Rare earth nanoparticles with intense red fluorescence, preparation method of rare earth nanoparticles and application of rare earth nanoparticles to cell imaging
A nanoparticle and red fluorescent technology, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nano-optics, etc., can solve the problems of large size of rare earth fluorescent materials and difficulty in entering cells for imaging, and achieve low cost, good biocompatibility and biosafety Sexuality and low cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1 The preparation of rare earth nanoparticles C:EuTb
[0022] Add 5 mL of polyethylene glycol 400 liquid, 0.25 mmol of europium nitrate solid and 0.25 mmol of terbium nitrate solid into the three-necked flask respectively to form a mixture with a molar ratio of europium ions: terbium ions of 55:1:1. Under an argon protective atmosphere, the mixture was heated to 100° C. and then continuously stirred for 30 minutes to form an emulsion. The temperature was gradually raised to 196° C. within 6 minutes and then the heating was stopped. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature while stirring. The reaction solution was centrifuged, and the resulting yellow precipitate was washed twice with acetone and pure water by centrifugation, and finally dried at 60°C for use.
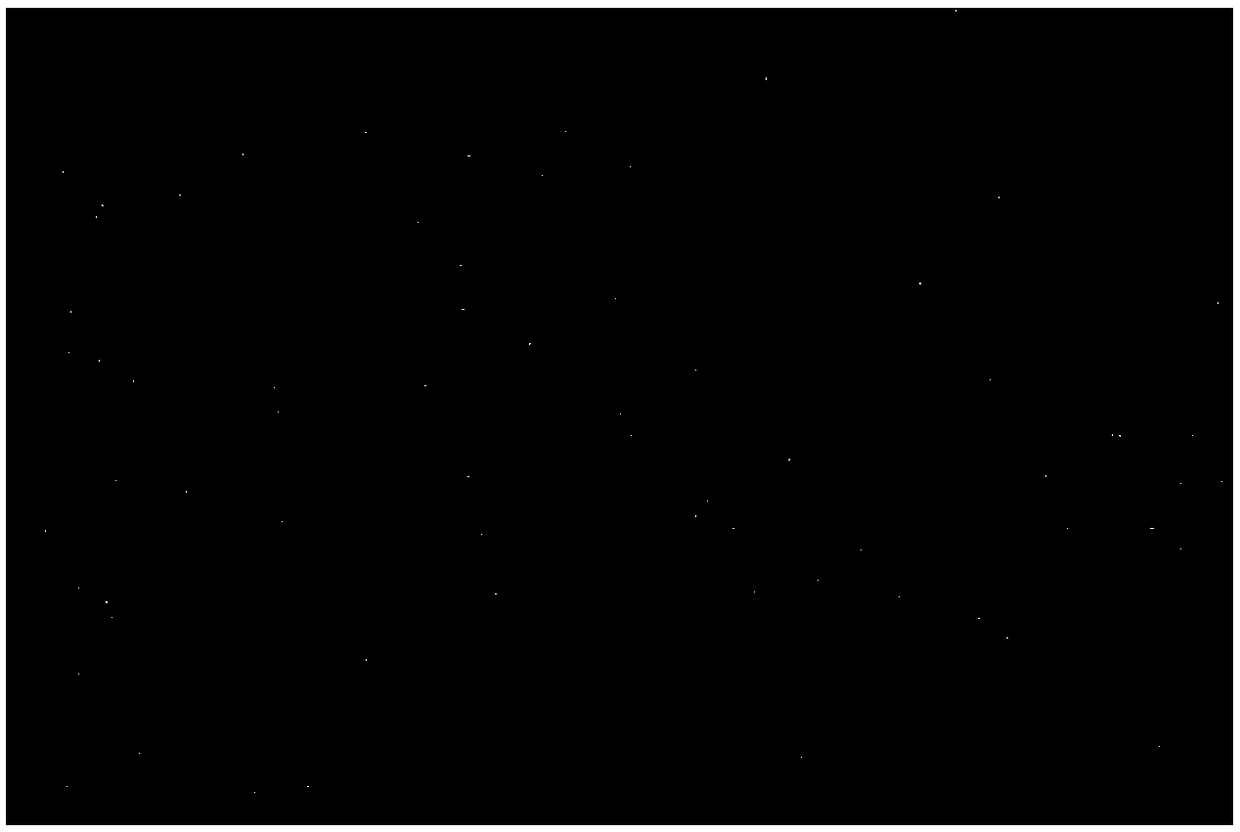
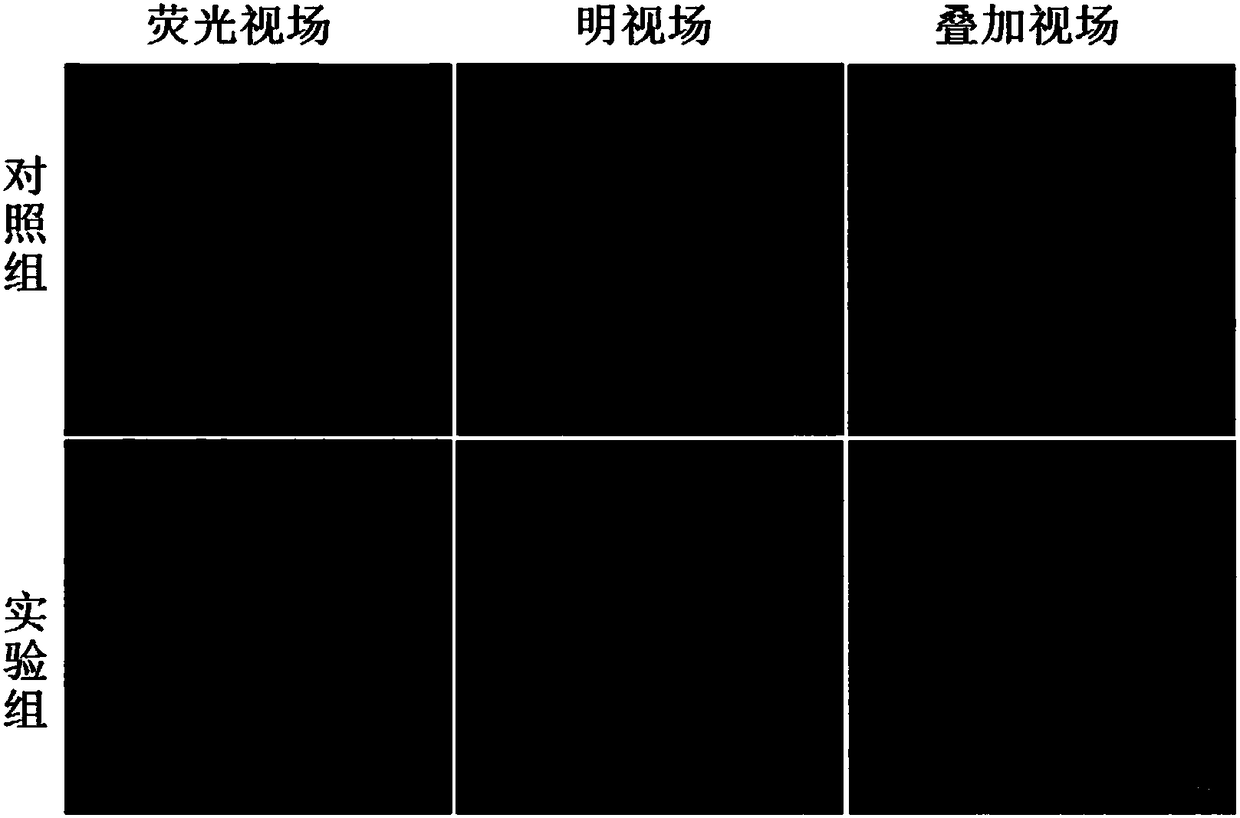
[0023] figure 1 is a transmission electron microscope image of the prepared rare earth nanoparticles C:EuTb, and C:EuTb is a spherical nanoparticle with a diameter of 3 to 5 nanometers. T...
Embodiment 2
[0024] The preparation of embodiment 2 rare earth nanoparticles C:EuTb
[0025] Add 5 mL of polyethylene glycol 400 liquid, 0.25 mmol of europium nitrate solid and 0.375 mmol of terbium nitrate solid into the three-necked flask respectively to form a mixture with a molar ratio of europium ions: terbium ions of 55:1:1.5. Under an argon protective atmosphere, the mixture was heated to 100° C. and then continuously stirred for 40 minutes to form an emulsion. The temperature was gradually raised to 196° C. within 6 minutes and then the heating was stopped. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature while stirring. The reaction solution was centrifuged, and the resulting yellow precipitate was washed twice with acetone and pure water by centrifugation, and finally dried at 60°C for use.
[0026] The electron microscope image of rare earth nanoparticles C:EuTb prepared in this example is similar to Example 1, and the C:EuTb is a spherical nanoparticle with a diameter of 2-...
Embodiment 3
[0027] The preparation of embodiment 3 rare earth nanoparticles C:EuTb
[0028] Add 5 mL of polyethylene glycol 400 liquid, 0.5 mmol of europium nitrate solid and 0.625 mmol of terbium nitrate solid into the three-necked flask respectively to form a mixture with a molar ratio of europium ions: terbium ions of 55:2:2.5. Under an argon protective atmosphere, the mixture was heated to 100° C. and stirred continuously for 50 minutes to form an emulsion. The temperature was gradually raised to 196° C. within 6 minutes and then the heating was stopped. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature while stirring. The reaction solution was centrifuged, and the resulting yellow precipitate was washed twice with acetone and pure water by centrifugation, and finally dried at 60°C for use.
[0029] The electron microscope image of the rare earth nanoparticles C:EuTb prepared in this example is similar to that of Example 1, and the C:EuTb is a spherical nanoparticle with a diameter...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com