Method for purifying graphite by co-heating hexafluoromanganate and antimony pentafluoride generating fluorine gas
A technology of potassium hexafluoromanganate and antimony pentafluoride, applied in fluorine/hydrogen fluoride, chemical instruments and methods, fluorine, etc., can solve problems such as adverse effects, achieve high environmental performance, simple process, and optimized equipment structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
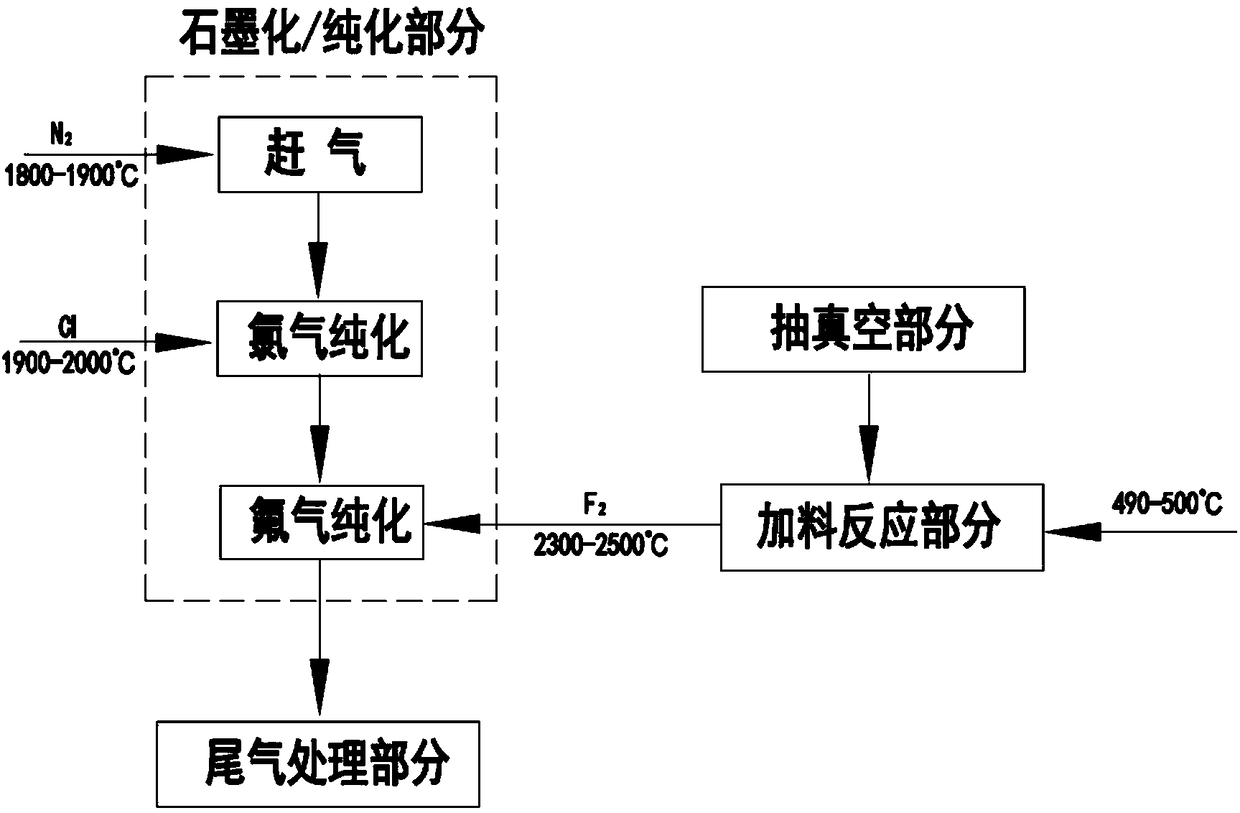
[0050] like figure 1 Shown, the method for the purification of graphite of potassium hexafluoromanganate and antimony pentafluoride co-heating produces fluorine gas, is characterized in that, comprises the following production steps:
[0051] (a) Vacuum part: vacuumize the fluorine gas reactor to remove the air in the reactor;
[0052](b) Feed reaction part: take antimony pentafluoride and potassium hexafluoromanganate at a mass ratio of 2 to 3:1, and add them to the reactor to react to generate fluorine gas, and the reaction temperature is 480 to 520°C;
[0053] (c) Graphitization / purification part: Arrange multiple groups of graphite products in the graphitization furnace according to the required spacing, fill in insulation material and resistance material in turn, and heat the graphitization furnace until the temperature of the furnace core is 1800 At ~1900°C, nitrogen gas is introduced to remove the air in the furnace core, and the heating rate is 10-30°C / min; when the g...
Embodiment 2
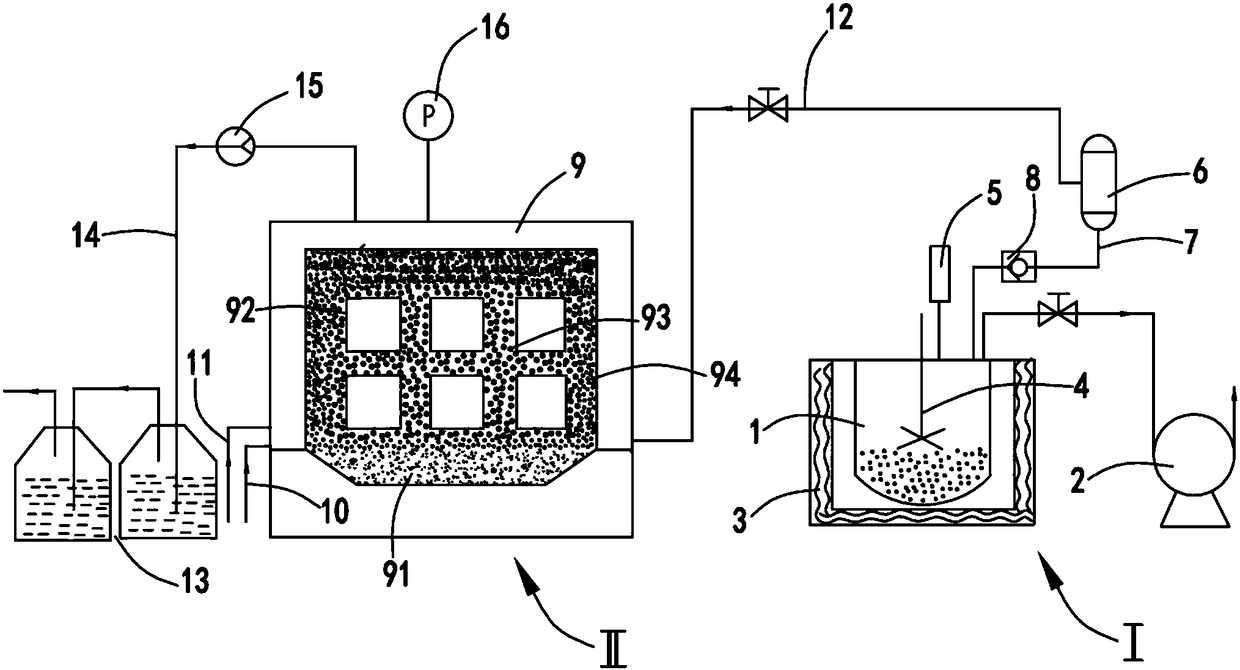
[0060] like figure 2 As shown, the system for co-heating potassium hexafluoromanganate and antimony pentafluoride to produce fluorine gas to purify graphite is characterized in that it includes a fluorine gas reaction unit I, and the fluorine gas reaction unit I includes:
[0061] Reactor 1 and a vacuum pump 2 for evacuating the inside of the reactor 1, a resistance heater 3 for heating the reactor 1 is installed on the outside of the reactor 1, and a thermocouple is arranged on the top of the reactor 1 5, the thermocouple 5 is used to monitor the heating temperature of the resistance heater 3; and
[0062] Furnace body unit II, the furnace body unit II includes:
[0063] Furnace body 9, furnace bottom material 91 is arranged at the bottom of said furnace body 9, graphite product is placed at furnace core 92, resistance material 93 is arranged around graphite product, heat insulating material 94 is arranged on the outside of resistance material 93, said One side of the furn...
Embodiment 3
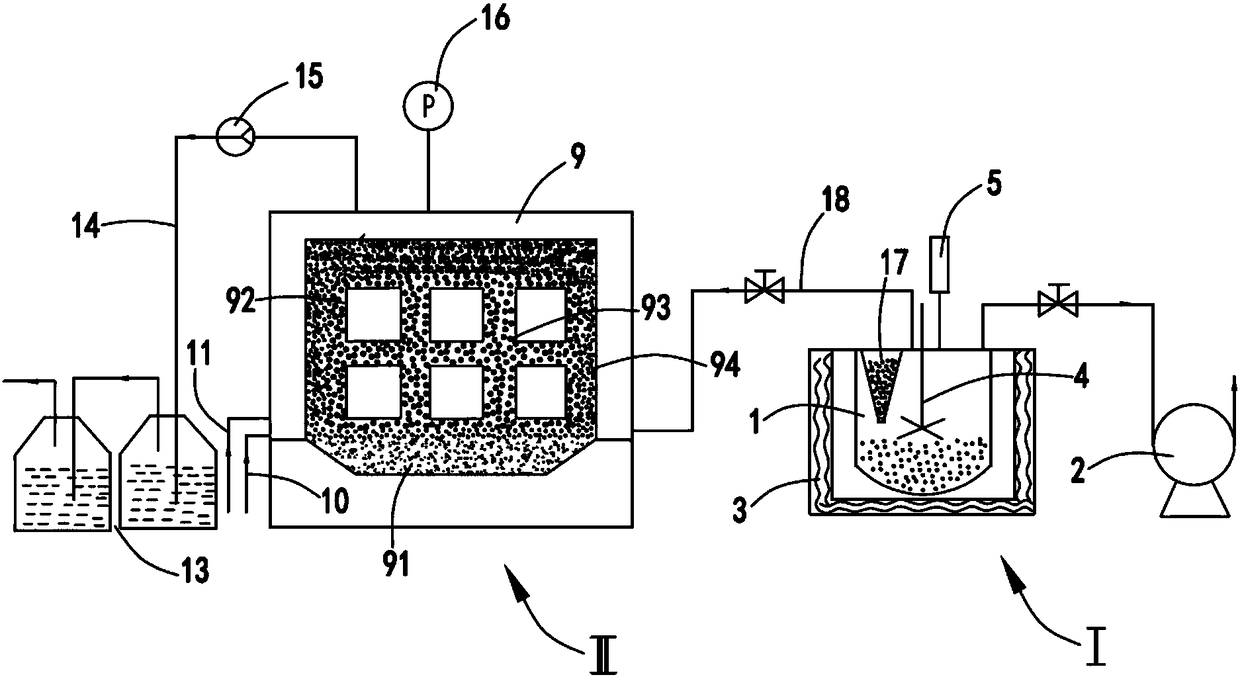
[0070] like image 3 As shown, the system for co-heating potassium hexafluoromanganate and antimony pentafluoride to produce fluorine gas to purify graphite is characterized in that it includes a fluorine gas reaction unit I, and the fluorine gas reaction unit I includes:
[0071] Reactor 1 and a vacuum pump 2 for evacuating the inside of the reactor 1, a resistance heater 3 for heating the reactor 1 is installed on the outside of the reactor 1, and a thermocouple is arranged on the top of the reactor 1 5, the thermocouple 5 is used to monitor the heating temperature of the resistance heater 3; and
[0072] Furnace body unit II, the furnace body unit II includes:
[0073] Furnace body 9, furnace bottom material 91 is arranged at the bottom of said furnace body 9, graphite product is placed at furnace core 92, resistance material 93 is arranged around graphite product, heat insulating material 94 is arranged on the outside of resistance material 93, said One side of the furna...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com