Planting method for Cichorium endivia rich in plurality of trace elements
A planting method and technology of trace elements, which are applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, planting substrates, fertilizers made of biological waste, etc., to achieve the effects of increasing growth rate, convenient operation and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
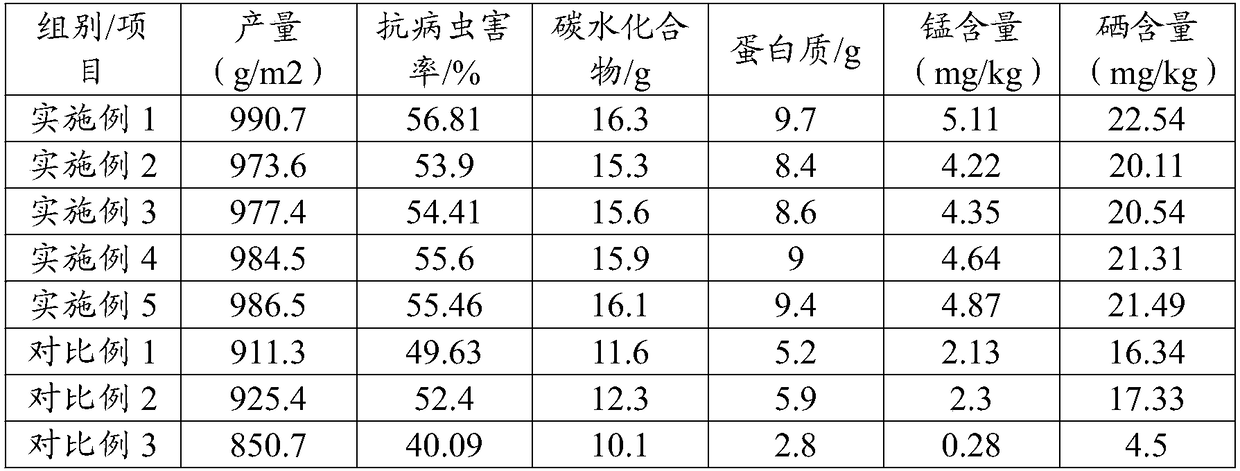
Embodiment 1
[0032] A method for planting bitter chrysanthemum rich in multiple trace elements, comprising the following steps:
[0033] (1) After the seeds are sterilized, put them in 30°C to accelerate germination for 1 day, and then the seeds will be white. Sow the seeds into the planting cup, add the substrate to cover, and pour water. Shade net, remove the sunshade net after emergence, set the seedlings when there are 2 to 3 true leaves, and leave 1 strong seedling per cup;
[0034] (2) When the seedlings grow 3 to 6 true leaves, water them thoroughly, and plant them with roots and soil on the planting plate in the cultivation tank;
[0035] (3) In the early stage of planting, the EC value of the nutrient solution is 0.8-1.3ms / cm, and in the later stage of growth, the EC value of the nutrient solution is 1.3-2.0ms / cm. It is tested every 7 days, replenished and adjusted in time, and the amount of water added each time is the initial 20-30% of the total amount, the nutrient solution is...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The present embodiment is a kind of bitter chrysanthemum planting method that is rich in various trace elements, and described nutrient solution is made up of the raw material of following weight part: 10 parts of traditional Chinese medicine dregs, 7 parts of red jade soil, 12 parts of soybean flour, 9 parts of bamboo charcoal, corn 6 parts of bran, 0.016 part of gallium nitrate, 0.02 part of copper sulfate, 0.5 part of ferrous chloride, 0.1 part of manganese sulfate, 0.005 part of zinc borate, 0.015 part of sodium molybdate, 0.01 part of sodium selenite, 3 parts of fermentation broth.
[0045] In this embodiment, a method for planting bitter chrysanthemum rich in various trace elements, the fermented liquid is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1 part of cottonseed cake, 4 parts of wheat bran, 5 parts of tapioca starch, 8 parts of selenium-enriched yeast, 3 parts xylitol.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Present embodiment is a kind of bitter chrysanthemum planting method rich in various trace elements, and described nutrient solution is made up of the raw material of following weight part: 12 parts of traditional Chinese medicine dregs, 9 parts of red jade soil, 15 parts of soya bean flour, 15 parts of bamboo charcoal, corn 8 parts of bran, 0.04 parts of gallium nitrate, 0.08 parts of copper sulfate, 0.9 parts of ferrous chloride, 0.15 parts of manganese sulfate, 0.009 parts of zinc borate, 0.02 parts of sodium molybdate, 0.02 parts of sodium selenite, and 5 parts of fermentation broth.
[0048] In this embodiment, a planting method of bitter chrysanthemum rich in various trace elements, the fermented liquid is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3 parts of cottonseed cake, 6 parts of wheat bran, 10 parts of tapioca starch, 12 parts of selenium-enriched yeast, 7 parts xylitol.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| transmittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com