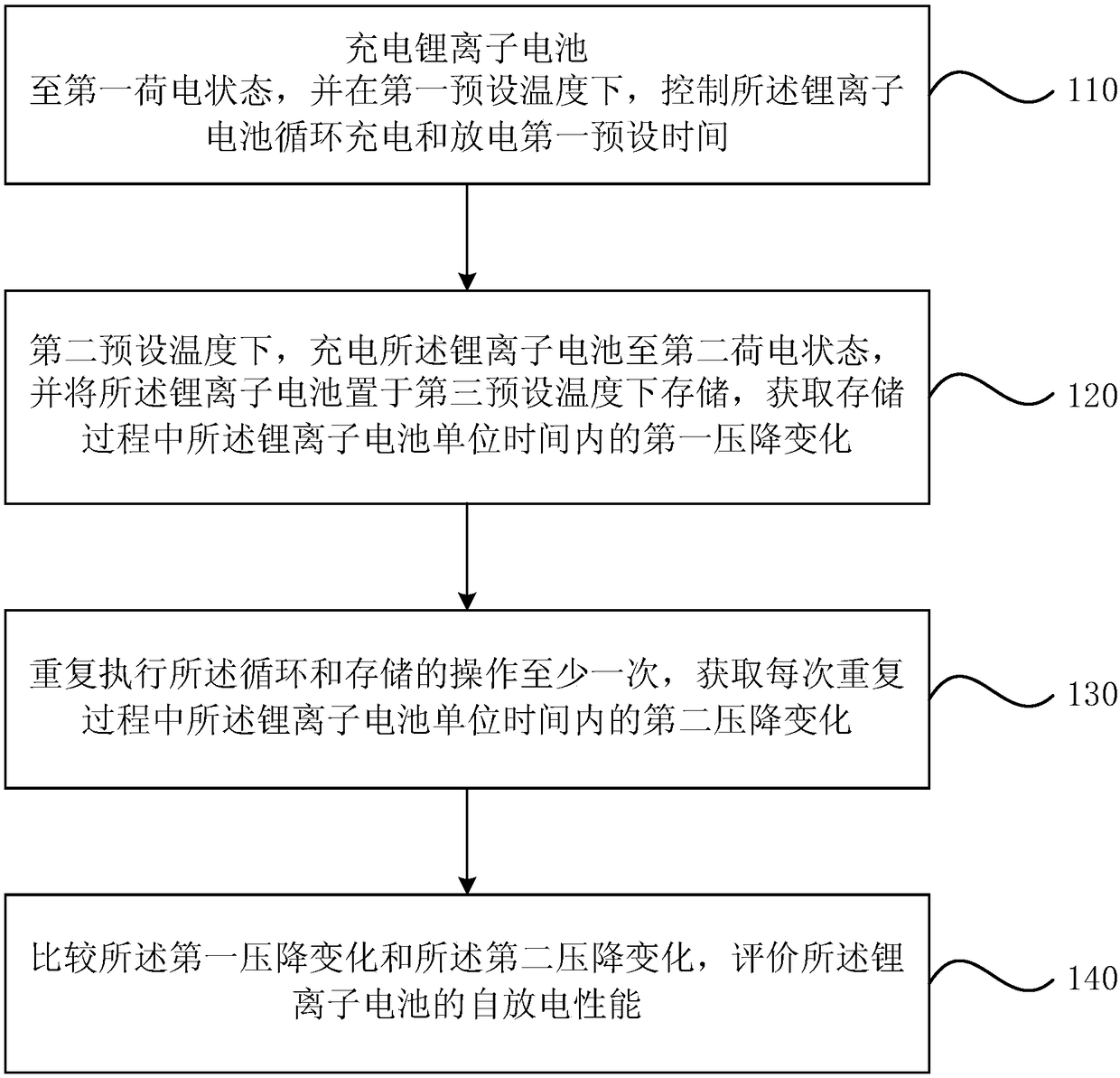
[0037] figure 1 It is a schematic flow chart of a method for evaluating self-discharge of a lithium-ion battery provided in the first embodiment of the present invention. The method for evaluating the self-discharge of lithium-ion batteries in the embodiments of the present invention can be applied to scenarios where it is necessary to quickly identify the influence of metal elements in new materials on the self-discharge performance of lithium-ion batteries. The new materials may include main materials, current collectors, and conductive materials. Exemplary main materials may include lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide, lithium cobalt oxide, graphite, silicon carbon and silicon oxygen; exemplary current collectors may include copper foil and aluminum foil; exemplary conductive agents may include superconducting graphite, Carbon black, acetylene black and graphene. The identifiable metal elements may include metal elements such as iron, copper, zinc, manganese, titanium, alu...
Embodiment 2
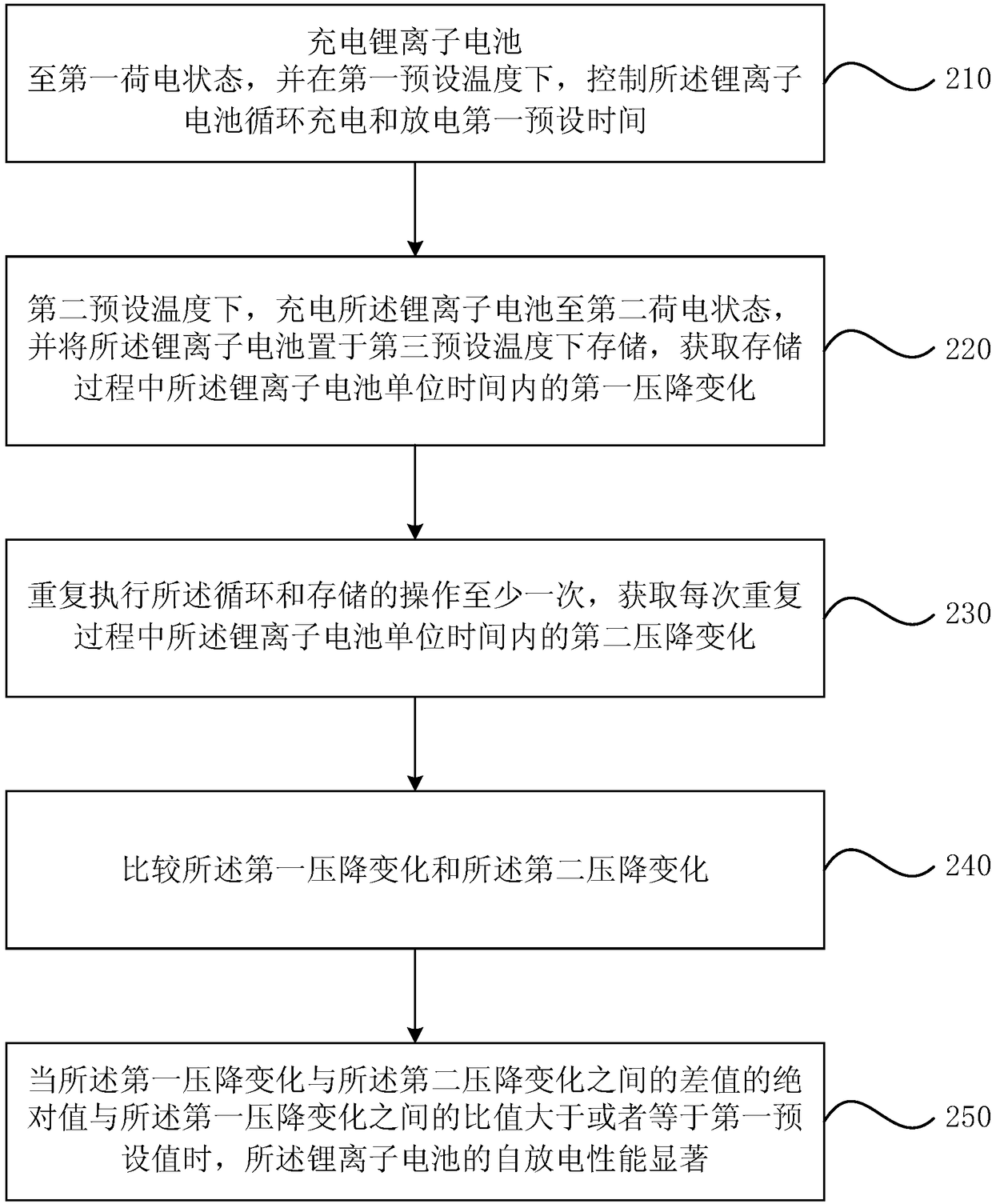
[0067] figure 2 It is a schematic flow chart of a method for evaluating self-discharge of a lithium ion battery provided by the second embodiment of the present invention, see figure 2 , On the basis of the first embodiment, the method includes:
[0068] S210: Charge the lithium-ion battery to a first state of charge, and control the lithium-ion battery to cycle charging and discharging for a first preset time at a first preset temperature.
[0069] S220. Charge the lithium ion battery to a second state of charge at a second preset temperature, and store the lithium ion battery at a third preset temperature, and obtain the unit time of the lithium ion battery during the storage process The first pressure drop changes within.
[0070] S230. Repeat the cycle and storage operations at least once, and obtain a second voltage drop change of the lithium ion battery per unit time during each repetition.
[0071] Wherein, the first preset temperature is greater than the second preset temper...
Embodiment 3
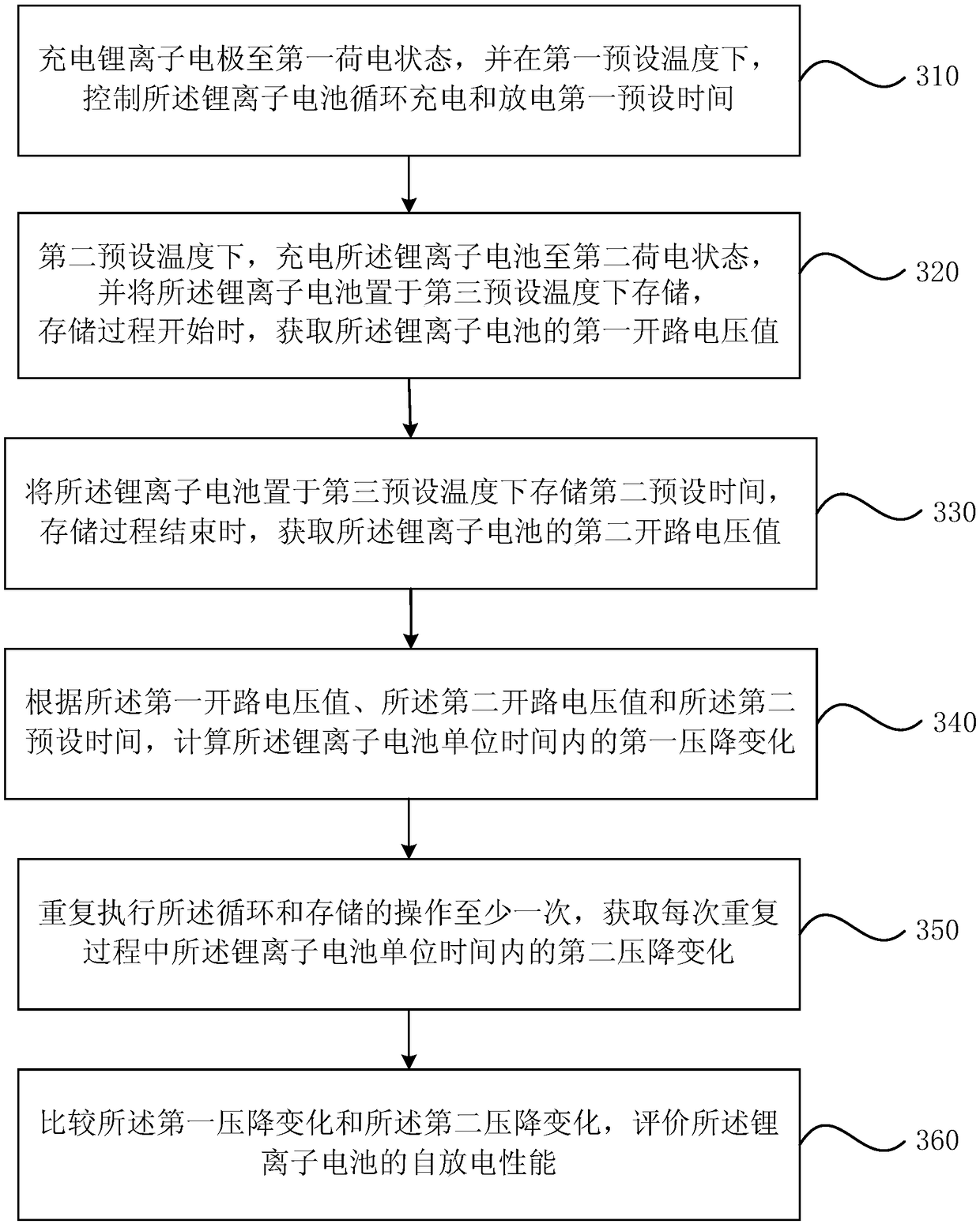
[0083] image 3 It is a schematic flow chart of a method for evaluating self-discharge of a lithium ion battery provided by the third embodiment of the present invention, see image 3 , On the basis of the first embodiment, the method includes:
[0084] S310. Charge the lithium-ion battery to a first state of charge, and control the lithium-ion battery to cycle charging and discharging for a first preset time at a first preset temperature.
[0085] S320. At the second preset temperature, charge the lithium ion battery to a second state of charge, and store the lithium ion battery at a third preset temperature. When the storage process starts, obtain the lithium ion battery The first open circuit voltage value.
[0086] S330. Place the lithium ion battery at a third preset temperature and store it for a second preset time, and when the storage process ends, obtain a second open circuit voltage value of the lithium ion battery.
[0087] Optionally, the second preset time may be 1 day to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com