Oxide film transistor and manufacturing method thereof
An oxide thin film and transistor technology, applied in the field of microelectronics, can solve problems such as limited capacitive coupling effect, inconformity with low energy consumption, portable applications, etc., and achieve the effects of simplifying process complexity, reducing process cost, and reducing operating voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0060] Example: Chitosan thin film is deposited on ITO conductive glass substrate, which has a strong electric double layer control effect. The thin film is used as gate dielectric to make InZnO thin film transistor, and the threshold voltage of the device is 0.6V. After applying a bias voltage with a pulse height of 2V and a pulse width of 5s on the gate electrode, the threshold voltage of the device drifted negatively to 0.3V.
[0061] Principle of manufacturing method
[0062] According to the above concept of the present invention, a method for manufacturing an oxide thin film transistor is provided, comprising the steps of: using an oxide semiconductor thin film as a channel of the transistor, which has electronic conductivity; using a solid electrolyte with proton conductivity as a gate dielectric, Therefore, the manufactured device is an n-type oxide thin film transistor; voltage pulses are applied to the gate electrode to realize optimization of device performance and ...
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1: Oxide thin film transistor (bottom gate type)
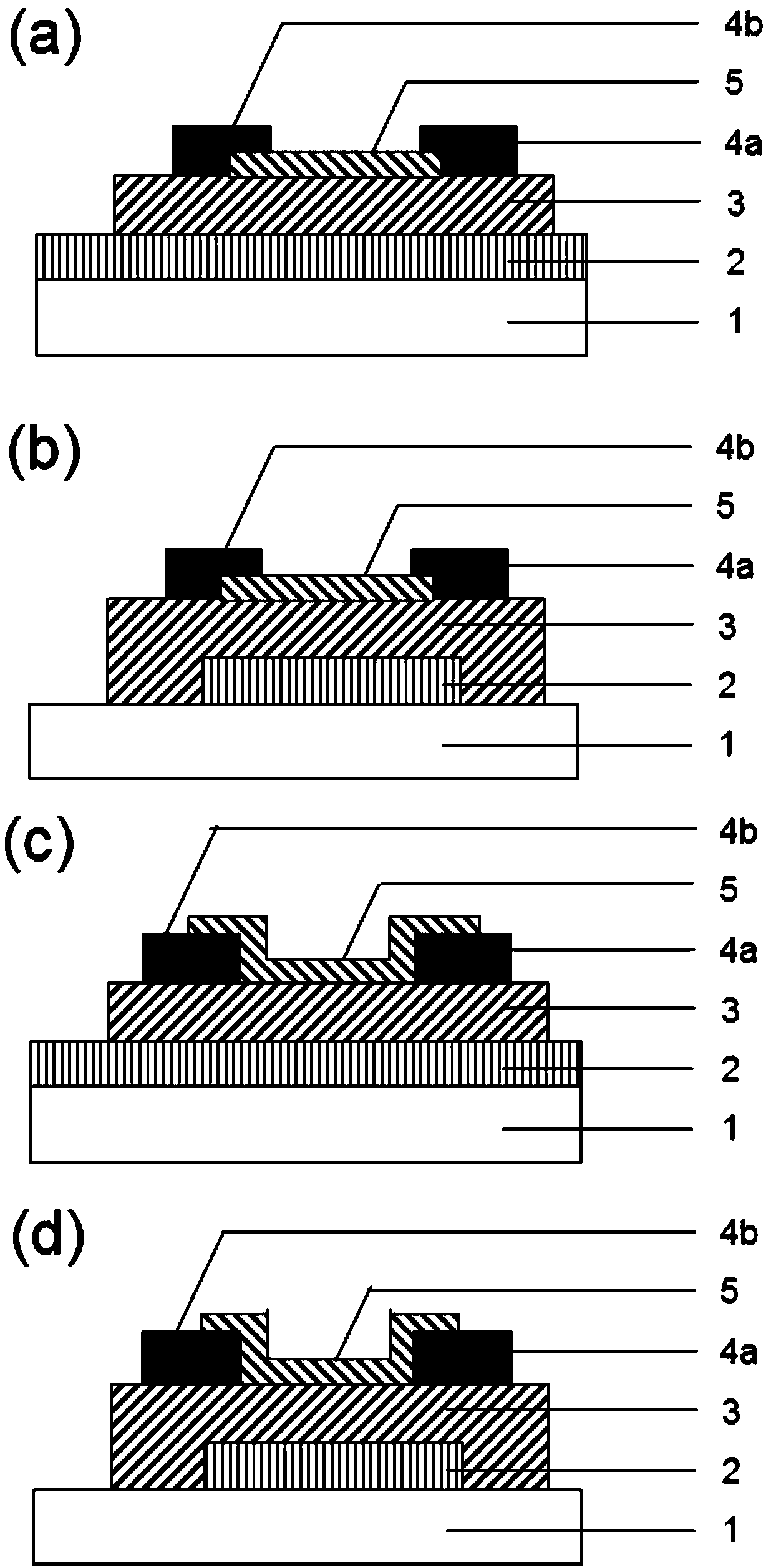
[0083] figure 1 (a)-1(d) respectively show four structures of bottom gate oxide TFTs according to an embodiment of the present invention, these four structures are respectively: bottom gate top contact type, see figure 1 (a) and 1(b), bottom gate bottom contact type, see figure 1 (c) and 1(d).
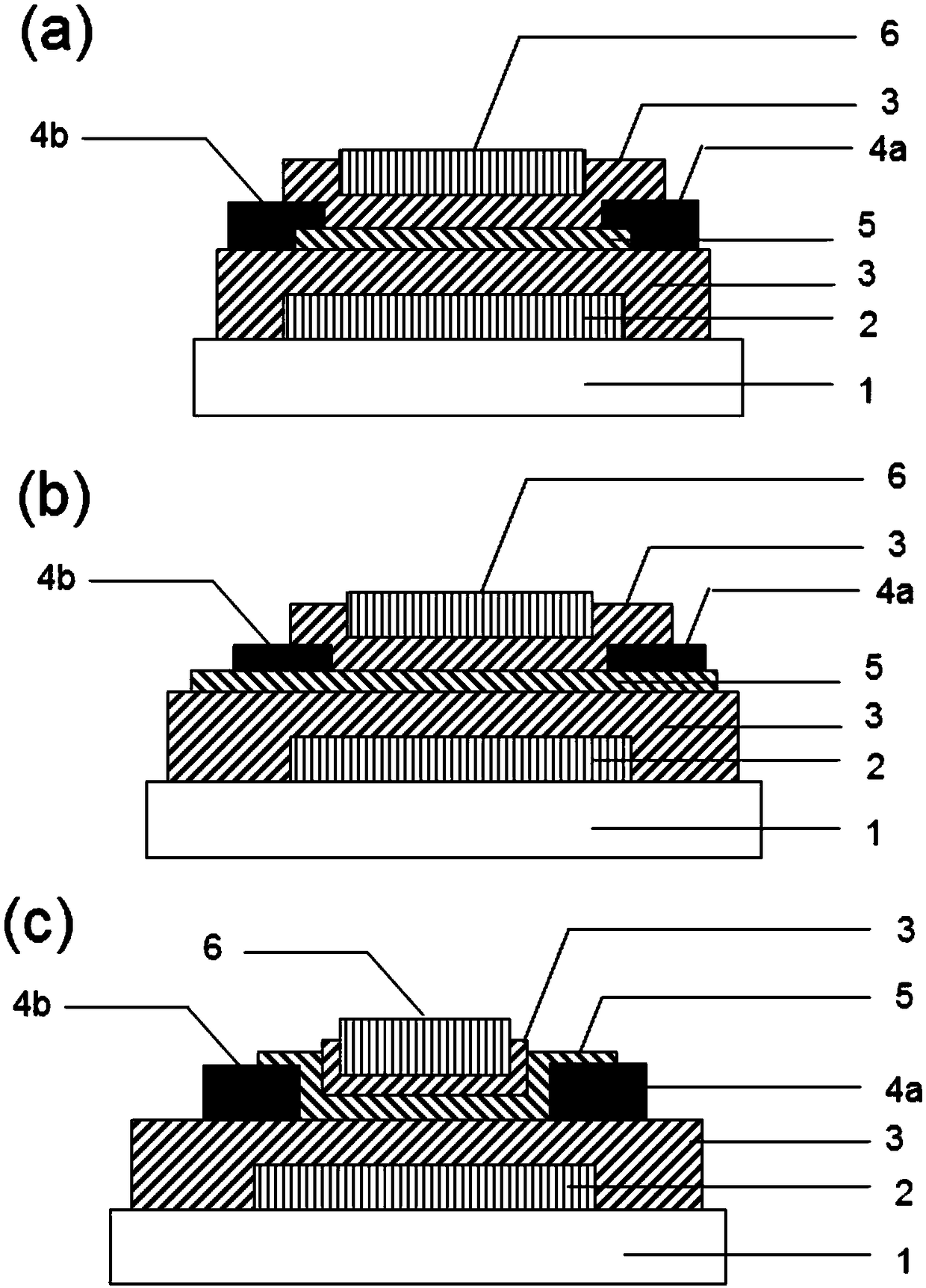
[0084] As shown in the figure, each bottom-gate oxide TFTs includes: an insulating substrate 1, a bottom-gate electrode 2, a gate dielectric layer 3, a drain 4a, a source 4b, and a channel 5, wherein one of the gate dielectric layers 3 One side is the bottom gate electrode 2, and the other side is the drain 4a, the source 4b, and the channel 5 between them.
[0085] The above-mentioned layered structure of the bottom-gate oxide TFTs is similar to that in the prior art, and will not be repeated here. It should be noted that the gate dielectric layer 3 is a solid electrolyte with proton conductivity. As mentioned abov...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Example 2: Oxide thin film transistor (top gate type)
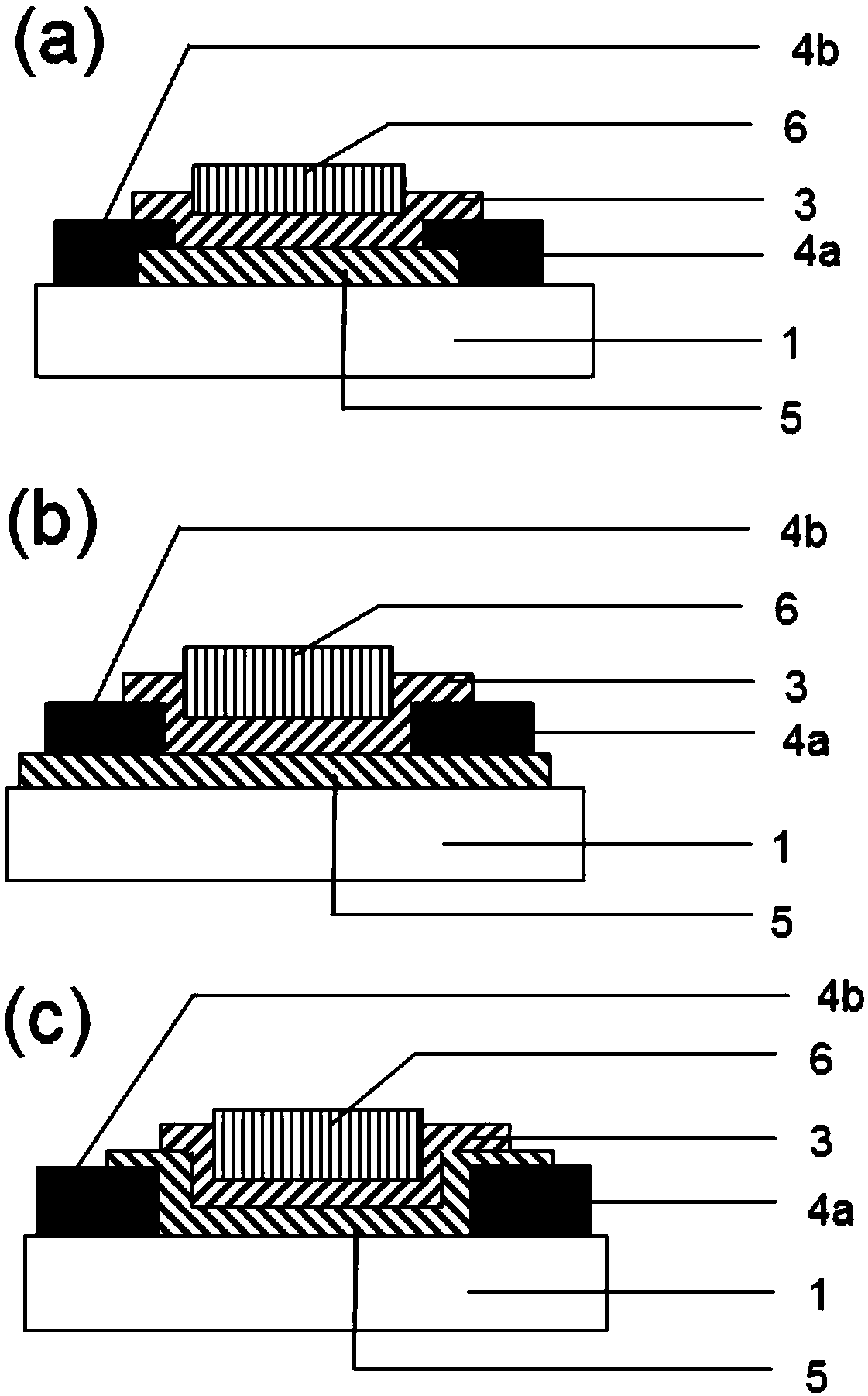
[0087] figure 2 (a)-2(c) respectively show three structures of top gate oxide TFTs according to another embodiment of the present invention, these three structures are respectively: top gate top contact type, see figure 2 (a) and 2(b), bottom gate bottom contact type, see figure 2 (c).
[0088] Similar to the previous embodiment, each top-gate oxide TFTs includes: an insulating substrate 1, a top-gate electrode 6, a gate dielectric layer 3, a drain 4a, a source 4b, and a channel 5, wherein the gate dielectric layer 3 One side is the top gate electrode 6, and the other side is the drain 4a, the source 4b, and the channel 5 between them.
[0089] The layered structure of the above-mentioned top-gate oxide TFTs is similar to that in the prior art, and will not be repeated here. It should be noted that the gate dielectric layer 3 is a solid electrolyte with proton conductivity. As mentioned above, the solid ele...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com