Method for reduction removal of heavy metal ions by phosphated nano zero-valent iron
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and heavy metal ions, which is applied in the field of environmental pollution control, can solve the problems of poor electronic selectivity, weak adsorption capacity of heavy metal ions, weak removal capacity of heavy metal ions, etc., to promote adsorption, promote the ability of adsorption and reduction of heavy metal ions, Effects of Changing Electron Transport/Transfer Properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0033] Example 1 phosphating nanometer zero-valent iron removes hexavalent chromium in polluted water (nano zero-valent iron dosage 0.2g / L, hexavalent chromium concentration is 5ppm);
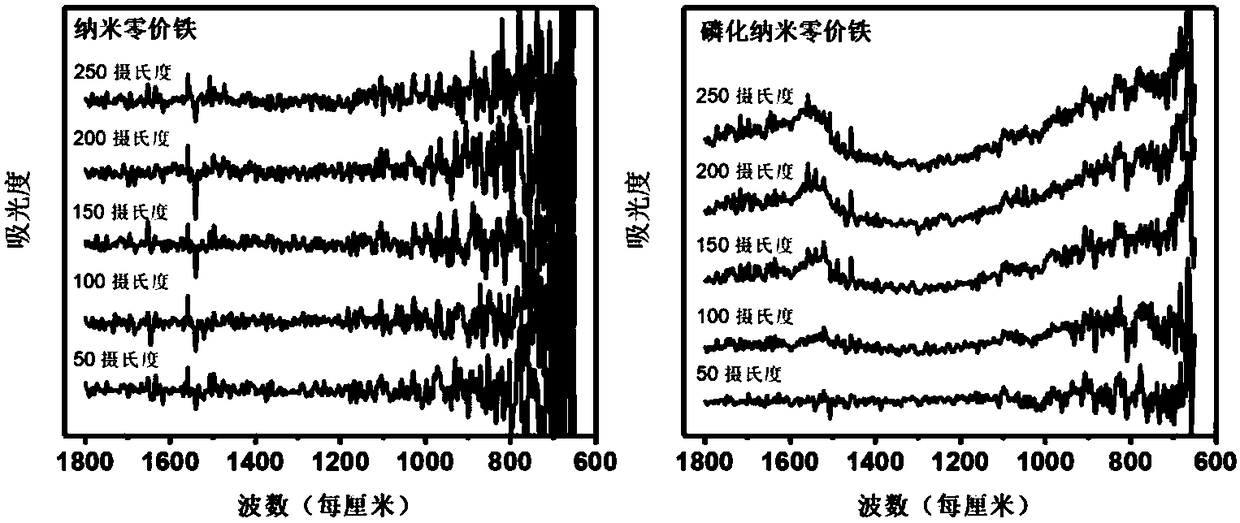
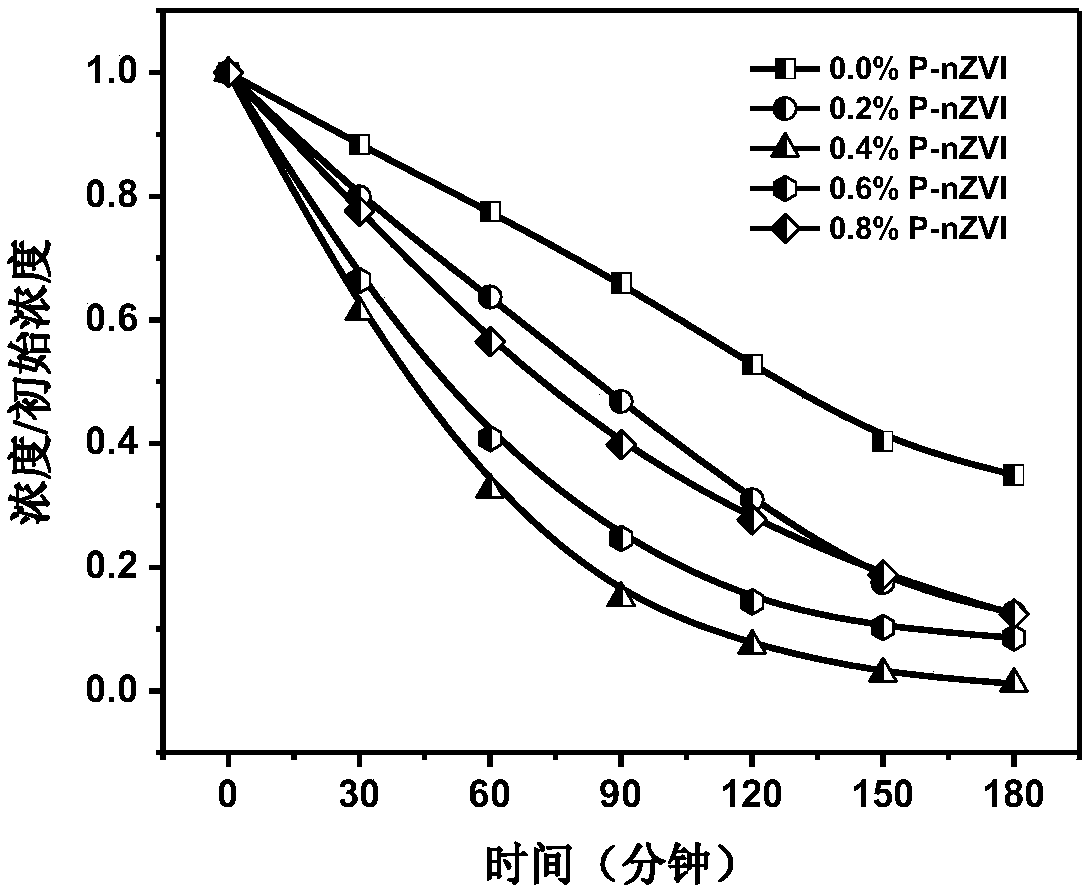
[0034] The 400mL concentration is 0.4mol L -1 The sodium borohydride solution was added dropwise to 1000mL with a concentration of 0.1mol L -1 In the ferric chloride hexahydrate solution (time control in 10min), then immediately add potassium dihydrogen phosphate solid (the molar ratio n of phosphate and iron is successively: 0.0%, 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6%, 0.8% , namely 0.0%, 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6%, 0.8% P-nZVI), aged for 2h, filtered with suction, dried with an infrared lamp under argon gas (about 2h), turned off the infrared lamp, and dried under argon gas Under the condition of cooling to room temperature, the phosphided nanometer zero-valent iron is obtained. Such as figure 1 As shown, during the heating process of phosphating nano-zero-valent iron, the infrared spectrum is at 1335cm -1 to 1087cm -...
example 2
[0036] Example 2 phosphating nanometer zero-valent iron removes hexavalent chromium in polluted water (the dosage of nanometer zero-valent iron is 1g / L, and the concentration of hexavalent chromium is 25ppm);
[0037] 400mL concentration is 1.0mol L -1 The sodium borohydride solution was added dropwise to 1000mL with a concentration of 0.25mol L -1 Ferric chloride hexahydrate solution (time control in 10min), then immediately add potassium dihydrogen phosphate solid (the molar ratio n of phosphate and iron is successively: 0.0%, 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6%, 0.8% , namely 0.0%, 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6%, 0.8% P-nZVI), aged for 2h, filtered with suction, dried with an infrared lamp (about 2h) under argon gas conditions, turned off the infrared lamp, and dried under argon gas Under the condition of cooling to room temperature, the phosphided nanometer zero-valent iron is obtained. Use 50mL of potassium dichromate solution with a hexavalent chromium concentration of 25mg / L to simulate chromium-cont...
example 3
[0038] Example 3 phosphating nanometer zero-valent iron removes hexavalent chromium in polluted water (the dosage of nanometer zero-valent iron is 2g / L, and the concentration of hexavalent chromium is 50ppm);
[0039] The 400mL concentration is 2mol·L -1 The sodium borohydride solution was added dropwise to 1000mL with a concentration of 0.5mol L -1 Ferric chloride hexahydrate solution (time control in 10min), then immediately add potassium dihydrogen phosphate solid (the molar ratio n of phosphate and iron is successively: 0.0%, 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6%, 0.8% , namely 0.0%, 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6%, 0.8% P-nZVI), aged for 2h, filtered with suction, dried with an infrared lamp (about 2h) under argon gas conditions, turned off the infrared lamp, and dried under argon gas Under the condition of cooling to room temperature, the phosphided nanometer zero-valent iron is obtained. Use 50mL of potassium dichromate solution with a hexavalent chromium concentration of 50mg / L to simulate chromium-con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com