A molybdenum oxide reagent used for organic pollutant degradation and a reaction method thereof
A technology for organic pollutants and oxides, applied in the field of chemistry, can solve the problems of low utilization efficiency of hydrogen peroxide, time-consuming and labor-intensive treatment, and aggravated equipment corrosion, so as to shorten the treatment time, reduce the treatment cost, and reduce the effect of corrosion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
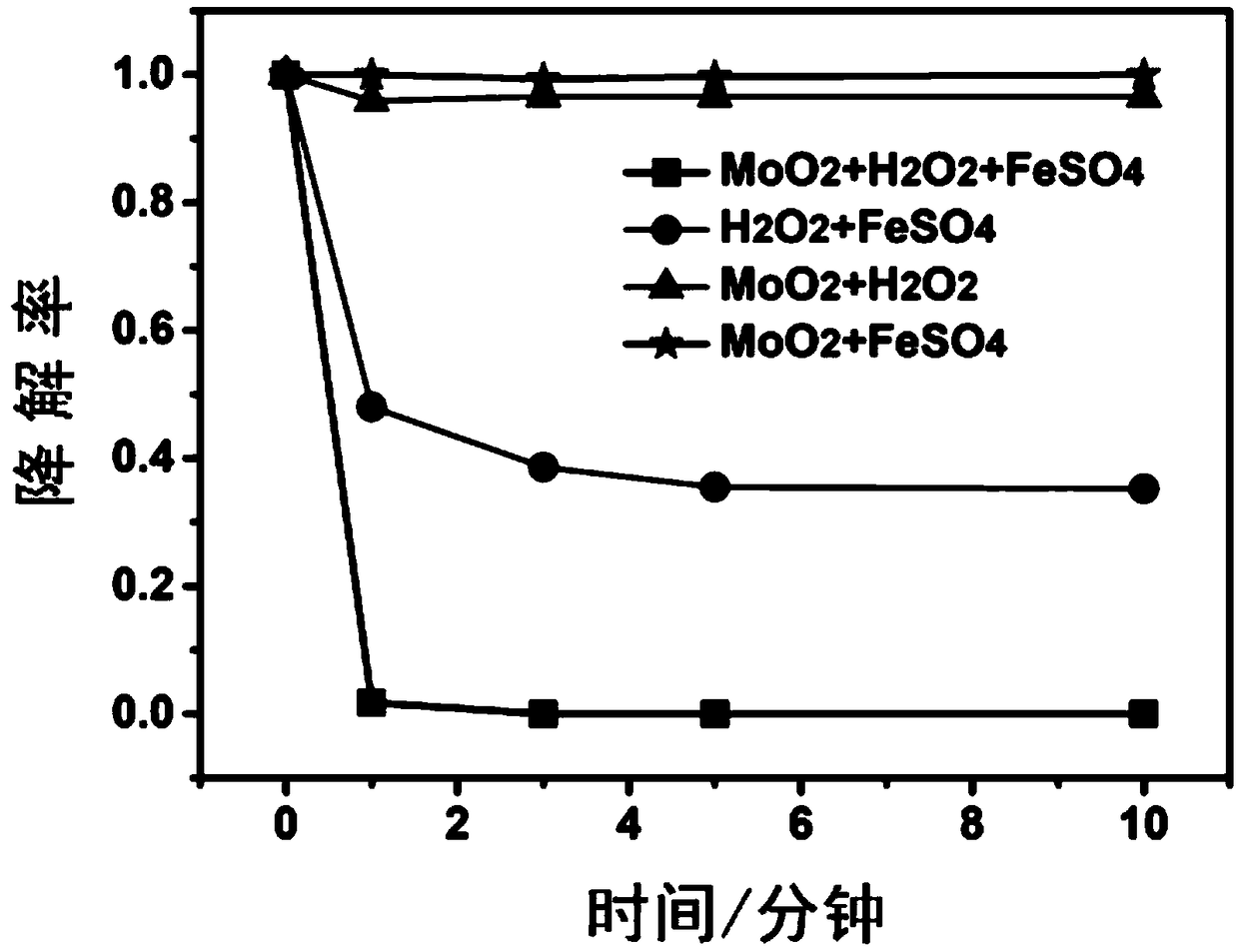
[0051] Do the following sets of control experiments, and degrade the pollutants after feeding according to the following conditions, and measure the concentration with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer:
[0052] A. 100 mL of rhodamine B dye solution to be treated at 20 mg / L, add 30 mg of molybdenum dioxide, adjust the pH to 4, add 3 mg of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, and 4 μL of 30 wt % hydrogen peroxide.
[0053] B. 100 mL of 20 mg / L Rhodamine B dye solution to be treated, adjust the pH to 4, add 3 mg of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, and 4 μL of 30 wt % hydrogen peroxide.
[0054] C. 100 mL of rhodamine B dye solution to be treated at 20 mg / L, add 30 mg of molybdenum dioxide, adjust the pH to 4, and add 3 mg of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate.
[0055] D. To 100 mL of 20 mg / L rhodamine B dye solution to be treated, add 30 mg of molybdenum dioxide to adjust the pH to 4, and 4 μL of 30 wt % hydrogen peroxide.
[0056] Experimental results such as figure 1 As shown, it can be kno...
specific Embodiment 2
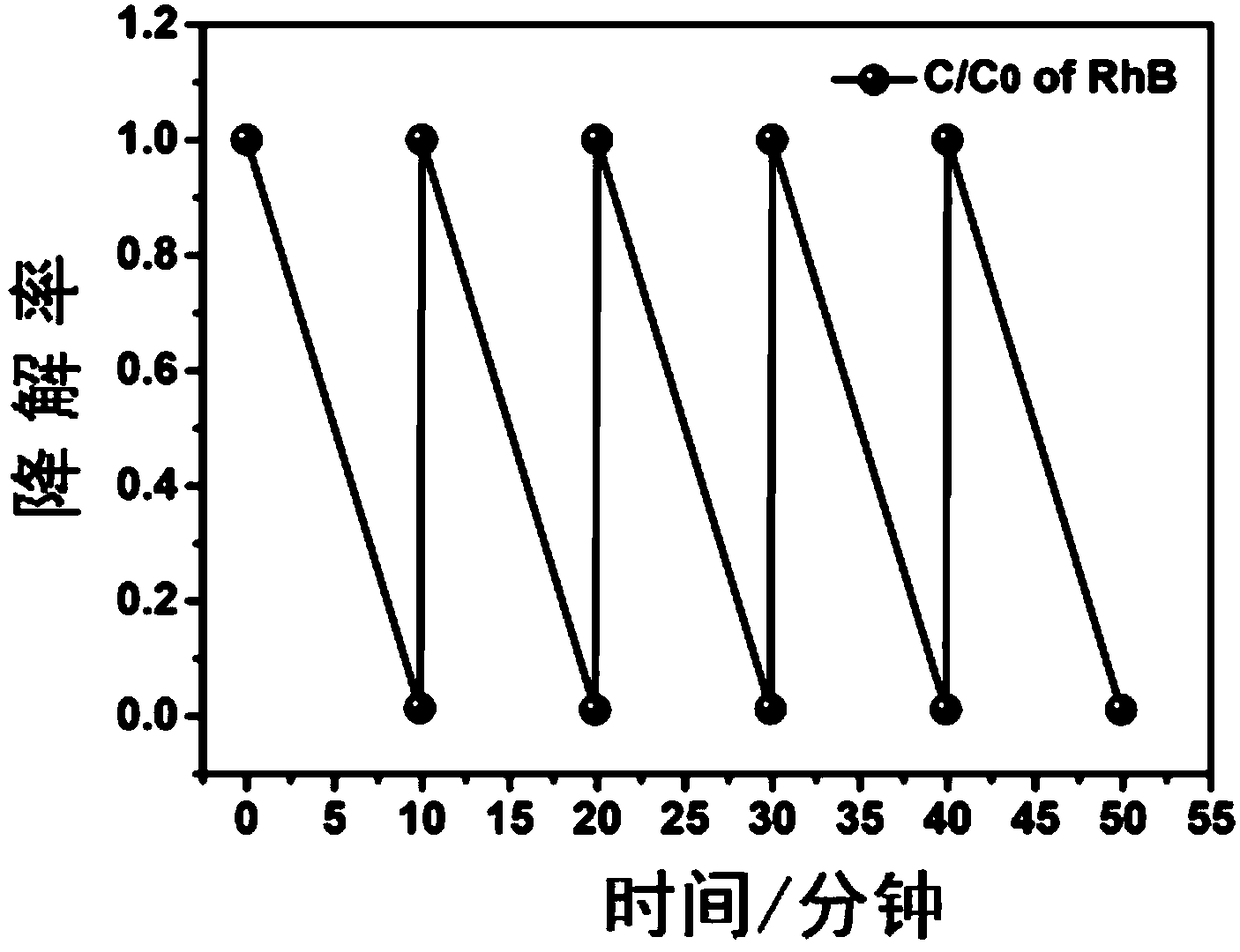
[0057] Step 1, add 30 mg of molybdenum dioxide to 100 mL of rhodamine B dye solution to be treated, adjust the pH to 4, add 3 mg of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, and 4 μL of 30 wt % hydrogen peroxide.
[0058] Step 2: After step 1, stir at room temperature for 20 minutes until the pollutants are completely degraded, then centrifuge to recover MoO 2 powder and wash with water multiple times to remove surface ionic magazines.
[0059] Step 3: Use another 100 mL of 20 mg / L rhodamine B dye solution to be treated, add recovered and washed molybdenum dioxide, adjust the pH to 4, add 3 mg of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, and 4 μL of 30 wt % hydrogen peroxide.
[0060] Step 4 Repeat steps 2 and 3 several times.
[0061] Experimental results such as figure 2 As shown, within 20 minutes, the degradation rate of organic pollutants remained above 100%, and with the increase of the number of cycles, the cocatalyst MoO 2 The speed is not reduced, and the stability is very good.
specific Embodiment 3
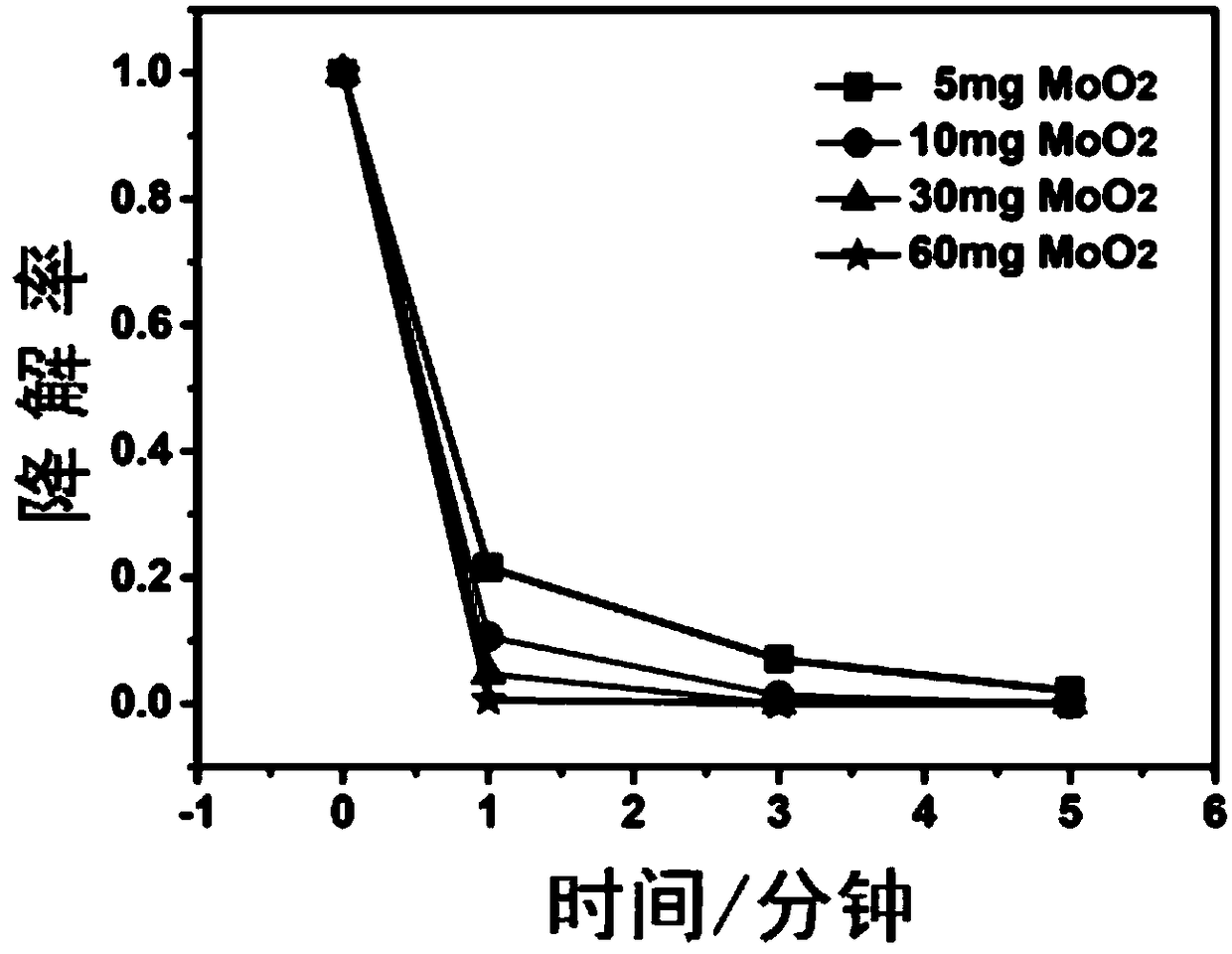
[0062] Do the following sets of control experiments, and degrade the pollutants after feeding according to the following conditions, and measure the concentration with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer:
[0063] A. 100 mL of rhodamine B dye solution to be treated at 20 mg / L, add 5 mg of molybdenum dioxide, adjust the pH to 4, add 3 mg of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, and 4 μL of 30 wt % hydrogen peroxide.
[0064] B. To 100 mL of 20 mg / L Rhodamine B dye solution, add 10 mg of molybdenum dioxide to adjust the pH to 4, add 3 mg of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, and 4 μL of 30 wt % hydrogen peroxide.
[0065] C. 100 mL of rhodamine B dye solution to be treated at 20 mg / L, add 30 mg of molybdenum dioxide, adjust the pH to 4, add 3 mg of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, and 4 μL of 30 wt % hydrogen peroxide.
[0066] D. 100 mL of rhodamine B dye solution to be treated at 20 mg / L, 60 mg of molybdenum dioxide was added to adjust the pH to 4, 3 mg of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, and 4 μL ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com