Method for recovering ammonium chloride from magnesium carbonatization waste liquid
A carbonation waste liquid and carbonation technology, applied in the direction of ammonium chloride, ammonium halide, etc., can solve the problems of waste of raw materials, environmental pollution, increased production costs, etc., to reduce energy consumption, reduce costs, improve The effect of utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
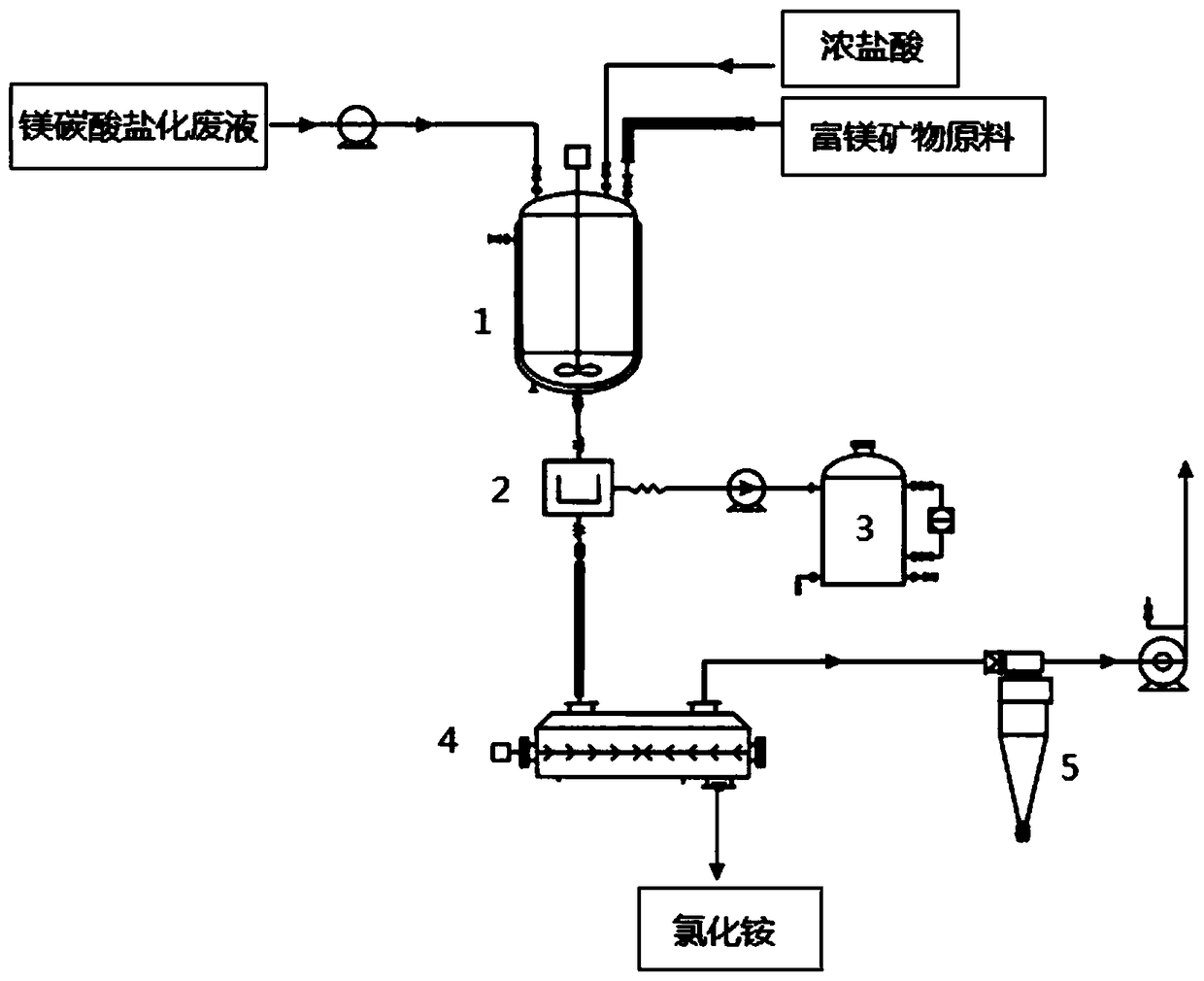
[0025] Such as figure 1 , A method for recovering ammonium chloride from magnesium carbonate waste liquid, including the following steps:
[0026] (1) Pump 500L of magnesium carbonate waste liquid with ammonium chloride concentration of 5.8mol / L into the ammonium chloride crystallization kettle, and the pump flow rate of the waste liquid is 20m 3 / h, stirring (150r / min) and adding concentrated hydrochloric acid to adjust pH 6;
[0027] (2) Transport 300kg of magnesium-rich mineral raw materials to the ammonium chloride crystallization kettle through the transport pipe chain for crystallization, the crystallization temperature is 50°C, and after the crystallization is completed, a suspension is obtained;
[0028] (3) Pass the suspension into a centrifuge for centrifugation (speed of 3000r / min, time of 20min) to obtain a solid product and a clear solution containing 2mol / L magnesium chloride, and send the clear solution to a magnesium-rich mineral concentration tank. To seal carbon di...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A method for recovering ammonium chloride from magnesium carbonate waste liquid, including the following steps:
[0031] (1) Pump 1000L of magnesium carbonate waste liquid with an ammonium chloride concentration of 5.8mol / L into the ammonium chloride crystallization kettle, and the pump flow rate of the waste liquid is 20m 3 / h, stir (150r / min) and add concentrated hydrochloric acid to adjust pH7;
[0032] (2) Transport 800kg of magnesium-rich mineral raw materials to the ammonium chloride crystallization kettle through the transport pipe chain for crystallization, the crystallization temperature is 50°C, and after the crystallization is completed, a suspension is obtained;
[0033] (3) Pass the suspension into a centrifuge for centrifugation (speed of 3000r / min, time of 20min) to obtain a solid product and a clear solution containing 2mol / L magnesium chloride, and send the clear solution to a magnesium-rich mineral concentration tank. To seal carbon dioxide; send the solid pr...
Embodiment 3
[0035] A method for recovering ammonium chloride from magnesium carbonate waste liquid, including the following steps:
[0036] (1) Pump 1500L of magnesium carbonate waste liquid with an ammonium chloride concentration of 5.8mol / L into the ammonium chloride crystallization kettle, and the pump flow rate of the waste liquid is 20m 3 / h, stir (200r / min) and add concentrated hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH to 7;
[0037] (2) Transport 1500kg of magnesium-rich mineral raw materials to the ammonium chloride crystallization kettle through the transport pipe chain for crystallization, the crystallization temperature is 50°C, and after the crystallization is completed, a suspension is obtained;
[0038] (3) Pass the suspension into a centrifuge for centrifugation (speed of 3000r / min, time of 30min) to obtain a solid product and a clear liquid containing 2mol / L magnesium chloride, and send the clear liquid to a magnesium-rich mineral concentration tank for use To seal the carbon dioxide; s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com