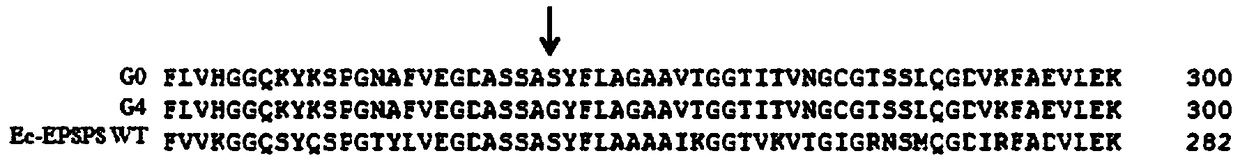Plant EPSPS mutant containing L195P and S247G as well as encoding gene and application thereof
A technology for coding genes and mutants, applied in plant EPSPS mutants and their coding genes and application fields, can solve the problems of low acceptance of transgenic crops, achieve the effects of maintaining the catalytic activity of biological enzymes, improving resistance, and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
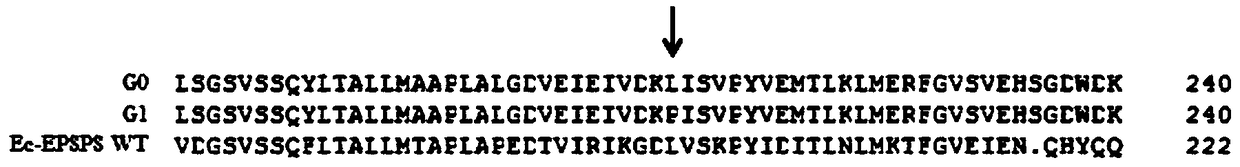
[0117] The soybean EPSPS mutant provided in this example is named G1, and its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.4.
[0118] The soybean EPSPS mutant G1 provided in this example is composed of wild-type soybean EPSPS (named as G0, the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2) corresponding to the No. The 195th position (the mutation site is located at the 212th position of the wild-type soybean EPSPS) is obtained by mutating the amino acid residue L to P.
[0119] The amino acid sequence alignment of soybean EPSPS mutant G1, wild-type soybean EPSPS and Escherichia coli EPSPS is as follows: figure 1 As shown, in the figure: the position indicated by the arrow is the mutation site, and Ec-EPSPS WT represents Escherichia coli EPSPS.
[0120] In addition, this embodiment also provides a nucleic acid molecule (ie, coding gene) encoding soybean EPSPS mutant G1, the base sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.3.
[0121] Both the soybean EPSPS mutant G1 and the nucleic a...
Embodiment 2
[0123] The soybean EPSPS mutant provided in this example is named G3, and its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.8.
[0124] The soybean EPSPS mutant G3 provided by the present embodiment is composed of the wild-type soybean EPSPS (named as G0, the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2) corresponding to the No. The 195th position (the mutation site is located at the 212th position of wild-type soybean EPSPS) is mutated from amino acid residue L to P and the 101st position (this site corresponds to the 114th position of wild-type soybean EPSPS) is mutated from amino acid residue P to S get.
[0125] The amino acid sequence alignment of soybean EPSPS mutant G3, wild-type soybean EPSPS and Escherichia coli EPSPS is as follows: figure 2 As shown, in the figure: the position indicated by the arrow is the mutation site, and Ec-EPSPS WT represents Escherichia coli EPSPS.
[0126] In addition, this embodiment also provides a nucleic acid molecule encoding soybean EPSPS...
Embodiment 3
[0129] The soybean EPSPS mutant provided in this example is named G4, and its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.10.
[0130] The soybean EPSPS mutant G4 provided by the present embodiment is composed of the wild-type soybean EPSPS (named as G0, the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2) corresponding to the E. coli EPSPS (the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.41). The 247th position (this position corresponds to the 265th position of the wild-type soybean EPSPS) is obtained by mutation of the amino acid residue S to G.
[0131] The amino acid sequence alignment results of soybean EPSPS mutant G4, wild-type soybean EPSPS and Escherichia coli EPSPS are as follows: image 3 As shown, in the figure: the position indicated by the arrow is the mutation site, and Ec-EPSPS WT represents Escherichia coli EPSPS.
[0132] In addition, this embodiment also provides a nucleic acid molecule encoding soybean EPSPS mutant G4, the base sequence of which is shown in SEQ I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com