A surface treatment method of a gallium arsenide substrate
A technology for surface treatment and substrate surface, applied in the field of material processing, can solve the problems of inability to ensure that the substrate surface is completely clean, unfavorable energy saving and emission reduction production efficiency, low processing effect and efficiency, etc., to ensure the quality of interface contact and improve product quality. Yield and device performance, the effect of ensuring surface cleanliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) The gallium arsenide substrate 2 is thinned according to the thickness required by the process, so that the thickness meets the process requirement. Gallium arsenide substrate has no fixed crystal orientation and size requirements;
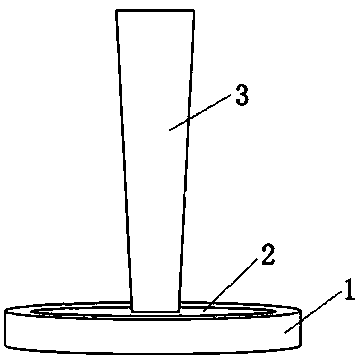
[0024] (2) see figure 1 , place the gallium arsenide substrate 2 to be processed on the stage 1 . The slide table 1 does not interact with the pulsed laser beam 3 and can completely carry the gallium arsenide substrate 2 without a fixed shape requirement.
[0025] (3) Adjust the pulse laser energy density to 0.1J / cm 2 , laser wavelength 248nm, frequency 1Hz;
[0026] (4) Applying the laser adjusted in step (3) to the surface of the gallium arsenide substrate evenly for 10 minutes;
[0027] (5) Turn off the pulsed laser, remove the gallium arsenide substrate obtained in step (4) from the loading stage and place it in deionized water for cleaning for 1 minute;
[0028] (6) drying the gallium arsenide substrate obtained in step (5) wi...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Step (1) and step (2) of this embodiment are the same as embodiment 1.
[0032] (3) Adjust the pulse laser energy density to 4.5J / cm 2 , laser wavelength 532nm, frequency 20Hz;
[0033] (4) Applying the adjusted laser light in step (3) to the surface of the gallium arsenide substrate evenly for 7 minutes;
[0034] (5) Turn off the pulsed laser, remove the gallium arsenide substrate obtained in step (4) from the loading stage and place it in deionized water for cleaning for 5 minutes;
[0035] (6) Drying the gallium arsenide substrate obtained in step (5) with hot nitrogen at a drying temperature of 60° C. for 5 minutes;
[0036] (7) After drying, a gallium arsenide substrate with a clean surface is obtained for subsequent production.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Step (1) and step (2) of this embodiment are the same as embodiment 1.
[0039] (3) Adjust the pulse laser energy density to 10J / cm 2 , laser wavelength 1024nm, frequency 30Hz;
[0040] (4) Applying the adjusted laser light in step (3) to the surface of the gallium arsenide substrate evenly for 4 minutes;
[0041] (5) Turn off the pulsed laser, remove the gallium arsenide substrate obtained in step (4) from the loading stage and place it in deionized water for cleaning for 10 minutes;
[0042] (6) Drying the gallium arsenide substrate obtained in step (5) with hot nitrogen at a drying temperature of 90° C. for 1 minute;
[0043] (7) After drying, a gallium arsenide substrate with a clean surface is obtained for subsequent production.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com