Preparation method of coal tar-based carbon material catalyst that can jointly remove nitrogen oxides and mercury in coal-fired flue gas
A technology for coal-fired flue gas and nitrogen oxides, applied in metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve complex process and low removal efficiency To achieve the effect of rich pore structure, good regeneration performance and smooth surface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Step 1, the purification of coal tar: adopt the method for underpressure distillation, its purpose is to remove quinoline insoluble matter in coal tar, reduce S, O, N content;
[0048] Step 2, in-situ loading, mix the coal tar and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) treated in step 1 and step 2 (the mass ratio of the two is 1:1), impregnate in SnCl 2 and manganese acetate ethanol solution, stirred at room temperature for 10-16h, and dried at 80°C to constant weight;
[0049] Step 3, carbonization, the coal tar loaded with Sn-Mn is carried out in a carbonization furnace, with an inert gas as a medium, and kept at 700 ° C for 2-4 hours to make a coal tar carbon material catalyst;
[0050] Step 4. Oxidation. Put the coal tar material after step 3 in an oxidation furnace, and heat it up to 200-500°C for 1-3 hours at a heating rate of 1-5°C / min in an air atmosphere to complete the oxidation process. , get SnO 2 -MnO 2 Loaded coal tar carbon material catalyst;
[0051] Among them,...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0058] Mn in preparation step 2 2+ Ethanol solution is selected as manganese nitrate ethanol solution;
[0059] Step 2, in-situ loading, mix the coal tar and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) treated in step 1 and step 2 (the mass ratio of the two is 4:1), impregnate in SnCl 2 And manganese nitrate ethanol solution, stirred at room temperature for 10-16h, and baked at 80°C to constant weight.
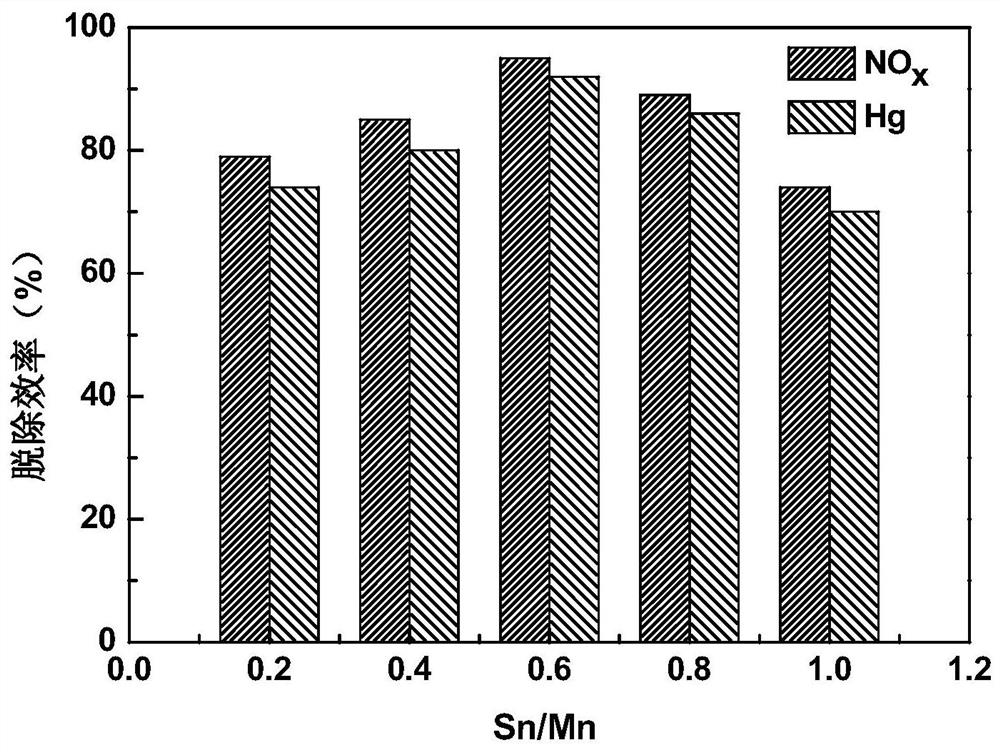
[0060] In the second step, the loading amount of Mn is fixed to be 10%, and the Sn / Mn ratio may be 0.6.
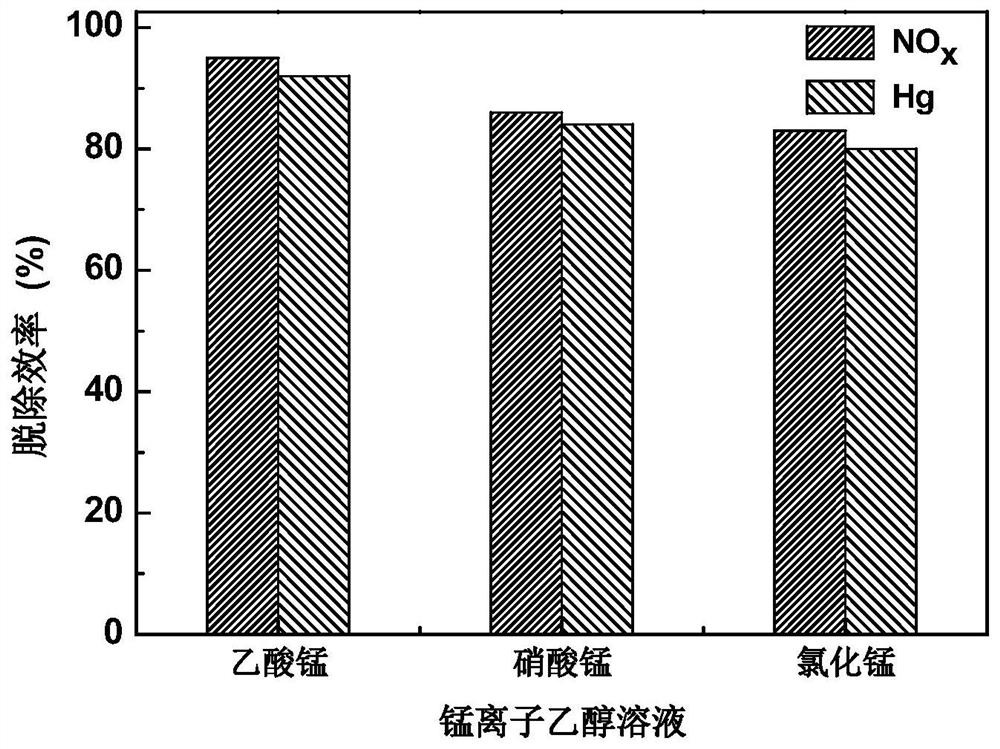
[0061] Nitrogen oxide and Hg removal activity evaluation experiments were carried out on the catalyst prepared in this embodiment. The experimental results show that the removal efficiency of nitrogen oxides can reach 86%, and the removal efficiency of Hg can reach 84%.
Embodiment 3
[0063] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0064] Mn in preparation step 2 2+ Ethanol solution is selected as manganese chloride ethanol solution;
[0065] Step 2, in-situ loading, mix the coal tar and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) treated in step 1 and step 2 (the mass ratio of the two is 2:1), impregnate in SnCl 2 And manganese chloride ethanol solution, stirred at room temperature for 10-16h, and baked at 80°C to constant weight.
[0066] In the second step, the loading amount of Mn is fixed to be 10%, and the Sn / Mn ratio may be 0.6.
[0067] Nitrogen oxide and Hg removal activity evaluation experiments were carried out on the catalyst prepared in this example. The experimental results show that the removal efficiency of nitrogen oxides can reach 83%, and the removal efficiency of Hg can reach 80%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com