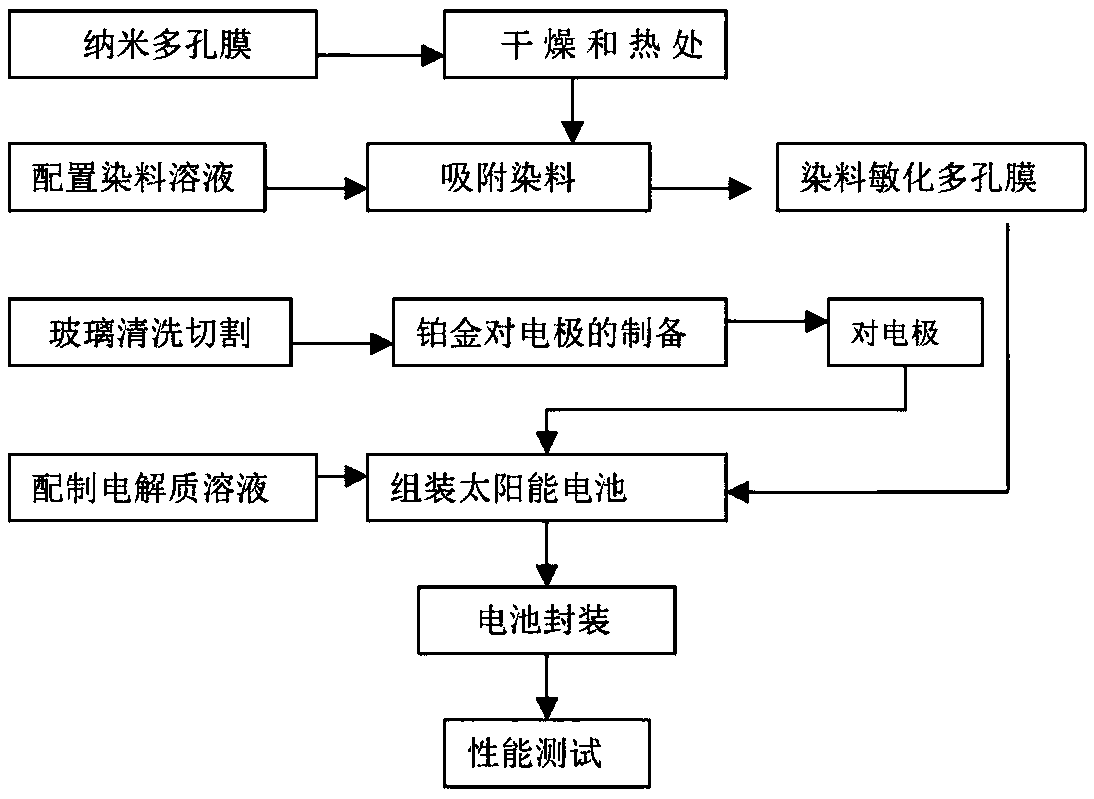
Preparation method of composite photovoltaic cell
A composite light and battery technology, applied in the field of optoelectronics, can solve the problems that dyes cannot fully absorb photons, hinder the photoelectric efficiency of photovoltaic cells, and reduce the utilization rate of light, so as to improve photoelectric conversion efficiency, reduce capacitance and electron migration, and reduce wear and tear. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Preparation of CuO-rGO material
[0055] Step 1: Add 15mL of 0.1mol / L Cu(NO 3 ) 2 solution and mix well, then add 15mL 0.1mol / L Na 2 CO 3 The solution was added drop by drop to form a blue-green colloidal precipitate; Step 2: After continuing to stir for 10 minutes, move the product into a hydrothermal kettle and put it in an oven at 180°C for 6 hours;
[0056] Step 3: After naturally cooling to room temperature, take out, wash, filter, and dry, and the final product obtained is CuO-rGO material. Preparation of CuO-rGO composite photovoltaic cells
[0057] Step 1: Preparation of CuO-rGO nanofilm by electrophoretic deposition
[0058] A) Rinse doped SnO with clean water 2 Conductive glass with smooth surface and no groove (FTO glass, 7Ω / m 2 ) to remove the visible particles on the surface; then soaked in distilled water, acetone, and absolute ethanol to ultrasonically clean them for 30 minutes respectively, and put them into a desiccator after natural drying for u...
Embodiment 2-5
[0069] Cu(NO 3 ) 2 The concentration of the solution was replaced by 0.04mol / L, 0.06mol / L, 0.08mol / L, 0.1mol / L, and Na 2 CO 3 The concentrations of the solutions were replaced by 0.04mol / L, 0.06mol / L, 0.08mol / L, and 0.1mol / L respectively, and the remaining methods and data were the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 6-10
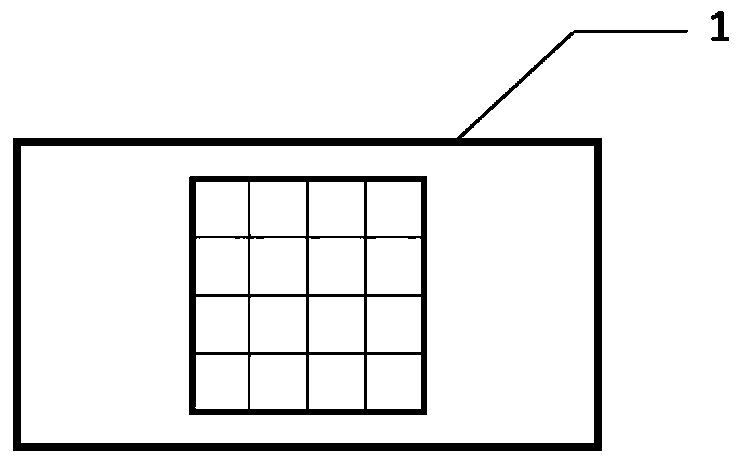
[0071]The electrophoretic deposition method of Example 1 to prepare the CuO-rGO nanofilm step 1) is replaced by the conductive glass 1 with a grid-like groove structure on the upper surface. Simultaneously embodiment 7-10 will the Cu(NO 3 ) 2 The concentration of the solution was replaced by 0.04mol / L, 0.06mol / L, 0.08mol / L, 0.1mol / L, and Na 2 CO 3 The concentrations of the solutions were replaced by 0.04mol / L, 0.06mol / L, 0.08mol / L, and 0.1mol / L respectively, and the remaining methods and data were the same as in Example 1. The conductive glass 1 with a grid-like groove structure on the upper surface has a grid spacing of 2 mm and a depth of 0.5 mm. For specific shapes, see image 3 .
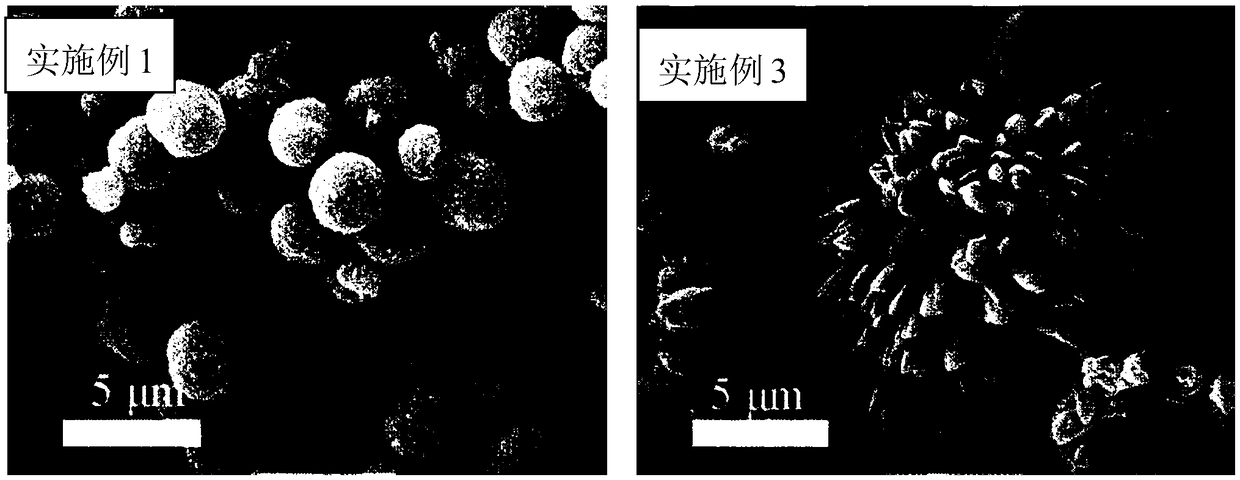
[0072] Preparation of Hierarchical Porous CuO-rGO Thin Film Cu in Implementation 1-10 2 (OH) 2 CO 3 The concentrations of colloidal raw materials are shown in Table 1.
[0073] Table 1 Fabrication of hierarchically porous CuO-rGO films Cu 2 (OH) 2 CO 3 The concentration of colloidal r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com