In-situ soil remedying composite material capable of efficiently removing heavy metals
A composite material, in-situ remediation technology, applied in the field of soil remediation, can solve problems such as long cycle and slow remediation time, and achieve the effect of reducing content, slowing nitrogen release, and avoiding ecological risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
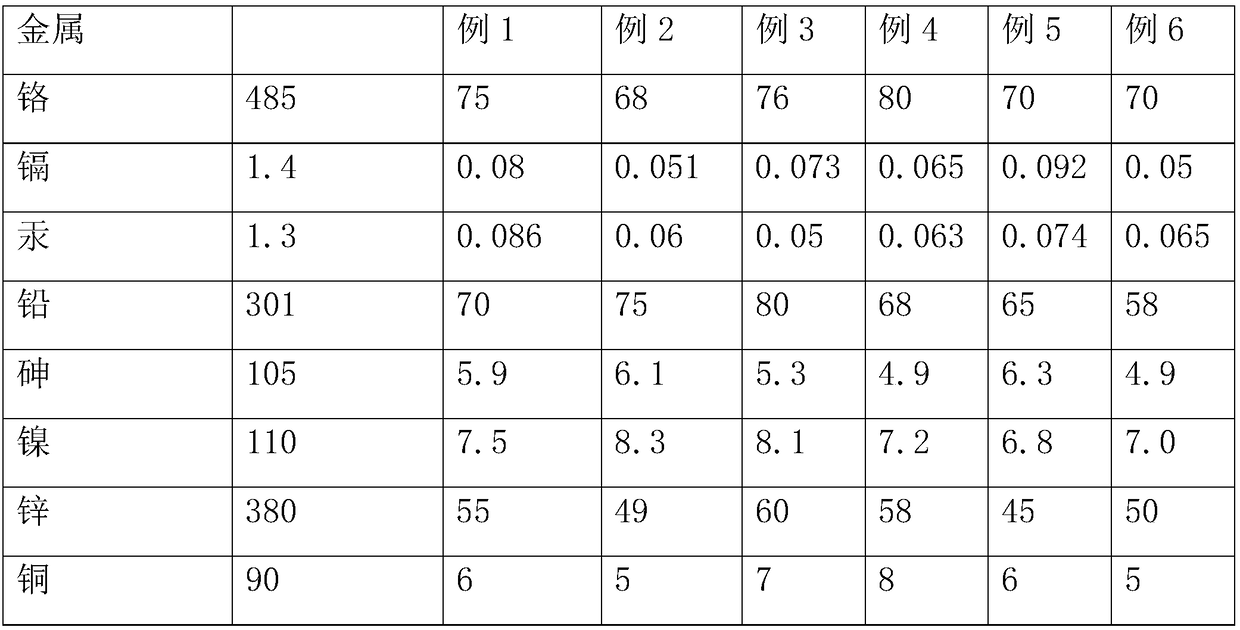
Embodiment 1
[0018] In the soil in-situ remediation composite material for efficiently removing heavy metals of this embodiment, the composite material raw materials include the following components in parts by weight:
[0019] 10 parts of sodium persulfate, 5 parts of sodium polyepoxysuccinate, 1 part of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 1 part of nano carbon, 1 part of serpentine, 5 parts of lignite humic acid, 1 part of surfactant, 4 parts of calcium dioxide , 4 parts of traditional Chinese medicine residue, 1 part of potassium permanganate, 1 part of red mud particles, 1 part of dithiocarbamate chitosan, 1 part of methacryloxyethyl trimethylammonium chloride, the traditional Chinese medicine residue Prepared by:
[0020] a. Wash the medicine residues of Ophiopogon japonicus, licorice, and Radix isatidis to a particle size of 80 mesh, then add a zinc chloride solution with a concentration of 3mol / L, and stir and mix thoroughly at a solid-liquid ratio of 1:2. Evenly, let stand at room temperature for 24...
Embodiment 2
[0026] In the soil in-situ remediation composite material for efficiently removing heavy metals of this embodiment, the composite material raw materials include the following components in parts by weight:
[0027] 20 parts of sodium persulfate, 10 parts of sodium polyepoxysuccinate, 5 parts of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 3 parts of nano carbon, 5 parts of serpentine, 10 parts of lignite humic acid, 3 parts of surfactants, 8 parts of calcium dioxide , 8 parts of traditional Chinese medicine residue, 3 parts of potassium permanganate, 5 parts of red mud particles, 5 parts of dithiocarbamate chitosan, 3 parts of methacryloxyethyl trimethylammonium chloride, the traditional Chinese medicine residue Prepared by:
[0028] a. Wash the medicine residues of Ophiopogon japonicus, licorice and Radix isatidis, dry and pulverize to a particle size of 100 mesh, then add a zinc chloride solution with a concentration of 3mol / L, and mix thoroughly at a solid-liquid ratio of 1:2. Evenly, let stand at ro...
Embodiment 3
[0034] In the soil in-situ remediation composite material for efficiently removing heavy metals of this embodiment, the composite material raw materials include the following components in parts by weight:
[0035] 10 parts of sodium persulfate, 10 parts of sodium polyepoxysuccinate, 1 part of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 3 parts of nano carbon, 1 part of serpentine, 10 parts of lignite humic acid, 1 part of surfactant, 8 parts of calcium dioxide , 4 parts of traditional Chinese medicine residue, 3 parts of potassium permanganate, 1 part of red mud particles, 5 parts of dithiocarbamate chitosan, 1 part of methacryloxyethyl trimethylammonium chloride, the traditional Chinese medicine residue Prepared by:
[0036] a. Wash the medicine residues of Ophiopogon japonicus, licorice, and Radix isatidis to a particle size of 80 mesh, then add a zinc chloride solution with a concentration of 3mol / L, and stir and mix thoroughly at a solid-liquid ratio of 1:2. Evenly, let stand at room temperature f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com