Leptosphaeria biglobosa specific sequence, LAMP detection primer and application
A technology of black shank bacteria and rapeseed, which is applied in the field of rapeseed black shank bacteria specific sequences and LAMP detection primers, can solve the problems of poor specificity of amplification, achieve control of false positives, fast and easy stability, and strong stability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Application of rapeseed blackleg pathogen specific sequence (SEQ ID NO.1) or primers designed for the sequence in the preparation of rapeseed blackleg pathogen (L.biglobosa) detection reagent:
[0031] For the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, LAMP primers were designed as follows:
[0032] F3:TAGGTGAACCTGCGGAAG
[0033] B3:GTTACTGACGCTGACTGC
[0034] FIP: GGAAAGGGACAGAAATTAAGCCAAAATTACCCTTCTATCAGGGGAT
[0035] BIP: TCTGATTCTACCCATGTTTTTTGCGAATTACAAGTGGTTTGAATTGTC
[0036] LB: GTGGGCTTGCCTGCCAAAA.
[0037] The LAMP amplification system is as follows:
[0038]
[0039] Bst 2.0 WarmStart DNA Polymerase was purchased from New England Biolabs.
[0040] The LAMP amplification procedure is as follows:
[0041] React at 65°C for 40 minutes; inactivate at 80°C for 5 minutes
[0042] 1000×SYBR Green I was added to the reaction product, and the positive reaction showed fluorescent green, indicating the presence of L.biglobosa; the negative control remained orange.
Embodiment 2
[0044] Specific detection and sensitivity detection of LAMP primers for L.biglobosa:
[0045] Specific detection of LAMP primers for L.biglobosa:
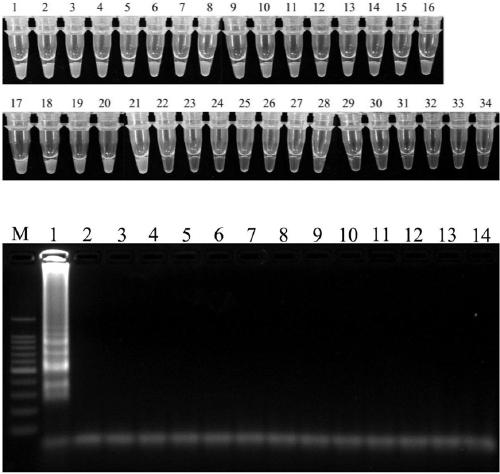
[0046] Using the method described in Example 1, the applicant has carried out LAMP detection to the bacterial strains described in Table 1, and the bacterial strains in Table 1 include 21 strains of L.biglobosa (including subspecies L.biglobosa 'brassicae' and L.biglobosa 'canadensis '), 2 strains of related bacteria L.maculans (including subspecies L.maculans'brassicae') and 10 strains of pathogenic fungi isolated from rapeseed (such as: Phoma sp, Phoma macrostoma, Phoma glomerata, Phoma herbarum, Botrytiscinerea, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Colletotrichum sp, Alternaria alternata, Chaetomium globosum,)
[0047] Table 1
[0048]
[0049]
[0050] Sensitivity detection of LAMP primers for rapeseed black shank
[0051] Genomic DNA of Rapeseed Blackleg Germ (HGHCT2-2) was diluted in a 10-fold concentration gradient, and its se...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: Field Application of LAMP-specific Detection Primers for Rapeseed Blackleg Germ
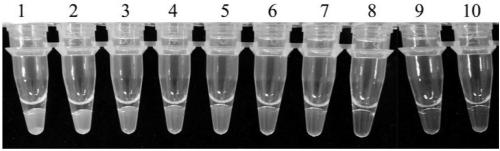
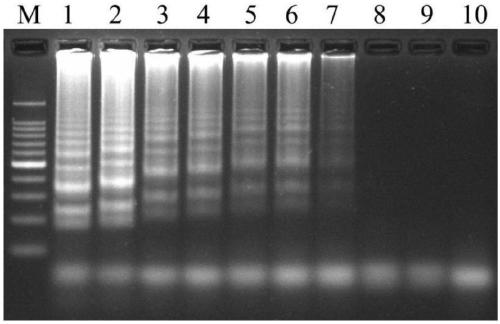
[0053] The stalks of rapeseed were collected from winter rapeseed production areas in China (Chibi, Hubei, Nanjing, Jiangsu, Qujing, Yunnan, Chengdu, Sichuan, Xinyang, Henan, Huizhou, Anhui, Hanzhong, Shaanxi, Huaihua, Hunan, Ningbo, Zhejiang, Guiyang, Guizhou, etc.) and randomly selected 7 The stalks of rapeseed with black shank and 6 rapeseeds with no symptoms, DNA was extracted from the diseased tissues, and the LAMP primers provided by the invention were used for LAMP detection. The results showed that all 7 rapeseed stalks with diseased Rapeseed black shank was detected, and 5 rape stalks also had the presence of rapeseed black shank on 6 rape stalks without symptoms, and only 1 strain did not detect the existence of the pathogen ( image 3 ), cultured 5 rapeseed stalks with no symptoms and tested positive in a moisture-retaining environment at 25°C. After 7 days, typical b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com