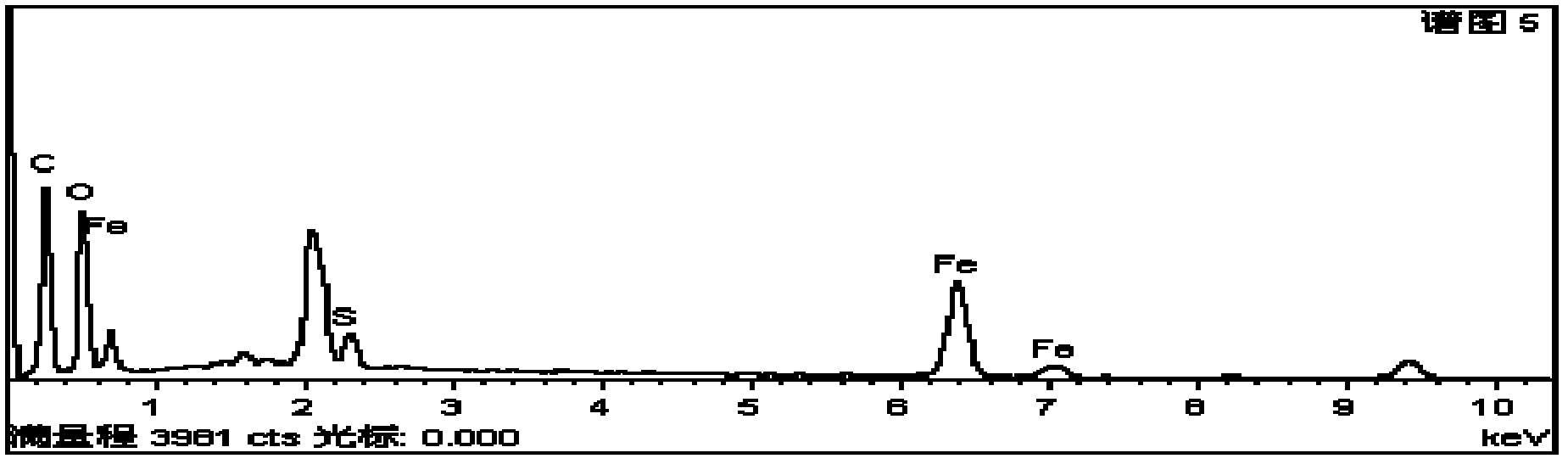
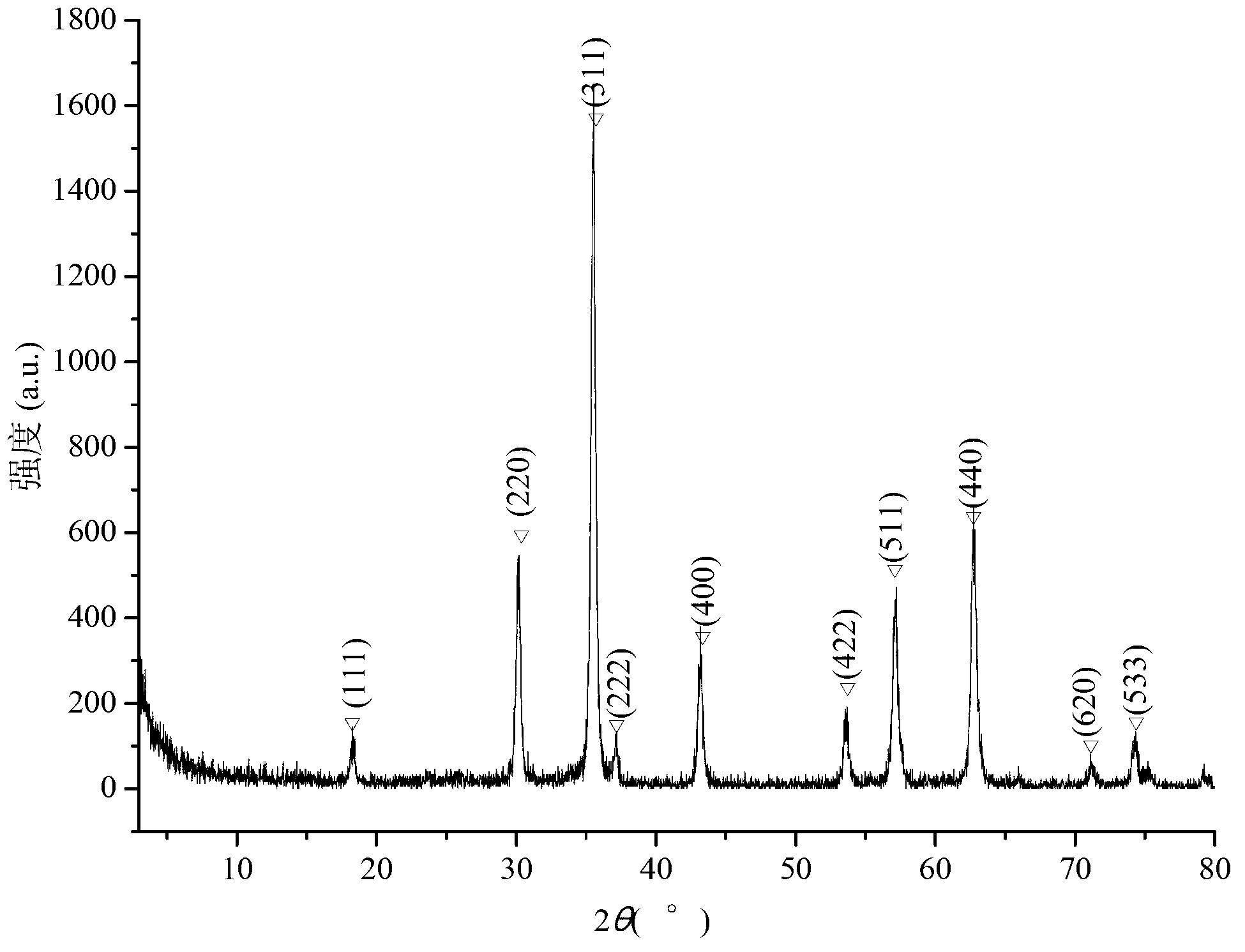
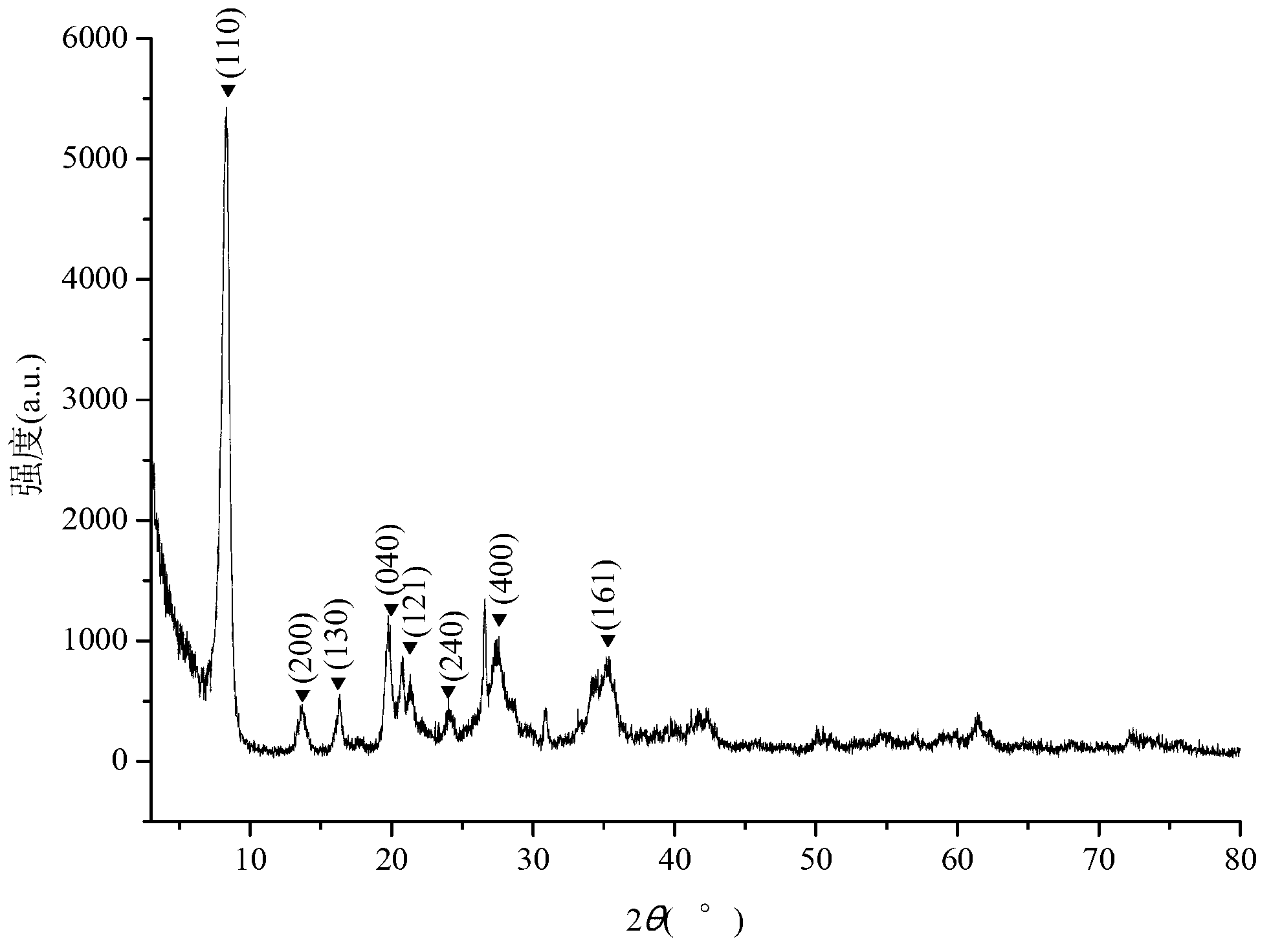
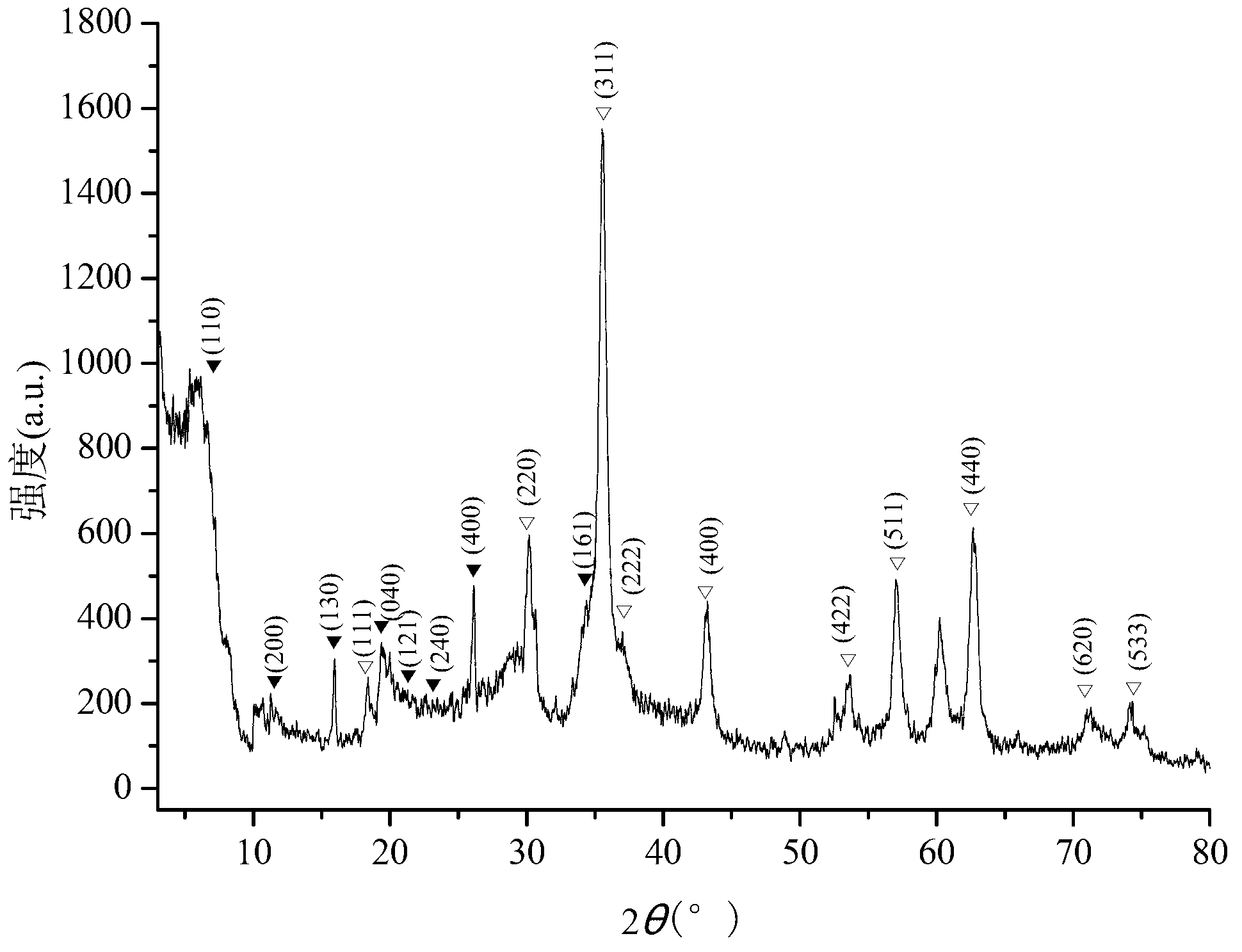
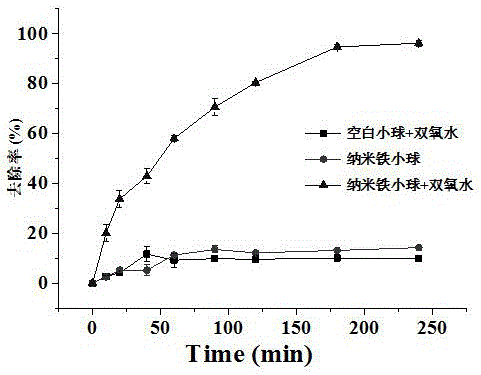
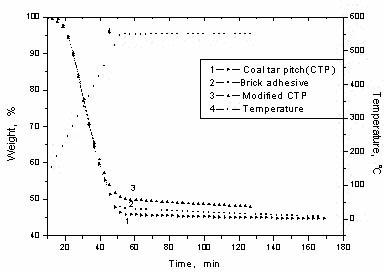
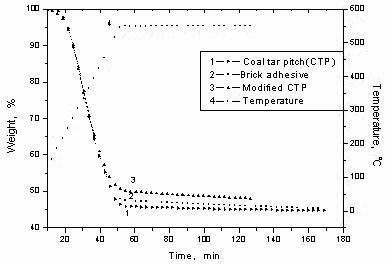
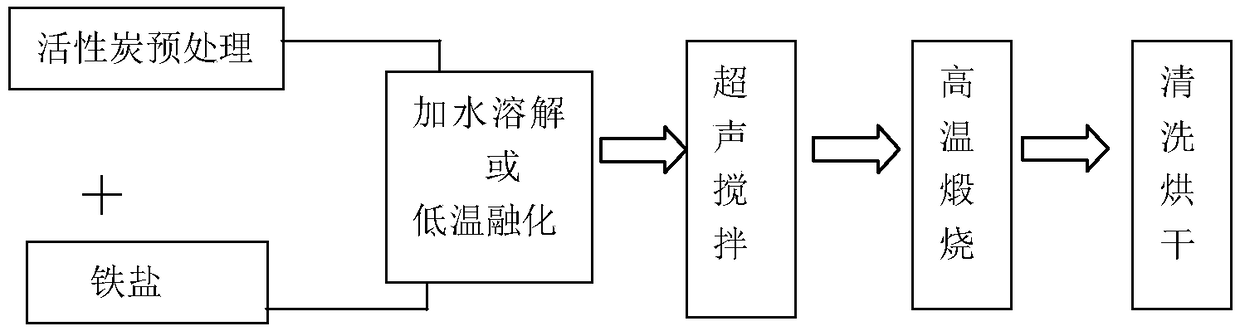
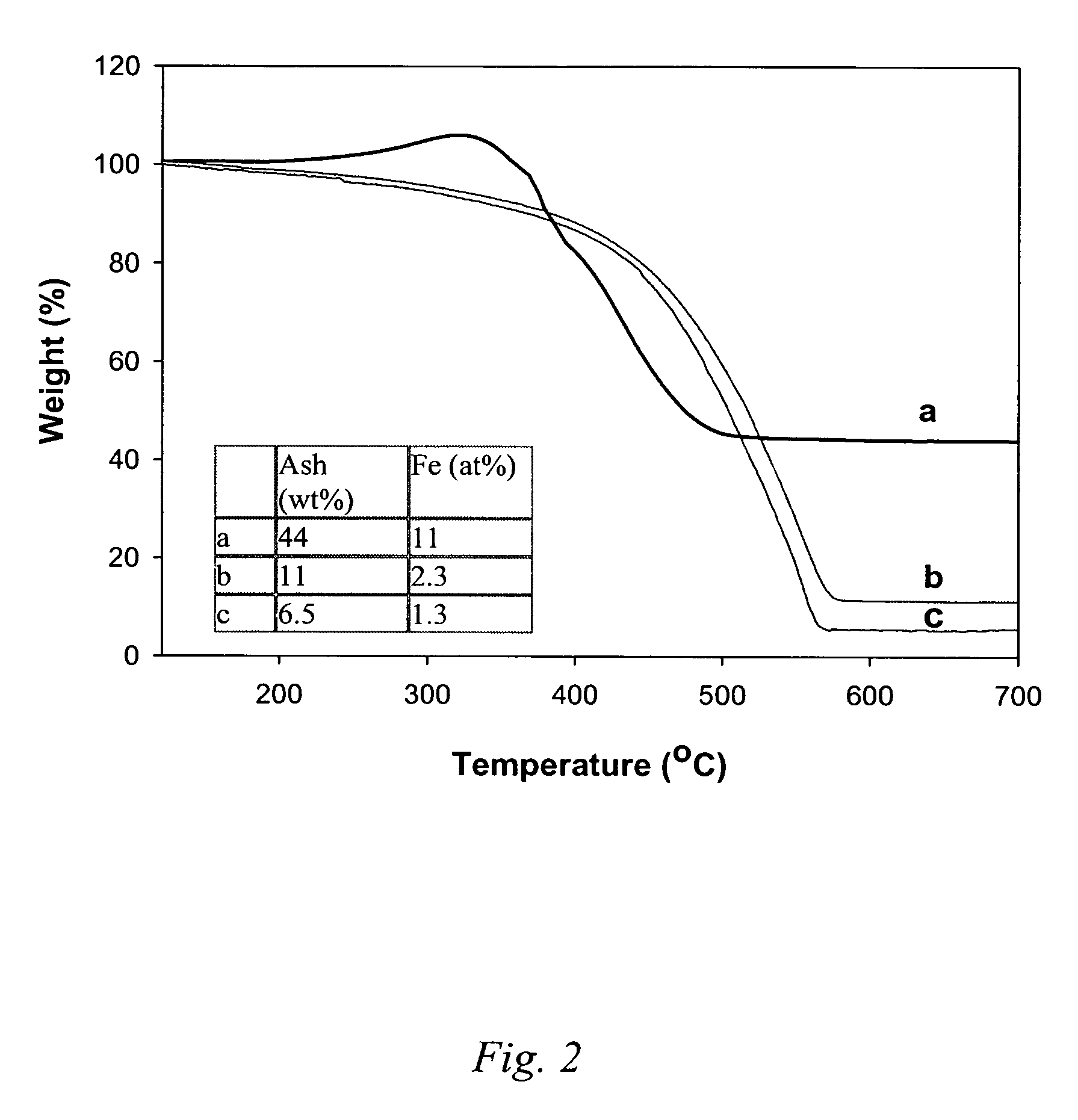
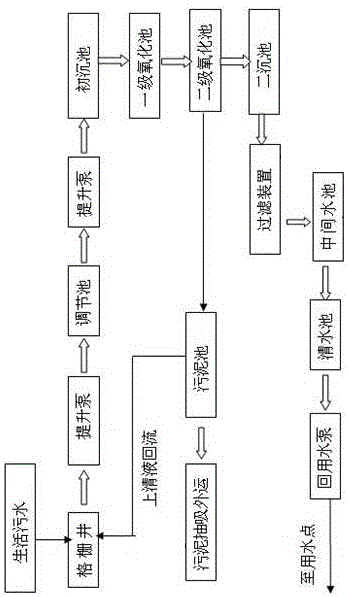
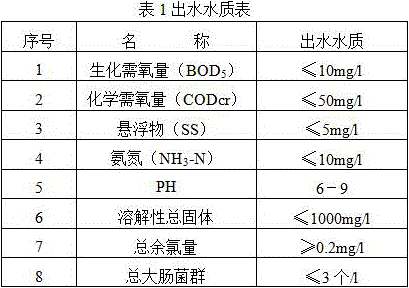
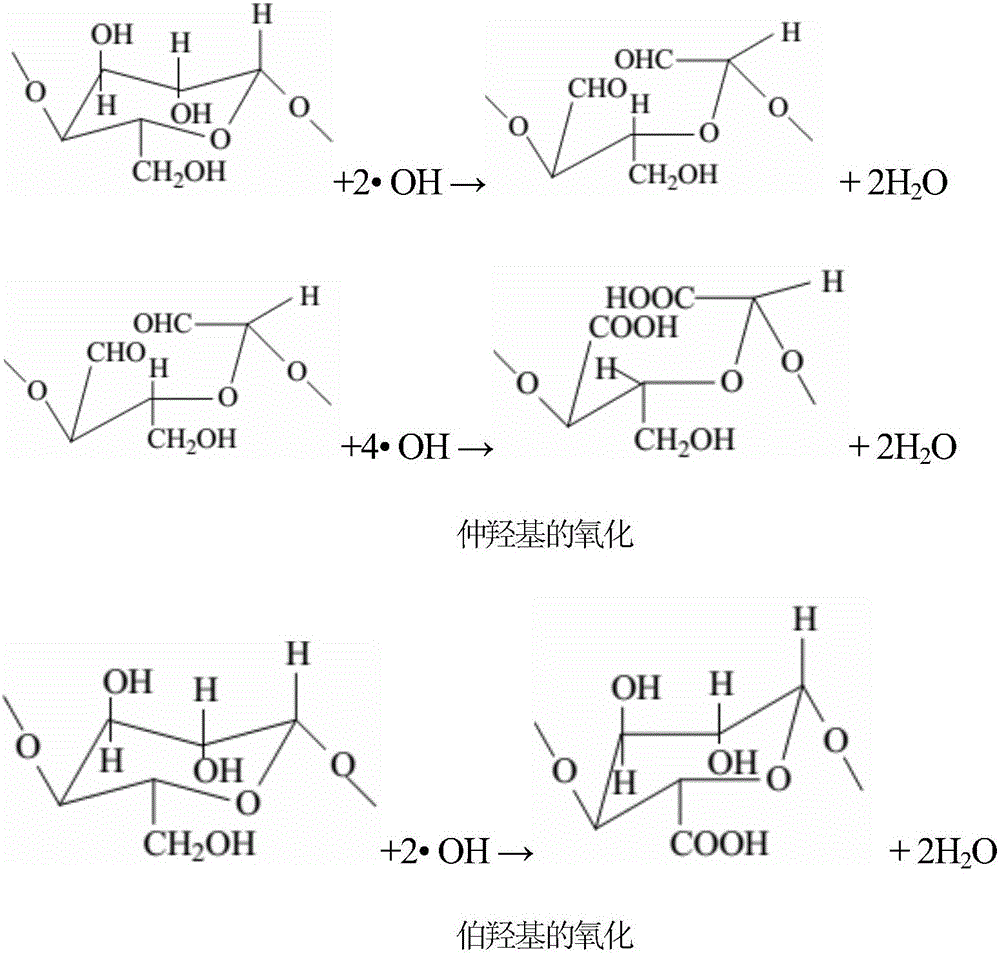
Patents
Literature
96 results about "Fenton's reagent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fenton's reagent is a solution of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) with ferrous iron (typically iron(II) sulfate, FeSO₄) as a catalyst that is used to oxidize contaminants or waste waters. Fenton's reagent can be used to destroy organic compounds such as trichloroethylene (TCE) and tetrachloroethylene (perchloroethylene, PCE). It was developed in the 1890s by Henry John Horstman Fenton as an analytical reagent.
Preparation method and application of heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst
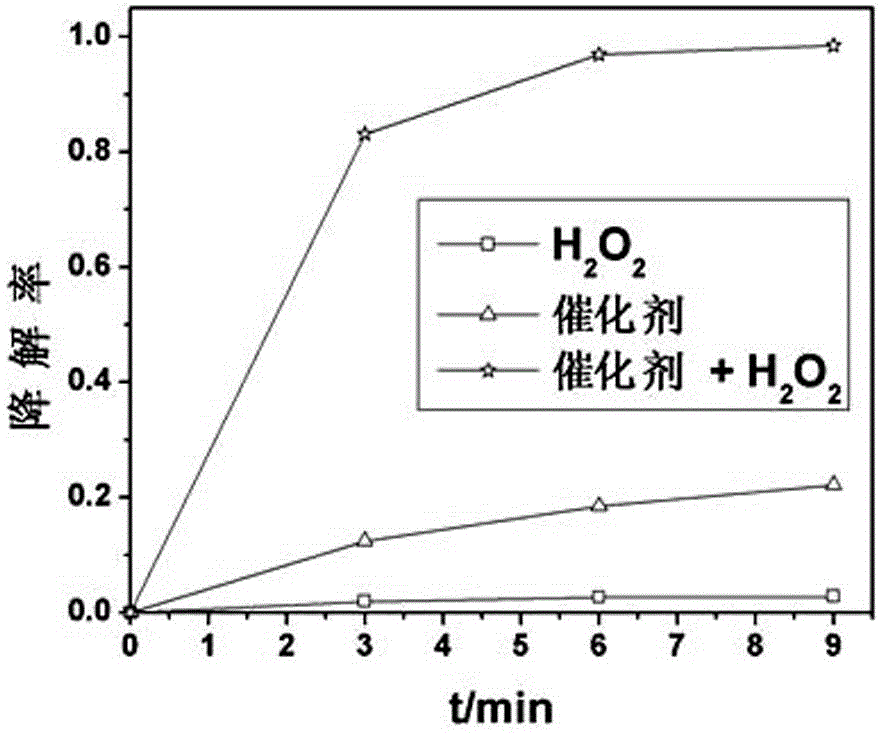
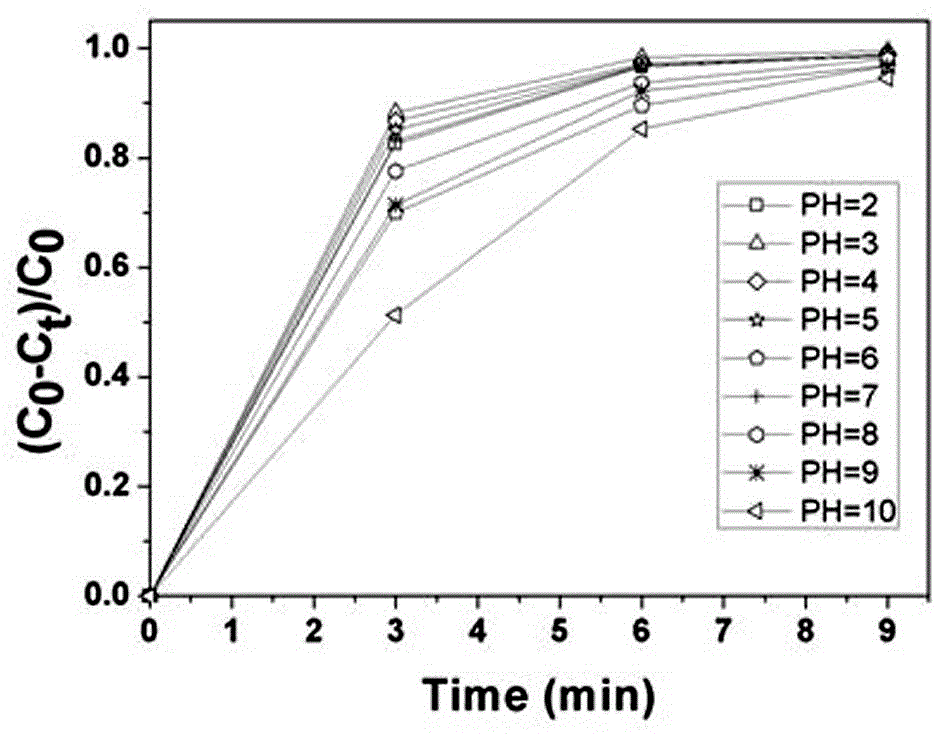
InactiveCN102909073ALow costEfficient degradationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsWaste water treatment from textile industryFiberCarbon fibers
Disclosed are a preparation method and application of heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. The preparation method includes the steps of firstly, dissolving complexing agent and metal salt in distilled water to respectively prepare complexing agent and metal salt solutions; secondly dropwise adding the metal salt solution into the complexing agent solution under the action of a magnetic mixer, and mixing for 20-60 after dropwise addition to obtain metal complex solution; and thirdly, impregnating activated carbon fiber in the metal complex solution for 1-24h, and subjecting taken-out activated carbon fiber to distilled water washing and drying to obtain the heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. The preparation method is simple, and conditions are mild. Environment-friendly hydrogen peroxide is used as oxidant, no extra ultraviolet light or even visible light is needed, and the heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst is capable of efficiently degrading organic pollutants such as dye within a wide pH range of 2-10. The heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst is well repeatable, and secondary pollution of the homogeneous Fenton reagent caused by iron ions is avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
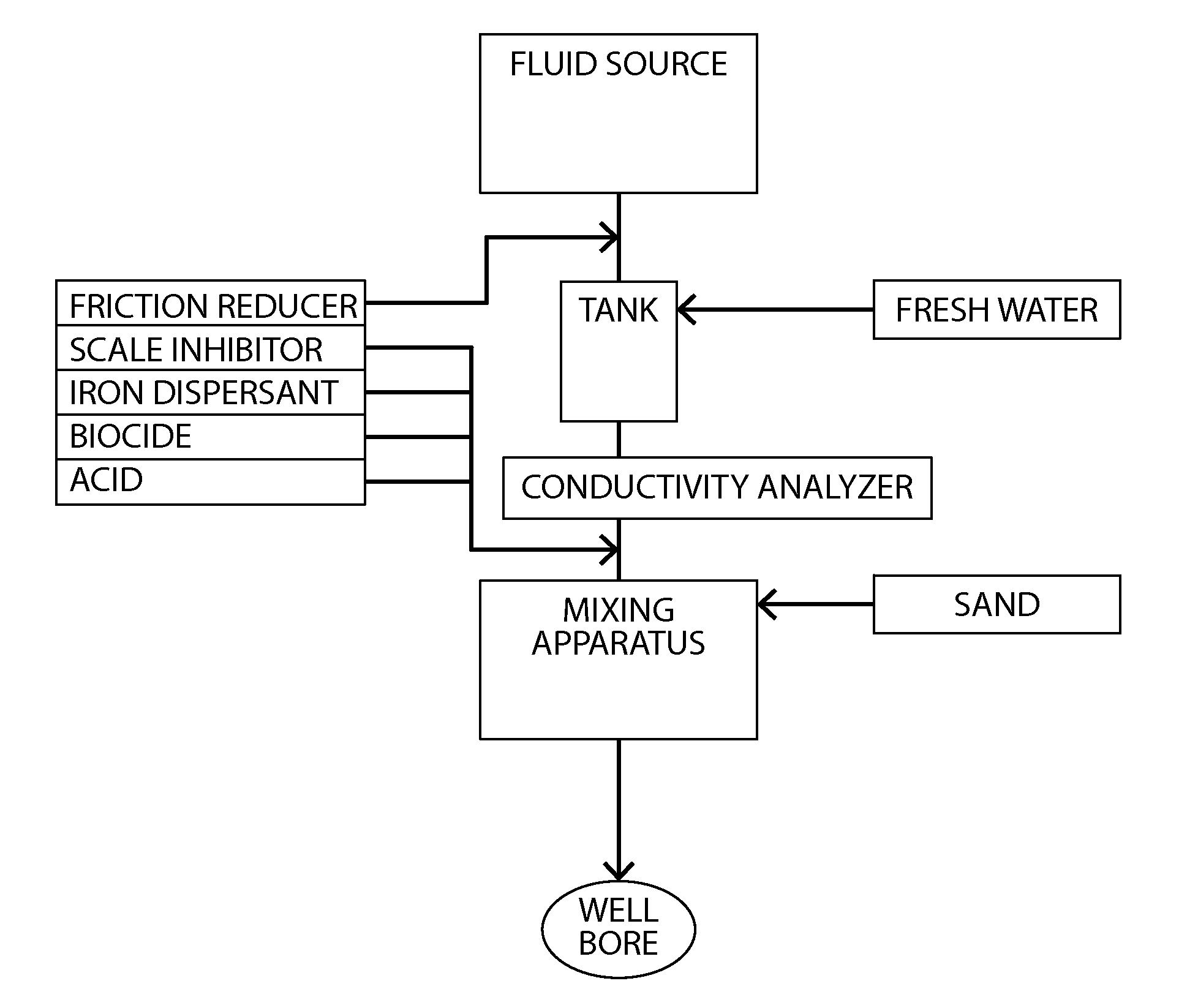
Fracturing fluid water reuse system and method
ActiveUS20120024525A1Low costIncreasing well productionFluid removalMixer accessoriesFracturing fluidHydraulic fracturing
Methods of processing a fluid recovered from an oil or gas extraction operation for reuse in a hydraulic fracturing fluid are described. The methods include providing an amount of a produced fluid composition containing iron and suspended solids and controlling at least one of the conductivity, iron content, oxidative strength, and pH of the composition, such that Fenton's reagent is formed in situ. Also described are hydraulic fracturing fluids produced using fluid recovered from an oil or gas production process and treated in accordance with the methods described herein as well as systems for preparing a hydraulic fracturing fluid having, as a fluid source, fluid recovered from an oil or gas production process that has been treated in accordance with the methods described herein.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Preparation method of activated carbon supported ferrous heterogeneous Fenton's reagent oxidation catalyst
InactiveCN102626627ANo secondary pollutionLow costWater contaminantsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActivated carbonSulfate
The invention discloses a preparation method of an activated carbon supported ferrous heterogeneous Fenton's reagent oxidation catalyst. The method comprises steps of: adding active carbon into acid solution, soaking and separating out activated carbon; cleaning the filtered and separated activated carbon with water and drying; adding the activated carbon into a ferrous sulfate solution, so that ferrous ions in the solution carry out load reaction on the surface of the activated carbon, and separating out the loaded active carbon; cleaning the loaded active carbon with alkali lye and drying. The present invention uses active carbon supported ferrous ion as Fenton's reagent oxidation catalyst, which can be reused, so as to increase the efficiency of resource use and generates no secondary pollution; as the catalyst can be recycled, wastewater treatment cost is greatly reduced; recycling of catalyst simplifies the process; and catalyst preparation technology has the advantages of simple process, mild condition, easiness to popularization and usage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Preparation method of attapulgite supported ferroferric oxide
InactiveCN103230796AImprove adsorption capacityReduce invalid decompositionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationCatalytic oxidationNitrogen
The invention relates to a preparation method of attapulgite supported ferroferric oxide, which is used for increasing the specific surface area of a Fe3O4 catalyst and improving the adsorption capacity of the catalyst surface to obtain better catalytic performance. The method takes attapulgite as a carrier and FeSO4.7H2O as an iron source, and comprises the following steps of: putting the attapulgite and FeSO4.7H2O at a mass ratio of (1:15)-(5:1) into a three-neck flask, adding a certain amount of water, and stirring for certain time under nitrogen protection at 40-80 DEG C; dropwise adding hydrogen peroxide with certain concentration according to a molar ratio of H2O2 to Fe<2+> of 1:3; adding a NaOH solution until pH is 10-13; transferring to a closed polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle; and settling for 8-16 hours at 120-200 DEG C. According to the method provided by the invention, the synthesized supported Fe3O4 has the advantages of simple method, low cost and large specific surface area, can form a Fenton's reagent with hydrogen peroxide, can effectively catalyze, oxidize and degrade organic wastewater to prevent secondary pollution, and is favorable for recovering and circularly utilizing the catalyst.
Owner:六安科瑞达新型材料有限公司
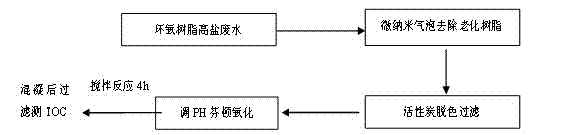
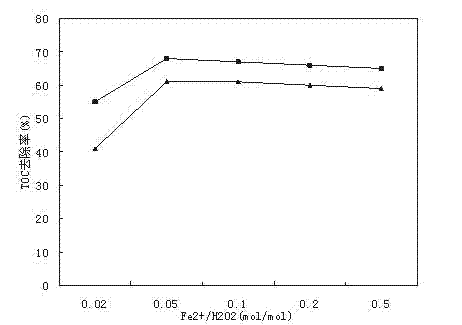
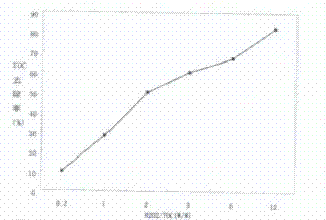
Epoxy resin high-salinity wastewater treatment method
InactiveCN102815827AReduce processing costsAvoid pollutionMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterMicro nanoEpoxy
The invention relates to an epoxy resin high-salinity wastewater treatment method, which comprises the following steps of: 1) removing aged resin in the epoxy resin high-salinity wastewater by the use of a micro-nano bubble generator; 2) using active carbon for decolouring such that TOC of the epoxy resin high-salinity wastewater is less than 2200 ppm; 3) adding hydrochloric acid into the outputted wastewater obtained from the step (2) so as to adjust pH value to 2-4, adding a Fenton's reagent for Fenton oxidation reaction, wherein the mol ratio of ferroporphyrin to hydrogen peroxide is 0.01-0.5; 4) adjusting the pH value of the outputted wastewater obtained from the step (3) to 9-10, adding a HPAC coagulant for coagulating sedimentation reaction so as to obtain a supernatant, making TOC of the epoxy resin high-salinity wastewater less than 200 ppm; 5) carrying out membrane filtration on the outputted wastewater obtained from the step (4), and removing visible impurities from the epoxy resin water; and 6) carrying out diaphragm electrolysis on the outputted water obtained from the step (5). The treatment method provided by the invention is environmentally friendly and economical.
Owner:JIANGSU KUMHO YANGNONG CHEM CO LTD +1
Treatment method of high salinity organic wastewater
InactiveCN102276082AAvoid wastingTake advantage ofMultistage water/sewage treatmentFenton reactionActivated carbon
A treatment method for high-salinity organic wastewater, the method adopts the process of combining adsorption, Fenton reaction and adsorbent desorption regeneration reuse, adsorbs a part of organic matter in the wastewater by activated carbon, and then adds Fenton reagent to remove a part organic matter, and then add chemical agents to desorb and regenerate the adsorbent for reuse. After the aforementioned steps, the treated wastewater can be discharged to a general domestic sewage treatment plant for final treatment, and the activated carbon in the adsorption process can basically be recycled after being regenerated. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple process, good treatment effect, convenient maintenance, no secondary pollution and the like.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
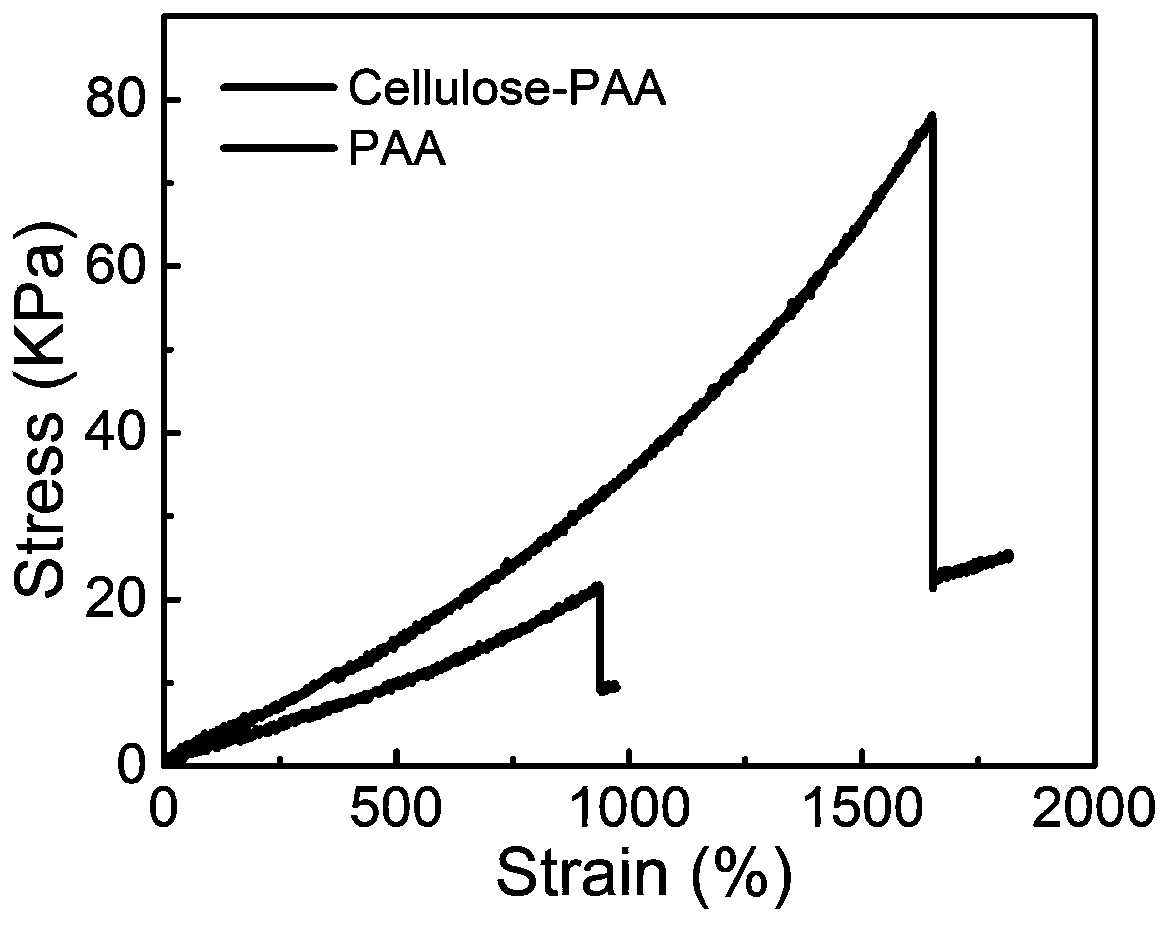
Nanocellulose-polymer composite hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110078866ABiodegradableImprove mechanical propertiesElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementPotassium persulfateMechanical property
The invention discloses nanocellulose-polymer composite hydrogel as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method of the nanocellulose-polymer composite hydrogel comprises the steps as follows: a nanocellulose dispersion and monomers are subjected to a free radical polymerization reaction under the action of an initiator and N,N'-methylene bisacrylamide to preparethe hydrogel, wherein the initiator is selected from one of potassium persulfate, ammonium persulfate and Fenton's reagents. The preparation method of the nanocellulose-polymer composite hydrogel hasthe advantages that the raw materials are widely sourced, the preparation method is simple, the reaction time is short and the like. The prepared nanocellulose-polymer composite hydrogel has good electrical conductivity, self-healing performance and mechanical properties and can be applied to the fields of flexible intelligent materials, capacitors or battery separators and the like.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for deep treatment on industrial wastewater discharged by styrene-butadiene rubber production device
ActiveCN103723878AEasy maintenance and operationLow running costMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationTreatment effectFiltration
The invention relates to a method for deep treatment on industrial wastewater discharged by a styrene-butadiene rubber production device and belongs to the field of wastewater multilevel treatment. Water treatment devices such as a pre-treatment unit, a sludge adsorption unit, an aerobic biochemical treatment unit, a flocculation and filtration unit and a high-grade oxidation treatment unit are orderly connected and combined; and discharged wastewater treated by the above water treatment devices has COD less than or equal to 40mg / L and NH3-N less than or equal to 5mg / L. The method solves the problem that the prior art has a high treatment cost and poor treatment effects, is a deep treatment method having the advantages of stable, safe and reliable operation, high pollutant removal rate and low operation cost, and realizes stable and standard discharge of industrial wastewater produced by a styrene-butadiene rubber production device. Compared with the prior art, the method reduces a high-grade oxidation phase Fenton's reagent use amount by about 30%, improves treatment depth by 15% and has an industrial application value.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Membrane post treatment
ActiveUS7867417B2Improve breathabilityReduce total pressure lossMembranesSemi-permeable membranesCross-linkMicrofiltration
Hydrophilic porous polymeric membranes with high permeabilities, and processes for the preparation thereof are disclosed. Membranes may be prepared by including a preferably hydrophilic cross-linkable component such as PVP (either by inclusion into the polymer dope prior to casting, or coating or quenching cast membranes); and treating the polymeric microfiltration or ultrafiltration membrane with a crosslinking agent to cross-link said cross-linkable component. Preferred cross-linking agents include Fenton's reagent.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Coated nano iron ball as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN105688764ANot easily oxidizedHigh activityFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater treatment compoundsCalcium alginatePhenol
The invention discloses a coated nano iron ball as well as preparation and application thereof. A preparation method of the coated nano iron ball comprises the following steps: firstly reducing ferrous ions to nano zero-valent iron via reducing agents such as phenols and the like in a tree leaf extraction solution to form a nano iron suspension, preparing the nano iron suspension into calcium alginate via a calcium alginate coating technology so as to coat the nano iron ball. The nano iron ball and hydrogen peroxide are prepared into a Fenton-type reagent; hydroxyl radicals can be released; the coated nano iron ball has strong oxidizability and is capable of mineralizing oily substances in the wastewater to achieve the purpose of deeply treating the wastewater. The method has the advantages of low cost, excellent effect, convenience in use and environment friendliness.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Multi-doped half-load type Fenton-assisting titanium dioxide photochemical catalyst as well as preparation method and application method
InactiveCN101862662ALess prone to secondary pollutionImprove photocatalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFiberPhotocatalytic reaction
The invention relates to a multi-doped half-load type Fenton-assisting titanium dioxide photochemical catalyst as well as a preparation method and an application method. La, Fe and N are doped so that TiO2 has visible light response. The load of ACF (Active Carbon Fiber) overcomes the disadvantages of difficult recovery and generation of second pollution of the TiO2. The creative addition of half-load type Fenton reagent solves the problems of low photocatalytic efficiency of the TiO2, large consumption of Fe<2+> of the traditional Fenton reagent, incapability of keeping concentration in flowing water, and the like. In the preparation method of the photochemical catalyst, tetra-n-butyl titanate is taken as a TiO2 precursor, absolute ethyl alcohol is taken as a solvent, and viscose-based activated carbon fibers are taken as carriers. The photochemical catalyst is prepared through drying, ultrasound processing, and calcining at a constant temperature. In the application method, ultraviolet light and visible light are taken as an excitation light source in a light-catalyzed reaction, the adding concentration of the photochemical catalyst is from 10 to 20g / L, and the adding concentration of hydrogen peroxide is from 10 to 30 mM. The photochemical catalyst has the advantages of simple preparation, high catalytic activity, easy recovery and visible light activity, and provides a basis for industrial applications.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
A kind of modified coal tar pitch material and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102276997ABenzopyrene content decreasedIncrease coking valueBuilding insulationsProcess engineeringCoal
The invention discloses a modified coal pitch material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The modified coal pitch material is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of raw coal pitch, 100 parts of water, 0.1-1 part of stabilizing agent and 1-20 parts of Fenton reagent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: fully freezing the rawcoal pitch at the brittleness temperature; smashing and screening to obtain coal pitch powder of which the granularity is less than 80 meshes; adding the water and the stabilizing agent; dispersing by virtue of a blender at the revolving speed of 1000-5000 rpm (revolutions per minute) to obtain a suspension, and then controlling the revolving speed at 1000-5000 rpm; dripping the Fenton reagent atconstant temperature, and reacting at room temperature for 30-90 minutes after the Fenton reagent is added to obtain the modified coal pitch. The content of carcinogen benzopyrene in the modified coal pitch prepared by the preparation method at constant temperature is greatly lowered, the coking value is higher, energy is saved, and consumption is reduced. The modified coal pitch material can be used for preparing a magnesia carbon brick binder and a road paving material after being simply processed, thereby avoiding environmental pollution. In addition, the preparation method is simple.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
A method for preparing a solid ferric oxide-loading activated carbon Fenton's reagent
InactiveCN109012671AHigh catalytic activityChemically stableWater treatment compoundsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsIron saltsPersulfate
The invention relates to a method for preparing a solid ferric oxide-loading activated carbon Fenton's reagent. The method includes fully mixing activated carbon pretreated with acid and an iron salt,and then performing high-temperature calcination. The obtained product is a solid particle substance that is ferric oxide-loading activated carbon. The method overcomes problems that traditional Fenton's reagents cannot be recovered, that iron mud formation from added iron ions requires secondary treatment, and that catalytic degradation activity is highly dependent on acidic environment conditions, and the like. The method is simple in process and low in cost, and the prepared product has advantages including stable chemical properties, no harm to environment, low iron ion dissolution rates,capability of activating hydrogen peroxide and persulfate to achieve catalytic degradation of organic matters, and high efficiency and high speed during application under neutral conditions.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Non-ferrous metal mine flotation wastewater treatment method
ActiveCN104030505AEasy to handleImprove processing efficiencyWaste water treatment from quariesMultistage water/sewage treatmentTherapeutic effectFenton oxidation
The invention discloses a non-ferrous metal mine flotation wastewater treatment method which comprises the following steps: adjusting the pH value of flotation wastewater to be weak acidity; under the conditions of stirring and ultraviolet lamp radiation, feeding a Fenton's reagent and a catalyst to perform ultraviolet-Fenton oxidation reaction; feeding an alkali liquid into the wastewater after the oxidation reaction in the stirring state to adjust the pH value, and subsequently adding a coagulation agent for coagulation and static settlement; feeding a potassium permanganate oxidant for secondary oxidation into the supernate after settling. According to the characteristics that the non-ferrous metal mine flotation wastewater contains heavy metals, a great variety of flotation reagents are used and the content is relatively high, coagulating sedimentation and a high-class oxidation technique are combined for synergic treatment, and secondary oxidation is adopted to further treat small molecule COD substances after high-class oxidation. The method is simple in process, good in wastewater treatment effect, high in treatment efficiency, stable in system operation, relatively low in wastewater treatment cost and wide in application prospect, and particularly has advantages that other methods do not have for non-ferrous metal flotation wastewater which is hard to treat.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST
Ferric aluminum silicon composite carbon-based electrode and application thereof in decoloration of wastewater
ActiveCN102126771ATo achieve the purpose of decolorizationSimple preparation processWater/sewage treatment by oxidationPerchloric acidHydroxyl radical
The invention discloses a ferric aluminum silicon composite carbon-based electrode and application thereof in decoloration of wastewater. A preparation method for the ferric aluminum silicon composite carbon-based electrode comprises the following steps of: mixing aqueous solution of tetraethyl orthosilicate, ferric perchlorate and aluminum choride and ethanol to obtain mixed solution; putting a carbon-based material into the mixed solution, stirring, heating to 75 to 85 DEG C, and adding ammonia water, so that iron, silicon and aluminum are deposited on the carbon-based material; and after performing a heat-preserving reaction completely, taking the carbon-based material out, drying for the first time, washing, and drying again to obtain the ferric aluminum silicon composite carbon-basedelectrode. The ferric aluminum silicon composite carbon-based electrode is used as a cathode of an electro-Fenton system, so a Fenton reagent can be provided continuously at the cathode and performs a Fenton reaction with hydrogen peroxide effectively to generate hydroxyl free radicals with high oxidability to oxidize organic matters in the wastewater, and the decoloration effect of the wastewater is desirable. The electrode has a simple preparation process, is low in cost, has low requirement on using environment and can be used under the condition of neutral pH, and the catalytic efficiencyis far higher than that of ferric oxides s.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
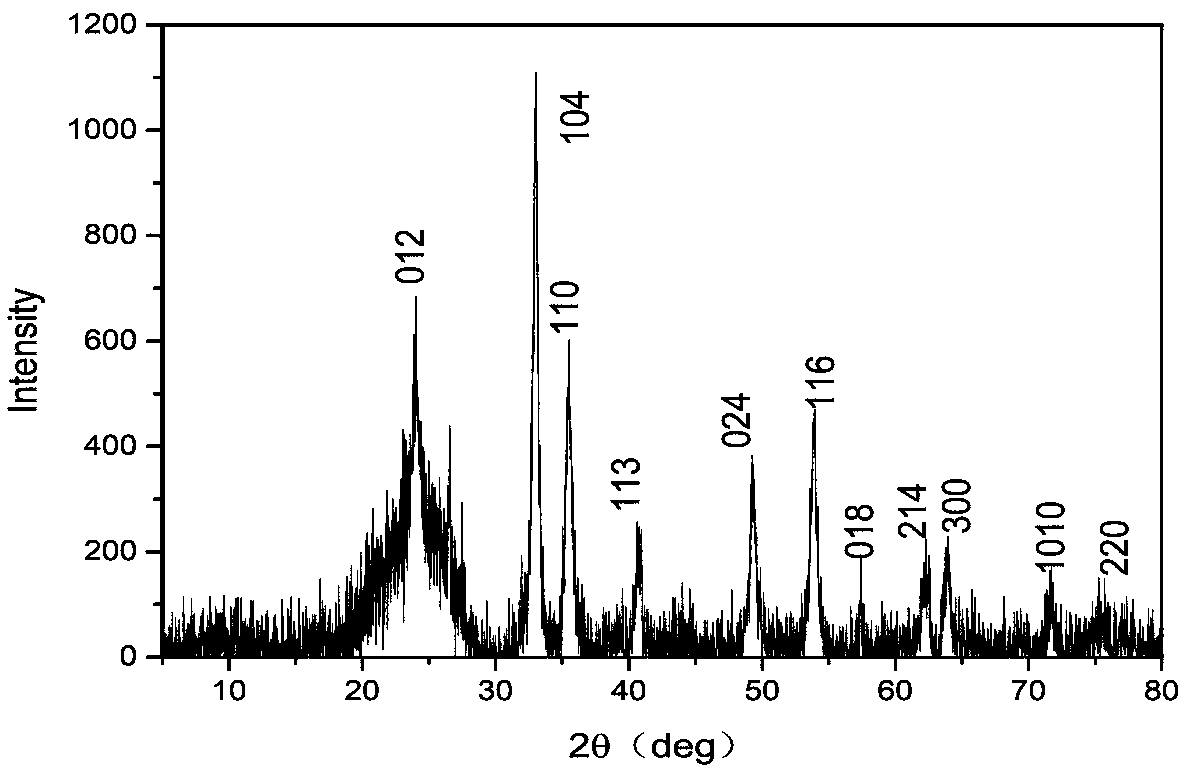
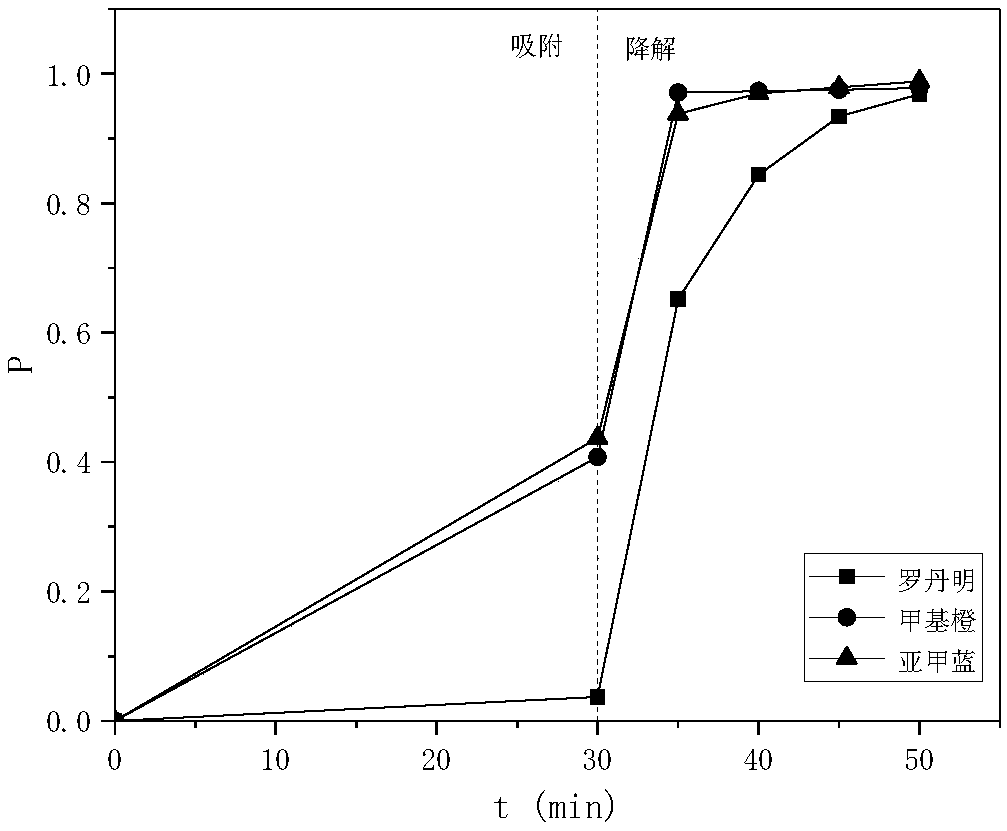
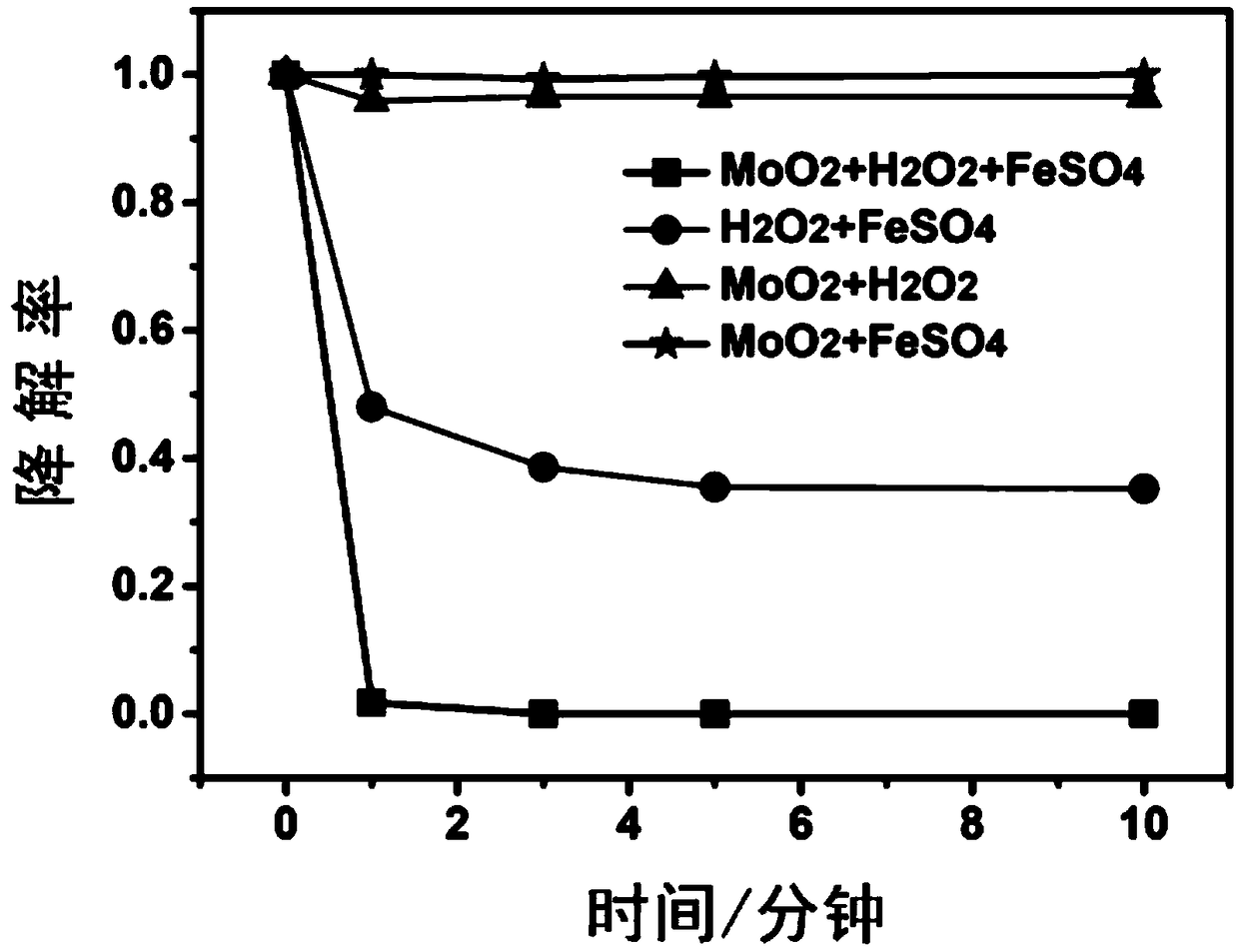
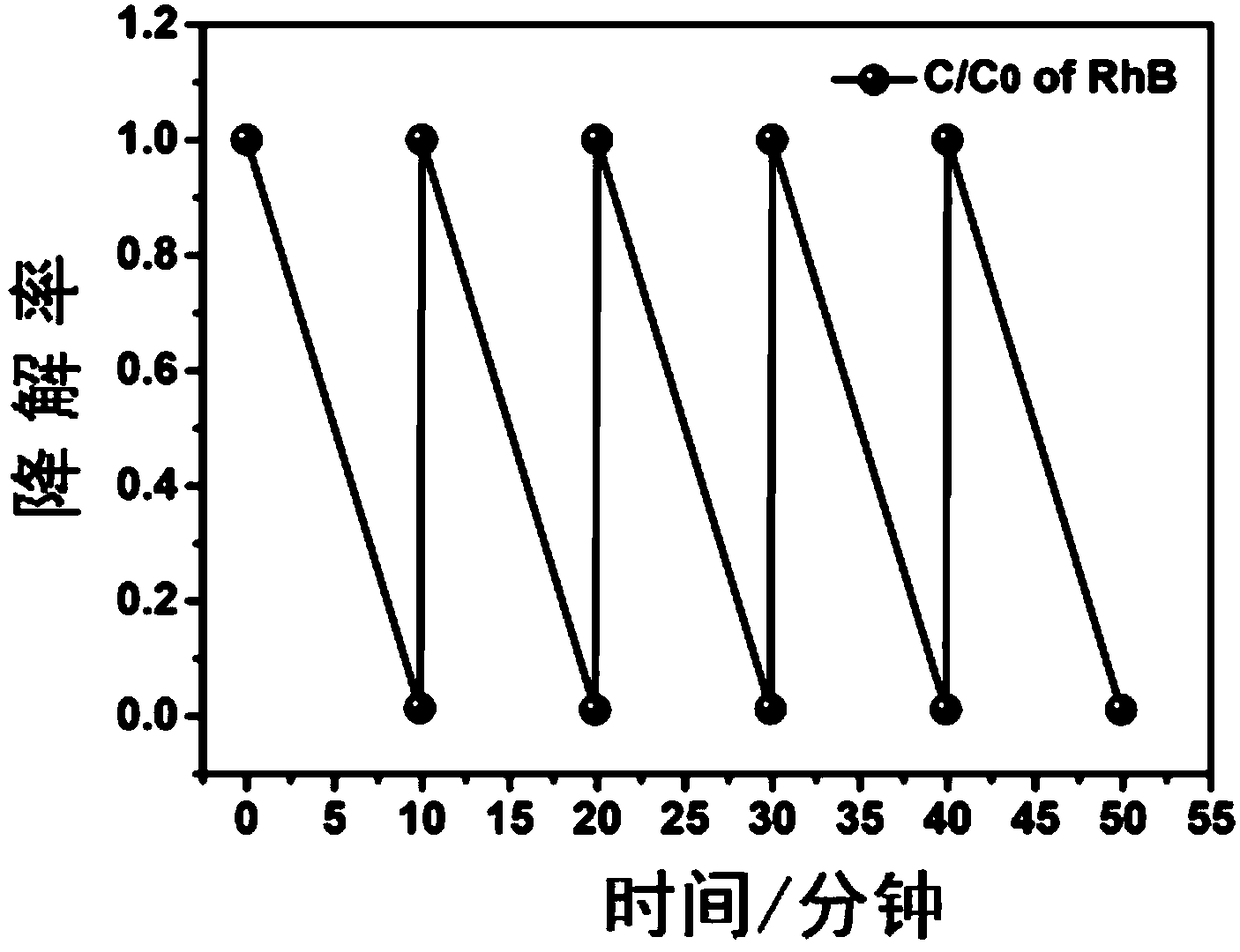
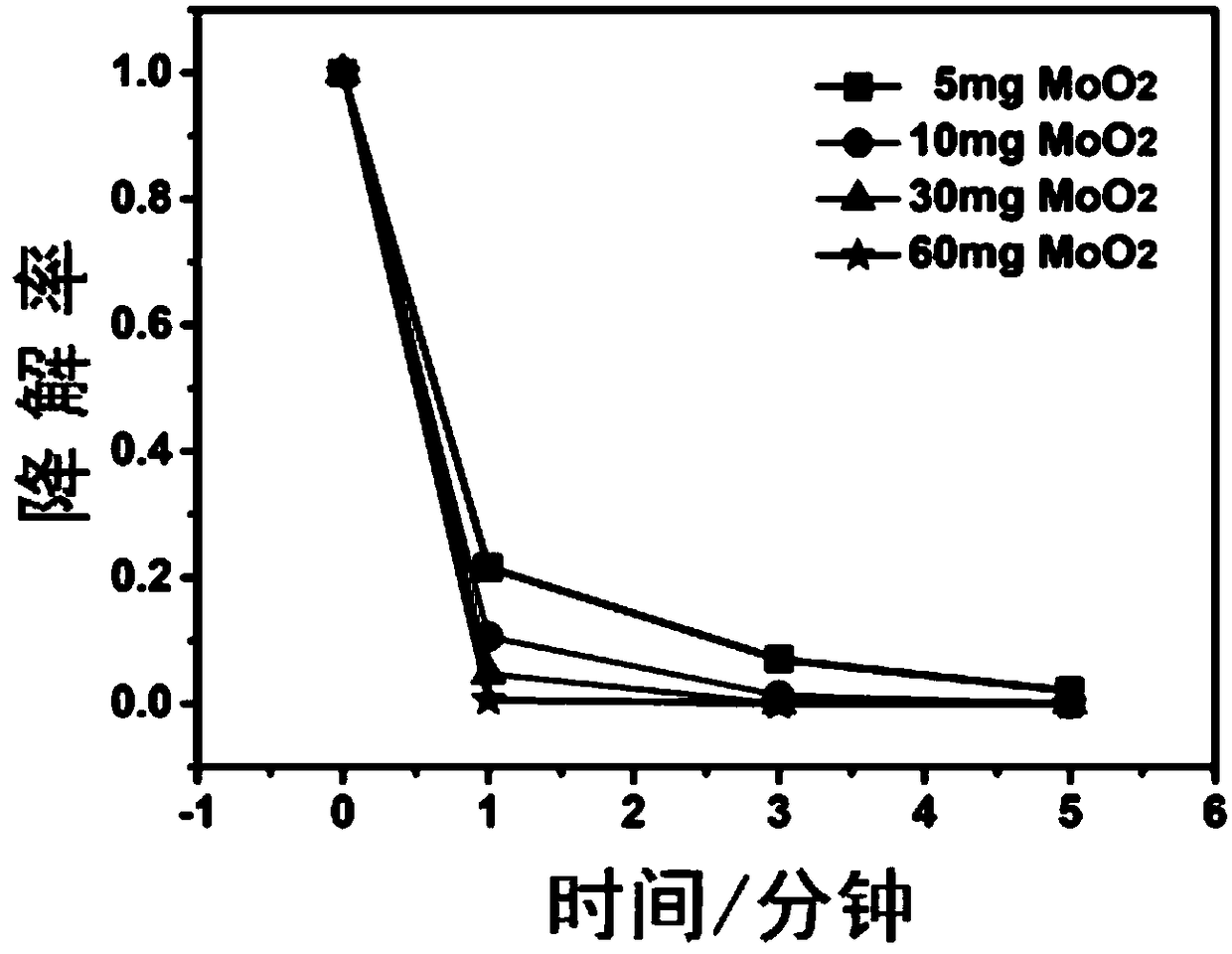
A molybdenum oxide reagent used for organic pollutant degradation and a reaction method thereof
InactiveCN108993524APromote degradationImprove degradation efficiencyWater contaminantsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsFenton reactionIron salts
The invention relates to the field of chemistry, particularly relates to organic pollutant treatment, and more particularly relates to a molybdenum oxide reagent used for organic pollutant degradation. The reagent includes a Fenton's reagent including an iron source and hydrogen peroxide, and also includes a molybdenum oxide mixed in the Fenton's reagent as a cocatalyst of the Fenton's reagent. After the molybdenum oxide is added as the cocatalyst, the Fenton reaction efficiency and the hydrogen peroxide utilization efficiency are greatly increased, dosage of an iron salt is reduced, and the molybdenum oxide reagent has high activity even in a condition that pH is high. The molybdenum oxide reagent can greatly increase the organic wastewater treatment efficiency of a Fenton technique, reduces the treatment cost, broadens the application range and has a good application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
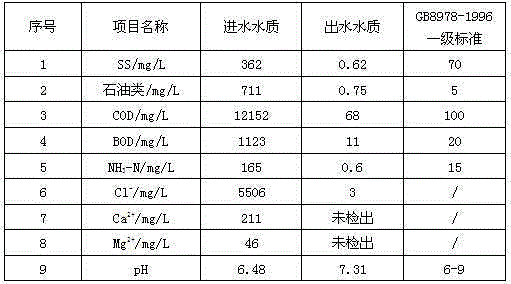
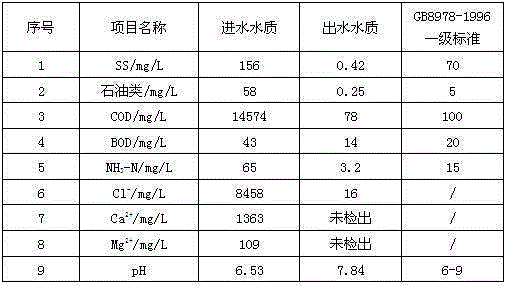
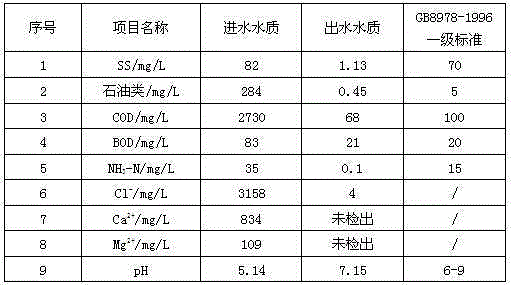
Up-to-standard discharge treatment technology of drilling wastewater from oil and gas fields
InactiveCN105366868ALow viscosityReduce hardnessWaste water treatment from quariesWater treatment compoundsWell drillingDivalent metal ions
The invention discloses an up-to-standard discharge treatment technology of drilling wastewater from oil and gas fields. The treatment technology comprises the following steps: (1) adjusting pH value of wastewater to 3-4.5; (2) adding a Fenton's reagent into wastewater treated in the step (1), degrading large molecular organic matter in the wastewater to low molecular organic matter and simultaneously removing sulfide in the wastewater and part of low molecular organic matter; (3) adjusting pH value of the wastewater treated in the step (2) to 8-10, adding a flocculating agent and a coagulant aid, and removing suspended matter and part of COD in the wastewater after gravity settling; (4) adding sodium carbonate and a flocculating agent into the wastewater treated in the Step (3), settling and removing divalent metal ion in the water; and (5) carrying out evaporative crystallization treatment on the wastewater treated in the Step (4), conducting circulating treatment on an concentrated solution and discharging condensate water up to standard. According to the invention, low-cost up-to-standard discharge treatment of drilling wastewater from a plurality of complex oil and gas fields can be realized.
Owner:SICHUAN YANGSEN PETROLEUM TECH CO LTD
Purification of carbon nanotubes based on the chemistry of fenton's reagent
The present invention is directed to methods of purifying carbon nanotubes (CNTs). In general, such methods comprise the following steps: (a) preparing an aqueous slurry of impure CNT material; (b) establishing a source of Fe2+ ions in the slurry to provide a catalytic slurry; (c) adding hydrogen peroxide to the catalytic slurry to provide an oxidative slurry, wherein the Fe2+ ions catalyze the production of hydroxyl radicals; and (d) utilizing the hydroxyl radicals in the oxidative slurry to purify the CNT material and provide purified CNTs.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Domestic sewage treatment process
InactiveCN105859033AEasy to handleTreatment involving filtrationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesFiberReclaimed water
The invention provides a domestic sewage treatment process, comprising the following steps: (1), primarily filtering with a grille well; (2), primarily settling with a primary settling tank; (3), chemically oxidizing with a primary oxidation tank; (4), biochemically treating with a secondary oxidation tank; (5), flocculating and settling with a secondary settling tank; (6), filtering with fiber balls; (7), sterilizing in a fresh water tank. Sewage is first chemically oxidized with Fenton's reagent so that refractory organics in the sewage are decomposed, the sewage is then biologically treated in the secondary oxidation tank, organics and heavy metal ions in the biochemically treated sewage are further removed via flocculating, and the swage is finally filtered with the fiber balls and sterilized; sewage treatment efficiency is improved, outgoing water quality reaches the standard for reclaimed water, and outgoing water is directly reclaimable.
Owner:NANJING HAIYI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG
Preprocessing method for producing ethyl alcohol through straw and application
InactiveCN106086084AIncrease productionAvoid unsafe factorsBiofuelsFermentationCellulosePretreatment method
The invention relates to the technical field of producing ethyl alcohol through lignin cellulose type raw materials, in particular to a preprocessing method for producing ethyl alcohol through straw and application. The method includes the following steps of firstly, smashing corn straw, screening the smashed straw through a 40# screen, and putting the material in a dryer for use; secondly, putting the corn straw and a Fenton's reagent in a triangular flask, conducting reaction for 24-72 h at room temperature, and sequentially conducting vacuum suction filtration, washing and drying on the corn straw to obtain the preprocessed corn straw. By means of the preprocessed straw, the enzymatic glucose yield is improved by 57%, and the method is easy to operate, free of high-temperature high-pressure equipment, low in equipment requirement, low in energy consumption and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Composite material for restoring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution and preparation method and application of composite material
InactiveCN108637005AHigh activityReduce dosageMaterial nanotechnologyContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonZinc
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental science, and particularly relates to a composite material for restoring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution and a preparation methodand application of the composite material. The composite material for restoring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution comprises carbon dot modified zinc oxide and a Fenton's reagent, and the massratio of the carbon dot modified zinc oxide to the Fenton's reagent is (1-10): (10-1). The invention further provides the preparation method and application of the composite material. Photocatalyticdegradation and oxidation degradation processes are organically bonded, the two parts are subject to the synergistic effect to achieve quick rapid degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and environmental heavy metal pollution information can be provided.
Owner:江苏金环科技有限公司
Membrane post treatment
ActiveUS20090230053A1Improve breathabilityReduce total pressure lossSemi-permeable membranesMembranesCross-linkMicrofiltration
Hydrophilic porous polymeric membranes with high permeabilities, and processes for the preparation thereof are disclosed. Membranes may be prepared by including a preferably hydrophilic cross-linkable component such as PVP (either by inclusion into the polymer dope prior to casting, or coating or quenching cast membranes); and treating the polymeric microfiltration or ultrafiltration membrane with a crosslinking agent to cross-link said cross-linkable component. Preferred cross-linking agents include Fenton's reagent.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Method for extracting micro plastics from human and animal excreta
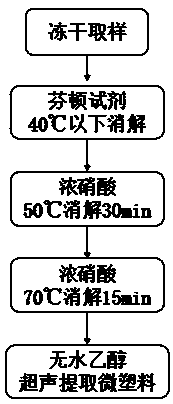
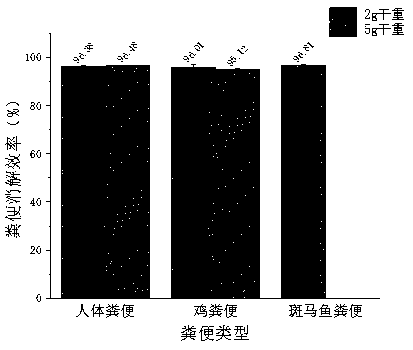
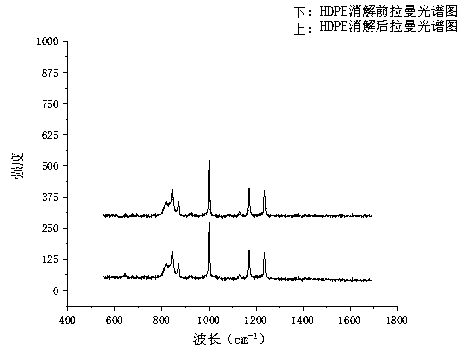
ActiveCN110243642AQuick extractionEfficient extractionSemi-permeable membranesPreparing sample for investigationFecesFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for extracting micro plastics from human and animal excreta, and belongs to field of environmental health risk assessment. The method comprises the steps of excrement freeze-drying, sample decomposition and sample extraction, wherein the decomposition process comprises the steps of treatment with a Fenton's reagent, decomposition of concentrated nitric acid and extraction of absolute ethyl alcohol. According to the method, the micro plastics can be extracted from human and animal excreta conveniently and quickly under the condition of guaranteeing minimized influence on the micro plastics, the types and abundance of the micro plastics in biological excreta are accurately analyzed, and powerful technical support and data support are provided for researching an enrichment and excretion rule of the micro plastics in vivo and health risk assessment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
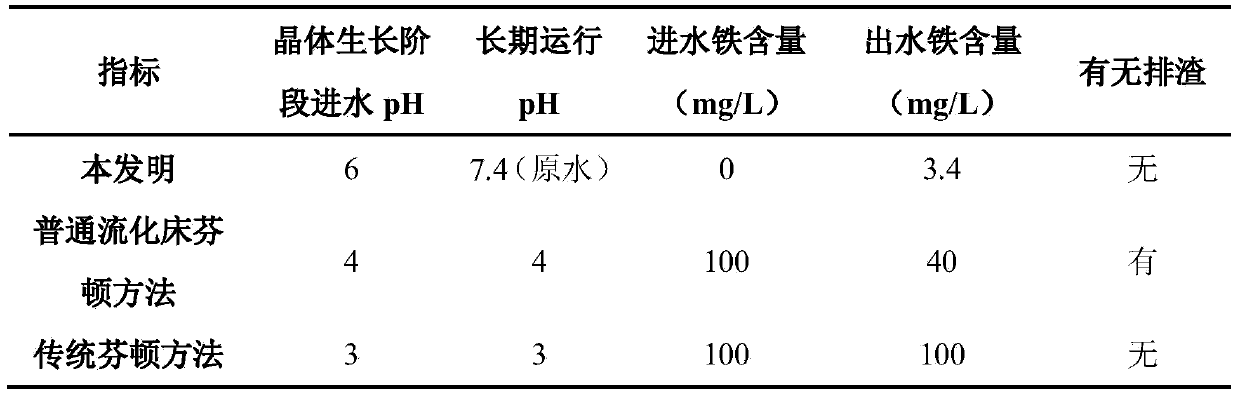
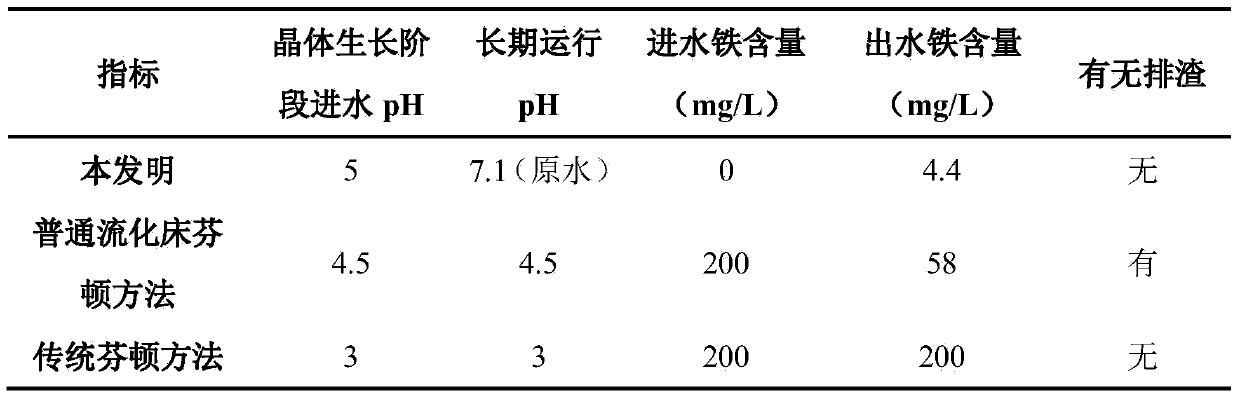
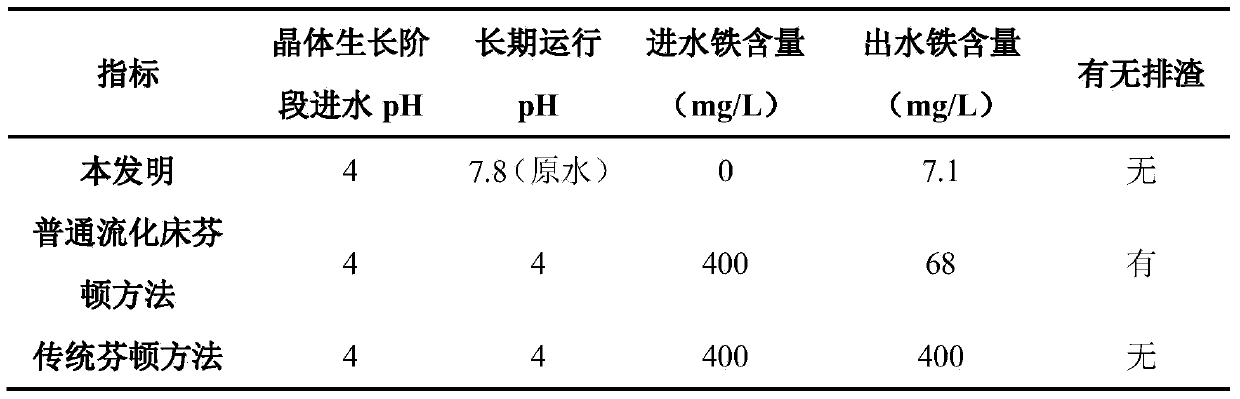
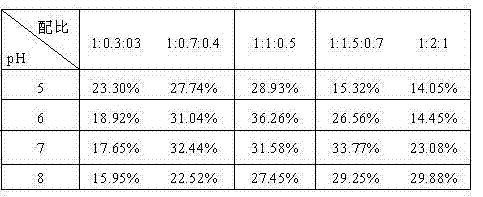
Fenton fluidized bed biochemical tail water advanced treatment method
ActiveCN104192979AChange the traditional conceptEasy to handleWater/sewage treatment by oxidationTreatment effectSlag
The invention discloses a Fenton fluidized bed biochemical tail water advanced treatment method and belongs to the field of wastewater treatment. The method comprises a crystal growth stage and a biochemical tail water advanced treatment stage; in the crystal growth stage, a Fenton agent is rapidly loaded on the surface of a filler and grow a crystal; in the biochemical tail water advanced treatment stage, the wastewater is oxidized and degraded by prolonging the time of the biochemical tail water staying in the fluidized bed and taking full advantage of the heterogeneous catalytic performance of the crystal growing on the surface of the filler, ferrous sulfate is not added in the treatment process any more, the target of discharging zero slags without producing iron cement or regulating acid-base is achieved, the method is economical, green and environment friendly, available cheap sands are chosen as the filler, the surface charge of the filler is negative and has a very strong combination action on iron oxide with positive charges, the more stable crystal is more rapidly formed, a better wastewater treatment effect is achieved, and the method is recycled, the service life is long, the design is reasonable, and the utilization ratio of the agent is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Method for processing degradation-resistant organic wastewater and multi-element catalyst adopted by method
ActiveCN104743652AAchieve strong oxidative degradationImprove conversion abilityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsWater/sewage treatment by reductionHigh concentrationSludge
The invention discloses a method for processing degradation-resistant organic wastewater through a Fenton-like multi-element catalytic oxidation technology. The method comprises the following steps: adding an oxidant into to-be-treated degradation-resistant organic wastewater and sufficiently mixing to obtain a mixture; introducing the mixture into a reactor to perform oxidization and reduction reaction; filling the reactor with a multi-element catalyst; processing the wastewater until the COD Cr removal rate is 25-35%. The invention further relates to a multi-element catalyst used for processing degradation-resistant organic wastewater. The method is used for degradation-resistant organic wastewater, a multi-element Fenton-like reagent comprising a catalytic oxidant is coppered with catalytic oxidization action to generate a series of free radical reactions, so that output of high-concentration high-strength hydroxyl free radical is realized, the transfer ability of hydrogen peroxide is greatly improved, and the strong-oxidization degradation of degradation-resistant organic substances in the wastewater by the hydroxyl free radical is realized. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the reaction conditions are gentle, much acid or alkaline is not required to regulate the pH value, sludge is not generated in the processing process, and the method can be used for pretreatment and posttreatment of the degradation-resistant organic substances, so that the up-to-standard emission is guaranteed, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:武汉森泰环保股份有限公司
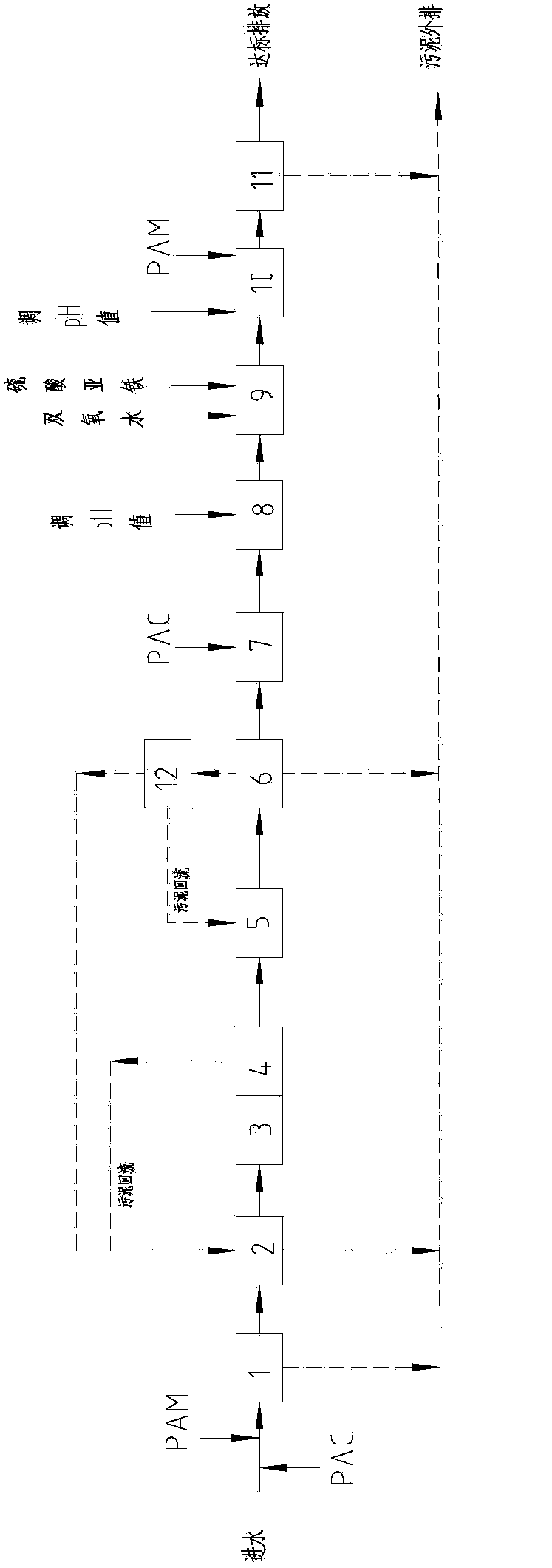
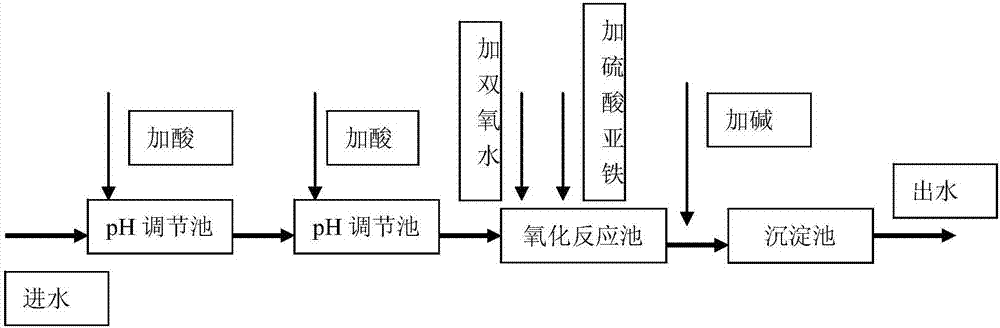
Fenton's reagent oxidation wastewater treatment method and device thereof
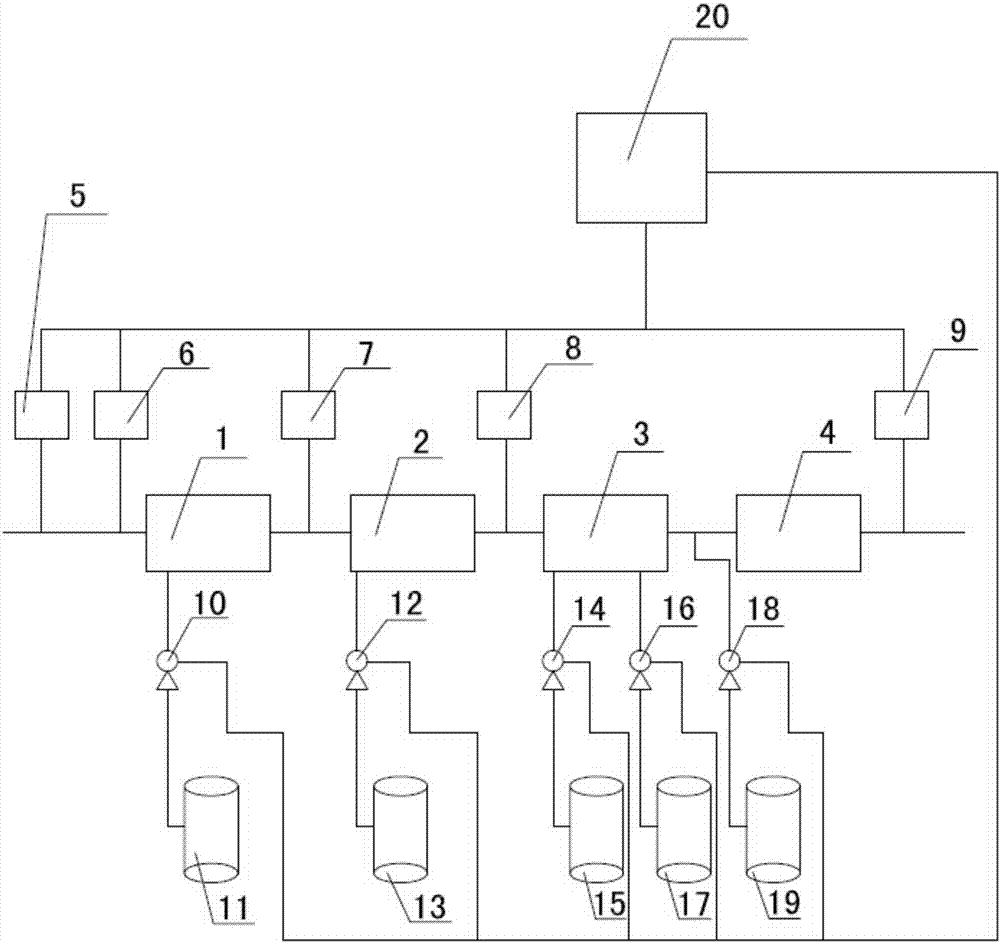
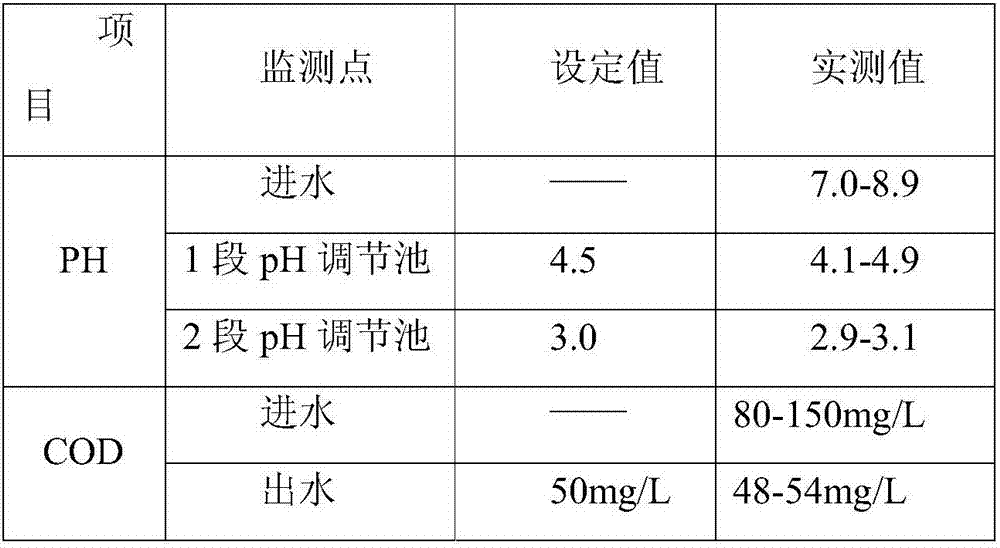
InactiveCN107473361AEasy to handleReduce processing costsWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsSulfatePh regulation
The invention belongs to the field of wastewater treatment technology and specifically relates to a Fenton's reagent oxidation wastewater treatment method and a device thereof. Wastewater to be treated enters a 1-stage pH regulating tank, and concentrated acid is extracted from a concentrated acid storage tank through an acid adding pump to carry out first-step pH regulation; an effluent from the 1-stage pH regulating tank enters a 2-stage pH regulating tank, and diluted acid is extracted from a diluted acid storage tank through an acid adding pump to carry out second-step pH regulation; an effluent from the 2-stage pH regulating tank enters an oxidation reaction tank, hydrogen peroxide and ferrous sulfate are added into an inlet of the oxidation reaction tank through a dosing pump, and a reaction is conducted after mechanical agitation or air agitation and mixing of the materials and wastewater; after pH regulation of an effluent from the oxidation reaction tank is achieved by addition of alkali, the effluent enters a sedimentation tank, and the effluent from the oxidation tank undergoes solid-liquid separation in the sedimentation tank and finally discharging is followed. Dosage of the oxidizer is controlled precisely so as to avoid less or excessive dosage of the drug. It is ensured that the treatment effect is stable, and treatment cost is effectively reduced. Degree of automation is high, and manual operation difficulty is reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Ex-situ remediation method suitable for chloronitrobenzene type polluted ground water
ActiveCN103626277ALow toxicityPromotes Oxygen RemovalWater/sewage treatment by reductionWater/sewage treatment by oxidationChemical oxygen demandIron reduction
The invention discloses an ex-situ remediation method suitable for chloronitrobenzene type polluted ground water. The method comprises the following steps: filtering polluted water to remove mechanical impurities, and then, adding reducing iron powder and stirring for reaction, wherein additive amount of the reducing iron powder is 30-40% of COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) content, and reducing chloronitrobenzene with zero-valent iron to generate ferrous ions Fe<2+> and phenylamine; 3-5 days later after reduction reaction, adding FeSO4.7H2O of which the additive amount is 30% of COD content, and stirring to realize miscibility; gradually adding H2O2 with mass concentration of 30% into a reaction solution to realize oxidizing reaction according to the additive amount of 3-5 times of COD content, and oxidizing the ferrous ions into ferric ions; after the oxidizing reaction, adding Ca(OH)2 according to the amount of 0.1-0.2% of mass of polluted water solution, and regulating pH to 6-9; and finally, removing sediment by virtue of filtering and separating. The ex-situ remediation method uses a zero-valent iron reduction treatment method and a Fenton's reagent oxidizing treatment method in combination, has an obvious remediation effect on the chloronitrobenzene type polluted ground water, and has high pollutant removal rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES
Preparation method of graphene oxide with hydrogen peroxide catalyst system
The invention belongs to the field of graphene technology, and particularly relates to a preparation method of graphene oxide. The preparation method particularly includes the steps: (1) raw materialpretreatment: uniformly mixing graphite and deionized water, adjusting the pH (potential of hydrogen) value of the system, and performing heating reaction to obtain acid mixed materials; (2) oxidization: cooling the acid mixed materials, and adding Fenton's reagents and deionized water to react mixture to obtain graphite oxide solution; (3) washing: centrifuging and washing the graphite oxide solution to reach neutral; (4) ultrasound: performing dilution, ultrasound and freeze drying on the solution acquired in the step (3) to obtain a graphene oxide product. The preparation method is simple to operate, mild in condition and free from pollution, and the prepared graphene oxide is high in monolayer rate.
Owner:嘉兴烯成新材料有限公司
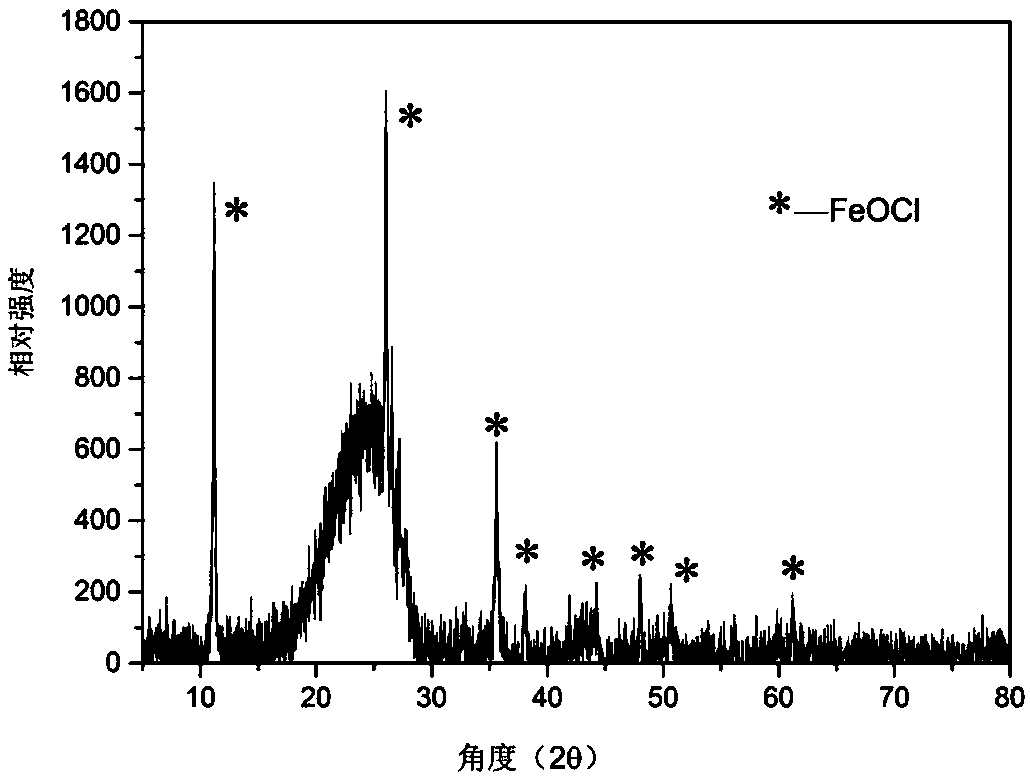
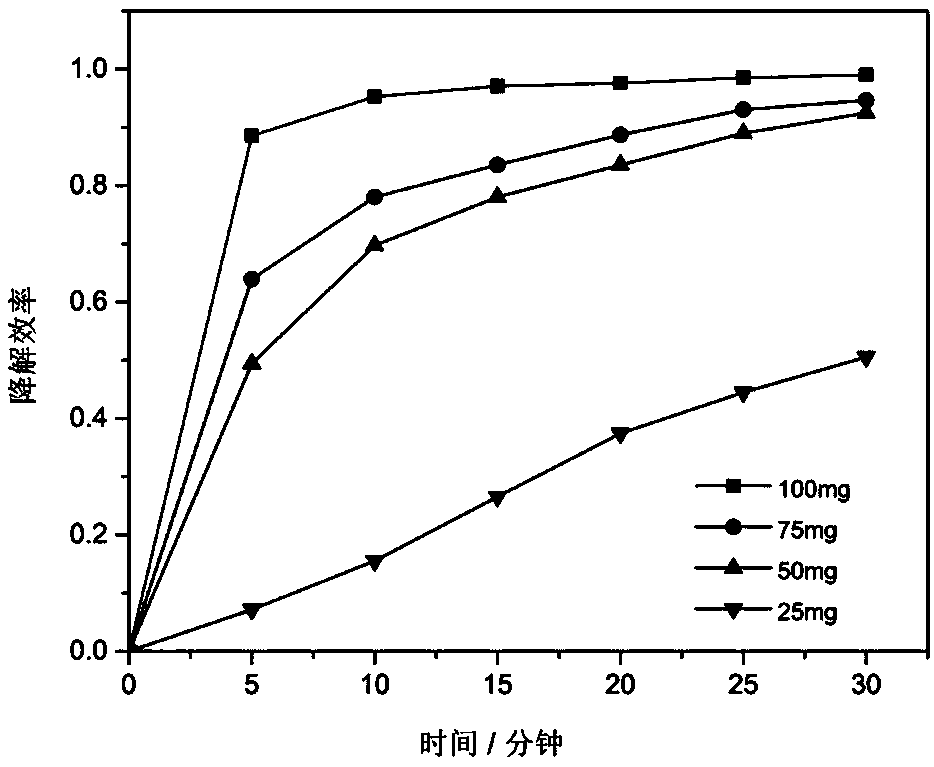
Supported iron oxychloride Fenton's reagent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109046397AGood dispersionImprove degradation efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater treatment compoundsDispersityPersulfate
The invention relates to a supported iron oxychloride Fenton's reagent and a preparation method thereof. The supported iron oxychloride Fenton's reagent only can form an oxidizing system with hydrogenperoxide or persulfate and can quickly and effectively degrade pollutants. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing ferric trichloride and activated carbon pretreated with dilute acid, and then placing into a sealed container, calcining for a period of time under high temperature, cooling and then cleaning and drying. The invention can solve the problems of poor dispersity, insufficient catalytic activity, large actual dosage, low stability, easiness in suffering from reagent loss and ion dissolving, and the like, of a conventional solid Fenton's reagent. The Fenton's reagent prepared according to the invention has a quick and efficient degrading effect on dye wastewater, can be conveniently recycled and regenerated, has an excellent recycling effect, is lowin dissolving concentration of iron ion and has lower subsequent treating pressure. The preparation method is simple, is high in degree of controllability, is suitable for large-scale production, is lower in production and use cost and has an industrial application prospect.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for removing dimethylamine in unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine wastewater treatment process
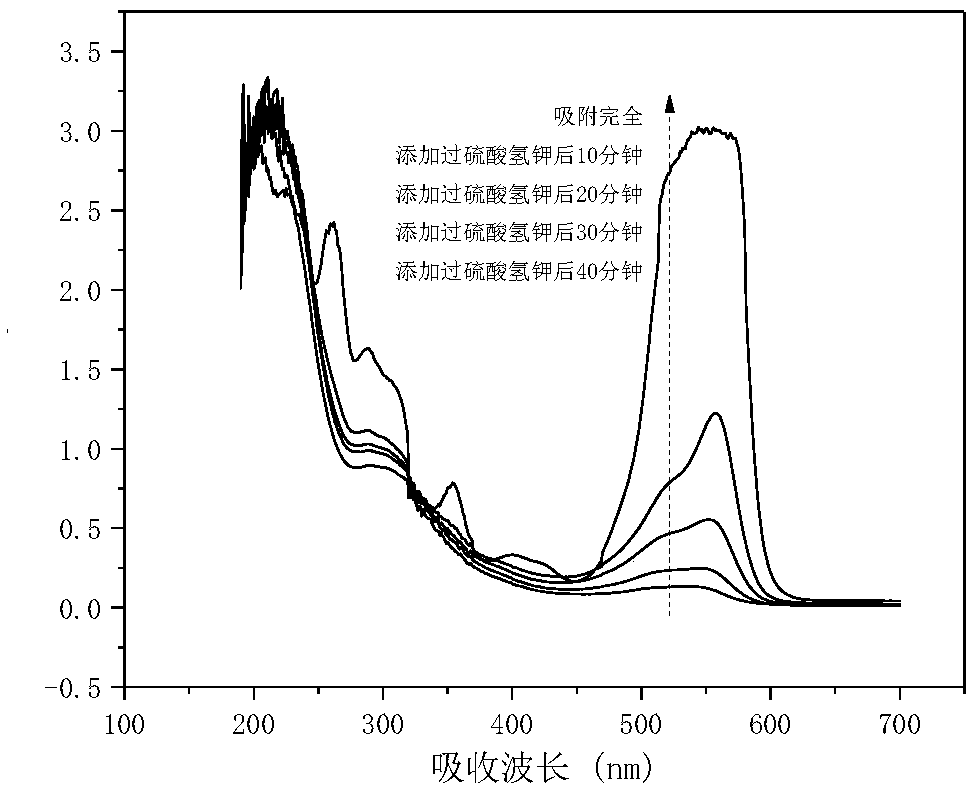
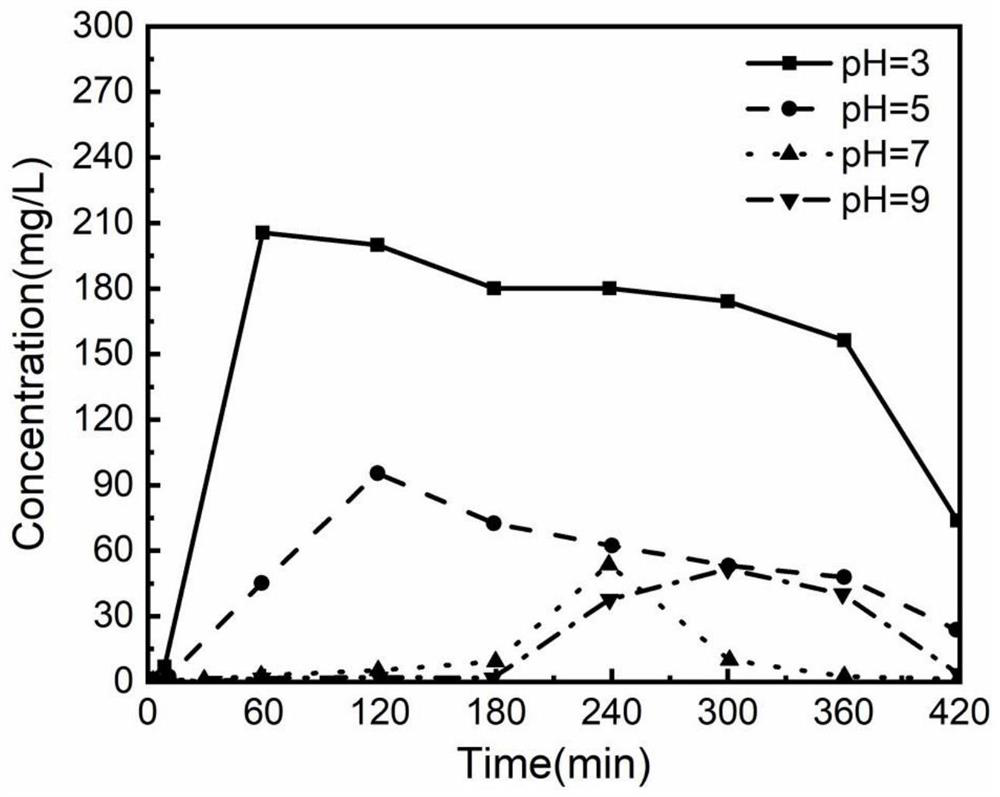
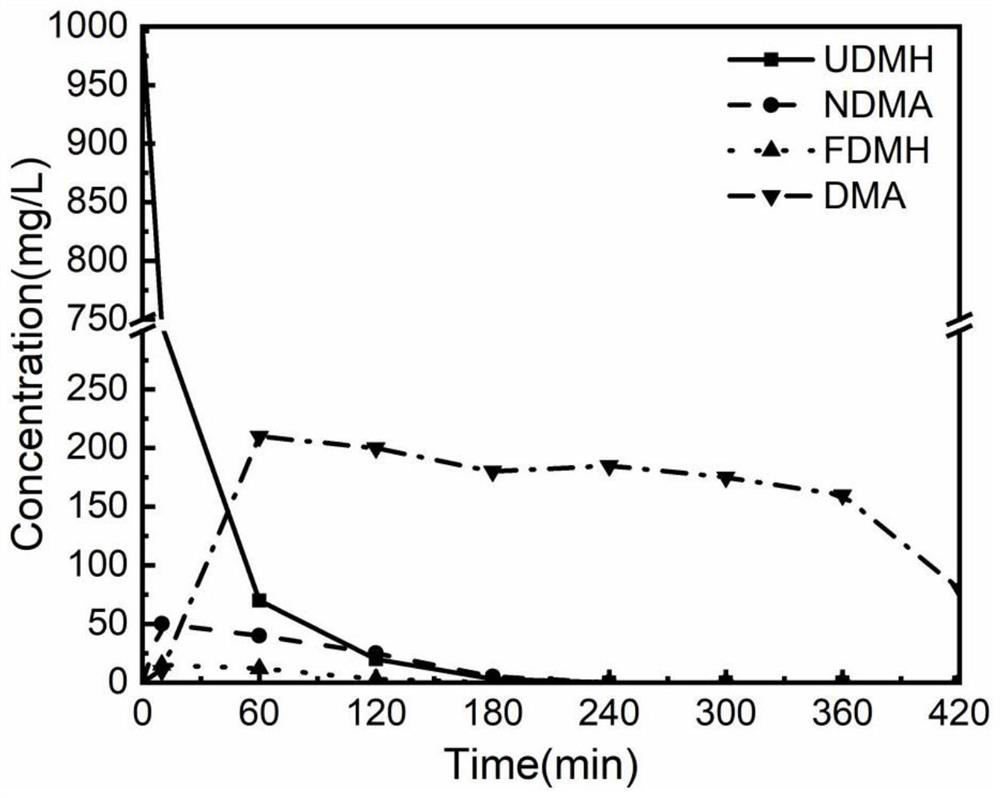
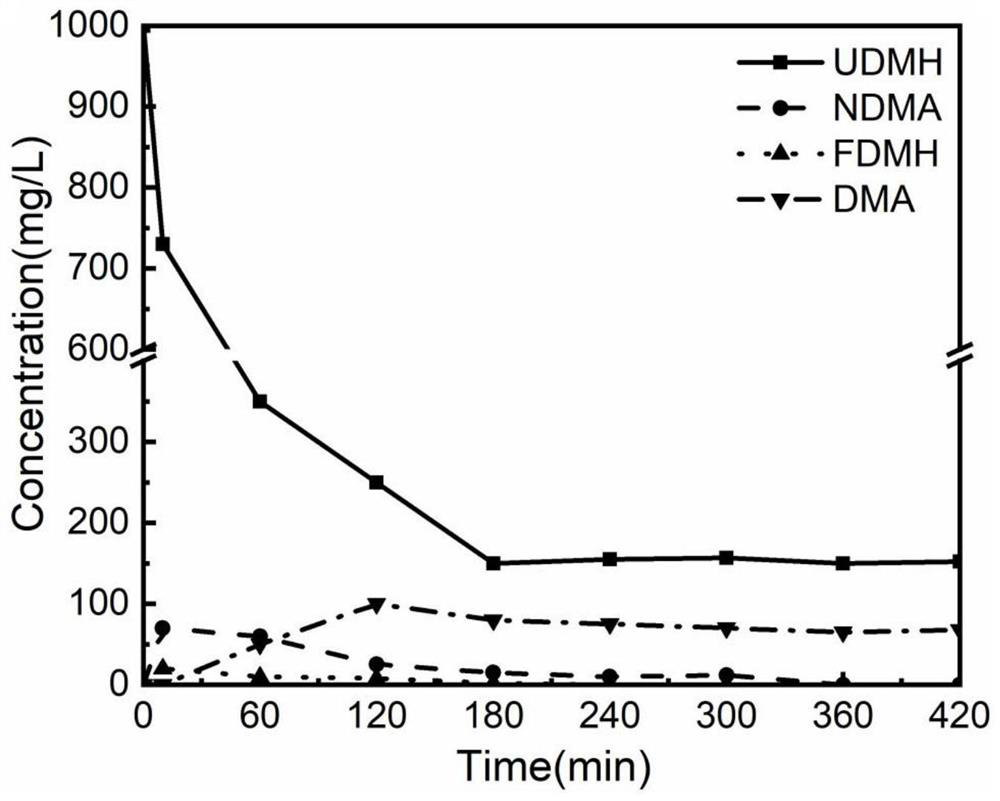
ActiveCN111606480ARemove completelyGood removal effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsNitrosoHydrazone
The invention provides a method for removing dimethylamine in the unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine wastewater treatment process, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The method for removing dimethylamine in the unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine wastewater treatment process comprises the following steps: mixing a Fenton reagent with unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine wastewater, adjusting the pH value to 2.5-6, and carrying out first Fenton treatment to obtain a treated crude solution; and adjusting the pH value of the treated crude liquid to 6-8, then mixing the treated crudeliquid with a hydrogen peroxide solution, carrying out second Fenton treatment on the obtained treated crude liquid-hydrogen peroxide mixed solution, and discharging the obtained second Fenton treatment solution after the concentration of dimethylamine in the obtained second Fenton treatment solution is lower than 5.0 mg / L. According to the removal method provided by the invention, unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine and nitrosodimethylamine and unsymmetrical hydrazone generated in the treatment process can be thoroughly removed through first Fenton treatment, the concentration of dimethylamine can be reduced to less than 5.0 mg / L through the second Fenton treatment, the risk of converting dimethylamine into a high carcinogen nitrosodimethylamine is reduced, and the process is simple.
Owner:中国人民解放军火箭军工程大学
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com