Method for recovering precious metal platinum in car dead catalyst through pyrogenic process
A waste catalyst and precious metal technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of increasing the extraction cycle, prolonging the extraction cycle, insufficient platinum capture, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing processing costs, reducing smelting costs, and easy industrialization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
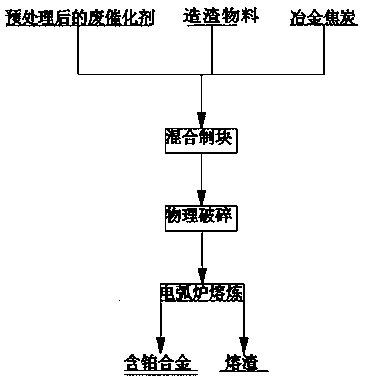
[0031] See attached figure 1 , first carry out pretreatment to waste automobile catalyst, then weigh 10kg through pretreated automobile waste catalyst (wherein SiO 2 60%, Al 2 o 3 12%, Pt700g / t) and 4.31kg of dried slagging agent (including 3.1kg of CaO, Al 2 o 3 0.81kg, MgO 0.4kg) and Fe 3 o 4 0.35kg and 0.2kg of metallurgical coke (with a fixed carbon content of 80%) were mixed evenly, and made into blocks, and then put into a DC electric arc furnace after physical crushing, and smelted in a DC electric arc furnace at a high temperature of 1600°C for 2 hours. After the slagging process, the slag automatically floats on the upper layer of the melt due to its low density, and the platinum-containing alloy sinks to the bottom of the melt due to its high density, so that the entire melt is divided into two parts, the upper layer is slag liquid, and the lower layer For platinum-containing alloys. After the smelting is completed, the upper slag liquid in the graphite cr...
Embodiment 2
[0033] See attached figure 1 , first carry out drying treatment to waste automobile catalyst, drying temperature is 150 ℃, drying time is 14h, then weigh 5kg through drying treatment waste catalyst (wherein SiO 2 60%, Al 2 o 3 12%, Pt700g / t) and 2.22kg of dried slagging agent (including 1.61kg of CaO, Al 2 o 3 0.41kg, MgO 0.2kg) and Fe 3 o 4 0.18kg and 0.15kg of metallurgical coke (with a fixed carbon content of 80%) were mixed evenly, and made into blocks, and then put into a DC electric arc furnace after physical crushing, and smelted in a DC electric arc furnace at a high temperature of 2000°C for 2 hours. After the slagging process, the slag automatically floats on the upper layer of the melt due to its low density, and the platinum-containing alloy sinks to the bottom of the melt due to its high density, so that the entire melt is divided into two parts, the upper layer is slag liquid, and the lower layer For platinum-containing alloys. After the smelting is co...
Embodiment 3
[0035] See attached figure 1 , first carry out drying treatment to waste automobile catalyst, drying temperature is 150 ℃, drying time is 16h, then weigh 7kg through drying treatment waste catalyst (wherein SiO 2 60%, Al 2 o 3 12%, Pt700g / t) and 3.05kg of dried slagging agent (including 2.2kg of CaO, Al 2 o 3 0.57kg, MgO 0.28kg) and Fe 3 o 4 0.25kg and 0.18kg of metallurgical coke (with a fixed carbon content of 80%) were mixed evenly, and made into blocks, and then put into a DC electric arc furnace after physical crushing, and smelted in a DC electric arc furnace at a high temperature of 1800°C for 2 hours. After the slagging process, the slag automatically floats on the upper layer of the melt due to its low density, and the platinum-containing alloy sinks to the bottom of the melt due to its high density, so that the entire melt is divided into two parts, the upper layer is slag liquid, and the lower layer For platinum-containing alloys. After the smelting is co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com