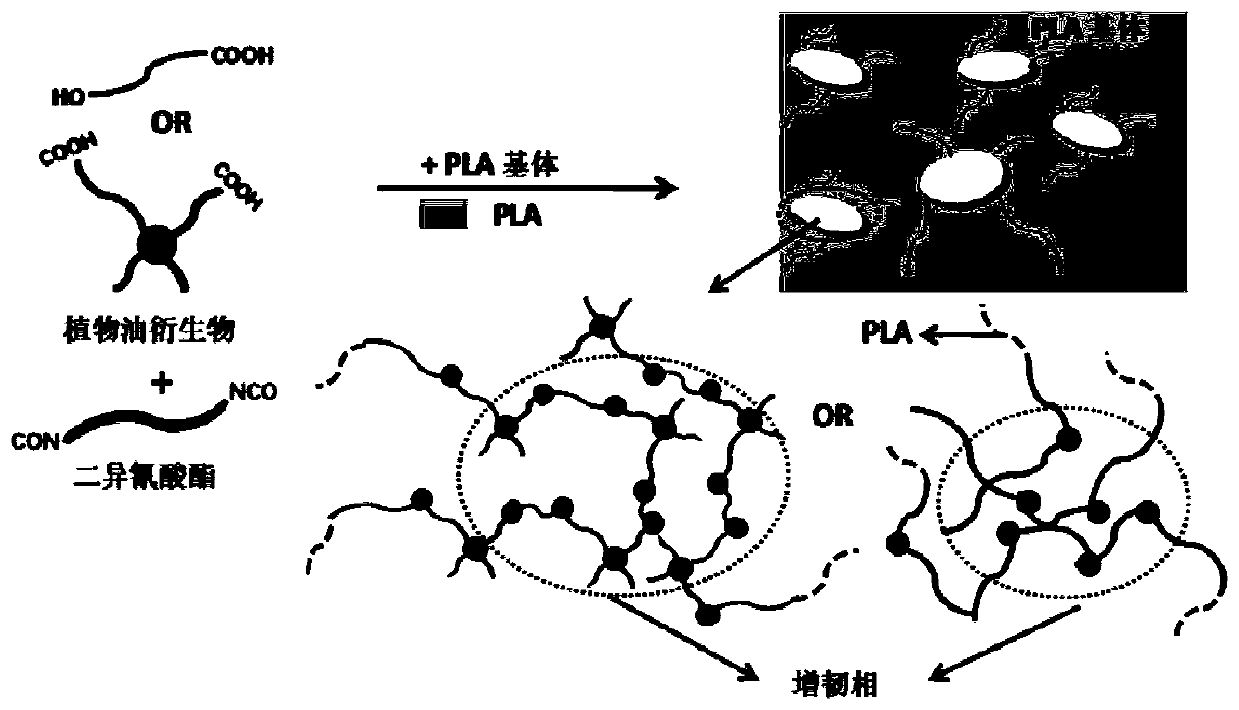
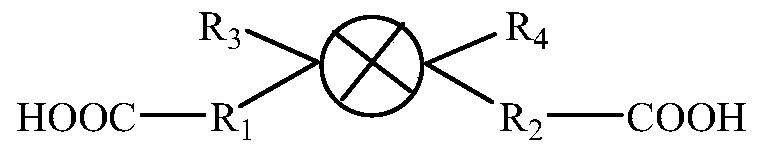
Method for preparing polylactic acid composites with high impact toughness by reactive blending of vegetable oil derivatives
A vegetable oil derivative and reactive technology, which is applied in the field of polymer materials, can solve the problems of poor water resistance of PLA composites, limited improvement of PLA impact toughness, and unfavorable molding processing, and achieves improved interface compatibility. Biodegradability, effect of good melt flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] The preparation of hydrogenated dimer acid (acid value 197.3mgKOH / g) and L-lysine ethyl diisocyanate (LDI) in situ polymerization toughened polylactic acid derived from vegetable oil is as follows:
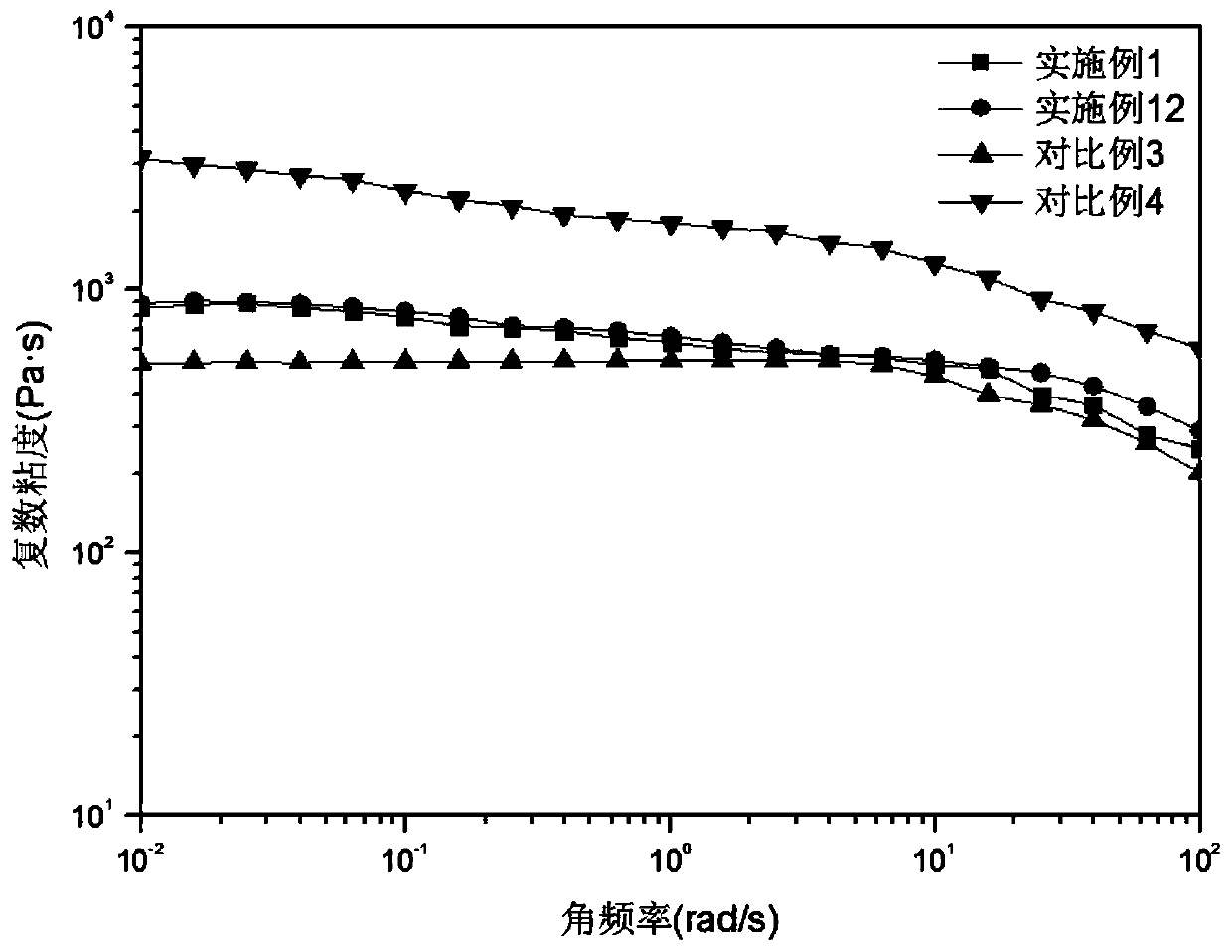
[0066] After drying 80kg of polylactic acid (PLA), heat it to melt in an internal mixer at a temperature of 165°C and a rotation speed of 100r / min, and mix it with hydrogenated dimer acid (DA) and L-lysine ethyl ester A total of 20kg of isocyanate (LDI) (the number of moles of carboxyl groups contained in DA is equal to the number of moles of isocyanate groups contained in LDI). Afterwards, 0.125kg of catalyst dibutyltin dilaurate (DBTDL) was added, and after the torque tended to be balanced, the material was taken out and hot-pressed at 175°C to obtain toughened polylactic acid. In this embodiment, a sample with width and thickness of 12.50×3.20mm and a remaining width of 10.00mm after making the notch is used to test the performance. The performance is shown in Table 1. ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] The preparation of hydrogenated dimer acid (acid value 197.3mgKOH / g) and L-lysine ethyl diisocyanate (LDI) in situ polymerization toughened polylactic acid derived from vegetable oil is as follows:
[0073]After drying 80kg of polylactic acid (PLA), heat it to melt in an internal mixer at a temperature of 165°C and a rotation speed of 100r / min, and mix it with hydrogenated dimer acid (DA) and L-lysine ethyl ester A total of 20kg of isocyanate (LDI) (the ratio of the moles of carboxyl groups contained in DA to the moles of isocyanate groups contained in LDI is 0.8:1). Afterwards, 0.125kg of catalyst dibutyltin dilaurate (DBTDL) was added, and after the torque tended to be balanced, the material was taken out and hot-pressed at 175°C to obtain toughened polylactic acid. In this embodiment, a sample with width and thickness of 12.50×3.20mm and a remaining width of 10.00mm after making the notch is used to test the performance. The performance is shown in Table 1. In addit...
Embodiment 3
[0075] The preparation of hydrogenated dimer acid (acid value 197.3mgKOH / g) and L-lysine ethyl diisocyanate (LDI) in situ polymerization toughened polylactic acid derived from vegetable oil is as follows:
[0076] After drying 80kg of polylactic acid (PLA), heat it to melt in an internal mixer at a temperature of 165°C and a speed of 100r / min, then mix it with hydrogenated dimer acid (DA) and L-lysine ethyl ester A total of 20kg of diisocyanate (LDI) (the ratio of the number of moles of carboxyl groups contained in DA to the number of moles of isocyanate groups contained in LDI is 1:1.2). Afterwards, 0.125kg of catalyst dibutyltin dilaurate (DBTDL) was added, and after the torque tended to be balanced, the material was taken out and hot-pressed at 175°C to obtain toughened polylactic acid. In this embodiment, a sample with width and thickness of 12.50×3.20mm and a remaining width of 10.00mm after making the notch is used to test the performance. The performance is shown in Tab...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| acid value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| acid value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| acid value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com