Compound biological ink and preparation method thereof
A bio-ink and bioactive molecule technology, applied in the field of composite bio-ink and its preparation, can solve the problems of low mechanical strength, unfavorable application, poor mechanical and structural stability of decellularized matrix hydrogel, etc., and achieve good bioactivity and reliability Effects of 3D printing properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
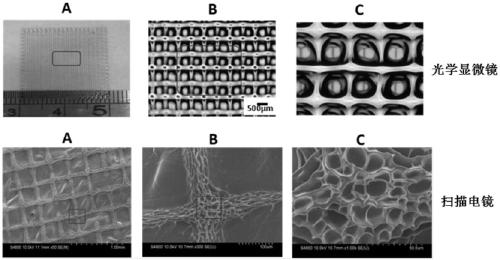
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
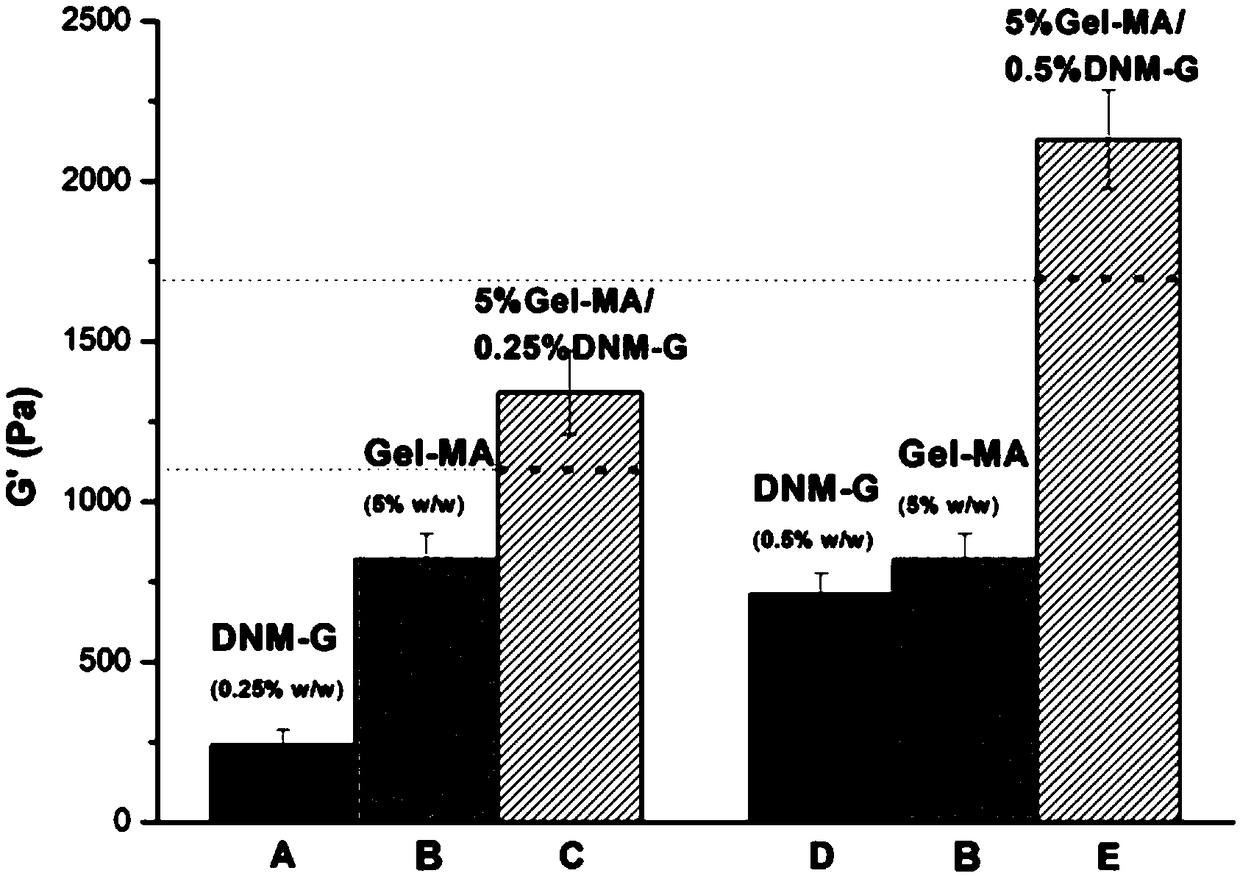
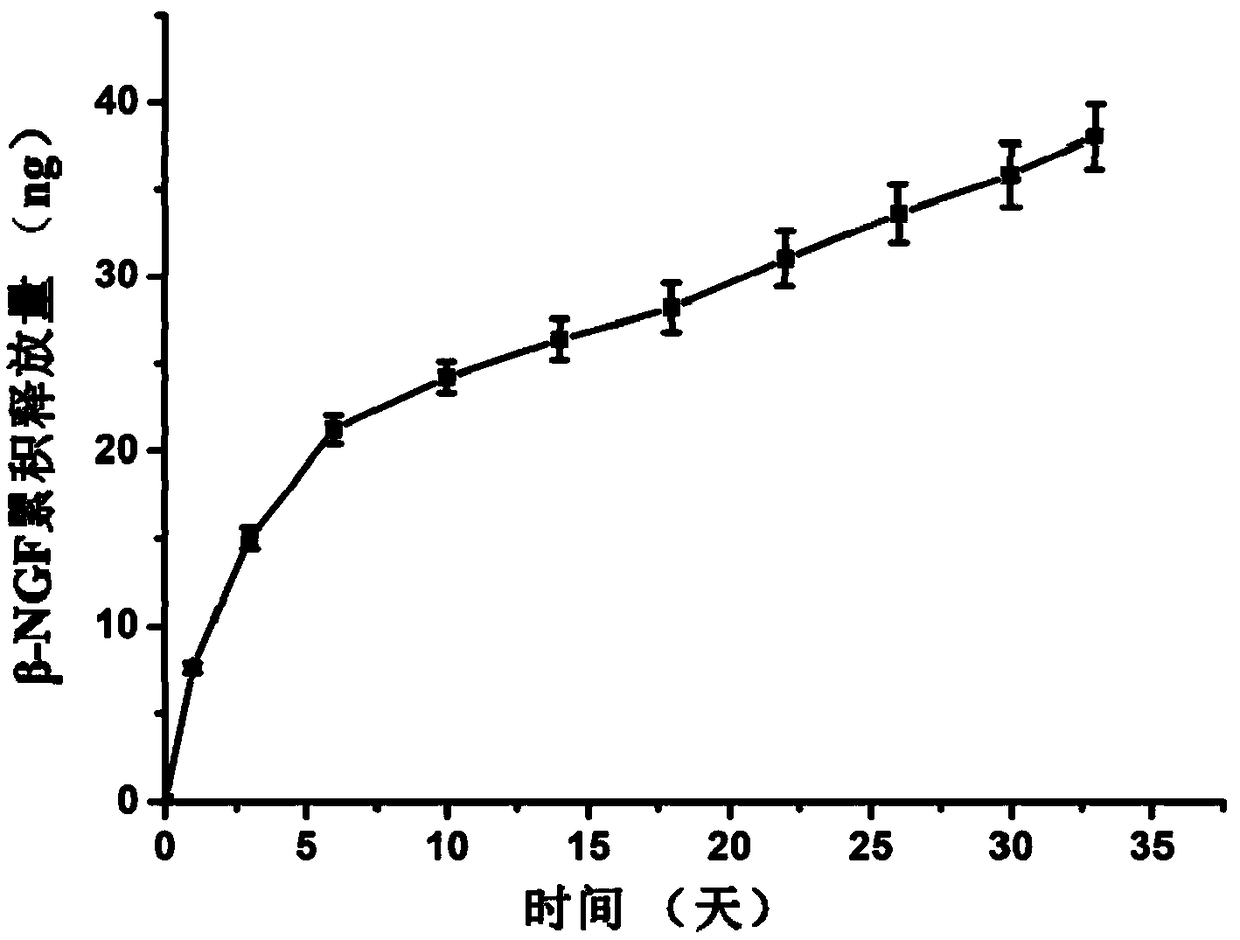
[0040] A kind of embodiment of composite biological ink of the present invention, its preparation raw material comprises the component of following mass percent concentration: acellular matrix hydrogel 1%, PLGA-PEG-PLGA 30%, factor is β-NGF (final concentration 60ng / ml), the balance is water.
[0041] The preparation method of above-mentioned composite biological ink comprises the steps:
[0042] (1) Preparation of acellular matrix hydrogel: after removing pig heart adipose tissue and connective tissue, use 1% trion x-100 aqueous solution, 7% sodium deoxycholate aqueous solution to repeatedly process successively to obtain acellular tissue; freeze-dry The decellularized tissue is then pulverized, treated with pepsin to obtain a viscous gel solution, then adjusted to pH (7.5) and ionic strength at 2°C, and heated to 39°C to obtain the decellularized matrix hydrogel, and the final concentration is controlled 1%.
[0043] (2) Quantitative PLGA-PEG-PLGA and β-NGF were dissolved ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A kind of embodiment of composite bio-ink of the present invention, its preparation raw material comprises the component of following mass percent concentration: decellularized matrix hydrogel 1%, double-bond modified hyaluronic acid 2%, factor is VEGF (final concentration 40ng / ml), the balance is water.
[0046] The preparation method of above-mentioned composite biological ink comprises the steps:
[0047] (1) Preparation of acellular matrix hydrogel: After removing porcine placental adipose tissue and connective tissue, use 2% trionx-100 aqueous solution and 5.5% sodium deoxycholate aqueous solution to repeatedly process successively to obtain acellular tissue; The decellularized tissue is then pulverized, treated with pepsin to obtain a viscous gel solution, then adjusted to pH (7.9) and ionic strength at 3°C, and heated to 38°C to obtain the acellular matrix hydrogel, and the final concentration is controlled as 1%.
[0048] (2) Quantitative double-bond-modified ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] A kind of embodiment of composite biological ink of the present invention, its preparation raw material comprises the component of following mass percentage concentration: acellular matrix hydrogel 2%, double bond modified gelatin 8%, factor is BDNF (final concentration is 20ng / ml), the balance is water.
[0051] The preparation method of above-mentioned composite biological ink comprises the steps:
[0052] (1) Preparation of acellular matrix hydrogel: After removing pig heart adipose tissue and connective tissue, use 3% trion x-100 aqueous solution, 4% sodium deoxycholate aqueous solution to repeatedly process successively to obtain acellular tissue; freeze-dry The decellularized tissue is then pulverized, treated with pepsin to obtain a viscous gel solution, then adjusted to pH (7) and ionic strength at 4°C, and heated to 37°C to obtain the decellularized matrix hydrogel, and the final concentration is controlled 2%.
[0053] (2) Quantitative double-bond-modified ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com