A gene gmlecrk-r for improving plant disease resistance and its application
A plant and gene technology, applied in the fields of plant molecular biology and plant genetic engineering, to achieve the effect of improving disease resistance and enhancing disease resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
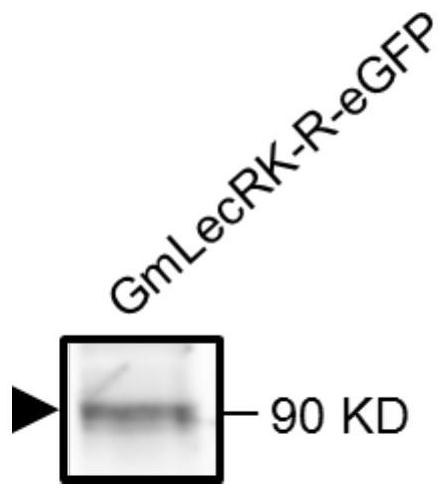
[0046] Example 1. Cloning and sequence structure analysis of GmLecRK-R gene
[0047] Seeds of soybean and Feng-47 were directly sown in pots filled with nutrient soil, cultivated in a greenhouse (21-23°C, 14h light / 10h dark), and 2-week-old plants were used for RNA extraction.
[0048] Total RNA extraction: using soybean leaves as materials, the total RNA was extracted using the RNA extraction kit from Omega Company in accordance with the instructions, and the RNA content and quality were detected with a spectrophotometer.
[0049] Reverse transcription to generate the first strand: take 0.7 μg RNA as a template, perform cDNA synthesis according to the instructions of Takara’s PrimeScript reverse transcriptase reagent kit, and dilute to 20uL for reaction. Take an appropriate amount of reverse transcription product for subsequent gene cloning PCR.
[0050] Use the first strand of cDNA as an RT-PCR template, and perform PCR in a conventional method to amplify the GmLecRK-R gene...
Embodiment 2
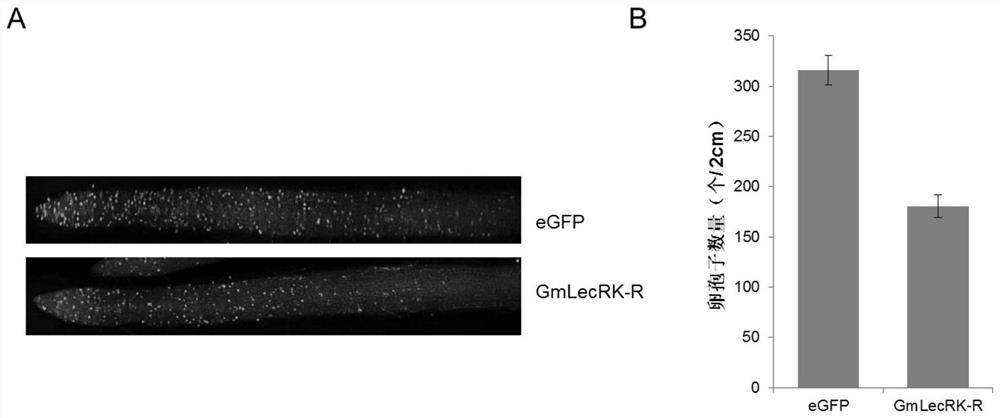
[0058] Example 2. Expression of GmLecRK-R gene in soybean root hairs:
[0059] The specific steps are briefly described as follows:
[0060] 1) Planting of soybean Hefeng-47:
[0061] Sow the seeds of soybean Hefeng-47 evenly in flower pots with vermiculite, cover the flower pots with black plastic film at the beginning or place the flower pots in a dark place for cultivation, and after the yellowed seedlings grow evenly, uncover Black plastic film, remove the seed coat, water (about 3 days to 4 days), and place under suitable light to cultivate (about 1 and a half days to 2 days), that is, the cotyledon of the six-day-old plant can be used for the experiment.
[0062] 2) Agrobacterium culture
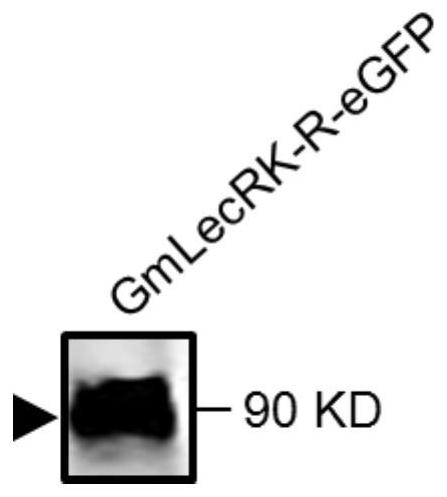
[0063] Single colonies of Agrobacterium rhizogenes K599 transfected with pBin::GmLecRK-R-eGFP vector and pBin::eGFP vector were picked from the plate, respectively, and inoculated into 2mL LB liquid medium (Kana 50ug / mL, Streptomyces 50ug / mL) on a constant temperature shaker at 30°C...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Embodiment 3. the cultivation of Phytophthora
[0075] Inoculate the transgenic Phytophthora sojae with red fluorescence on the solid V8 medium plate (G418 50ug / mL), or inoculate the Phytophthora nicotiana on the solid V8 medium plate. The inoculated V8 medium plate was cultured at 25°C in the dark for 5 days and then used for subsequent experiments.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com