Artificial gene editing system for rice
A gene editing and artificial technology, applied in the field of artificial gene editing system, can solve the problems of base editing efficiency limitation and low editing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Construction of recombinant plasmids
[0063] The technical route for constructing the carrier is as follows:
[0064] 1.1 pUbi:Cas9NG recombinant plasmid construction
[0065] Determine the amino acid sequence of Cas9NG as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and determine the gene sequence SEQ ID No.5 for expression in rice according to the amino acid sequence of Cas9NG, and artificially synthesize the 4299bp gene sequence shown in SEQ ID No.5 The nucleotide sequence was cloned into pUC57 and named as pUC57:Cas9NG (completed by Beijing Qingke Xinye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). Then SEQ ID No.12 (maize ubiquitin promoter UbiP), SEQ ID No.5, SEQ ID No.14 (Nos terminator) are cloned into the pCAMBIA1300 vector according to the direction from 5' to 3', named pUbi: Cas9NG.
[0066]The main components of the plasmid pUbi:Cas9NG are as follows: CaMV35S promoter (genebank accession number is FJ362600.1, nucleotide sequence from 10382 to 11162), hygromycin gene (genebank accession number is ...
Embodiment 2
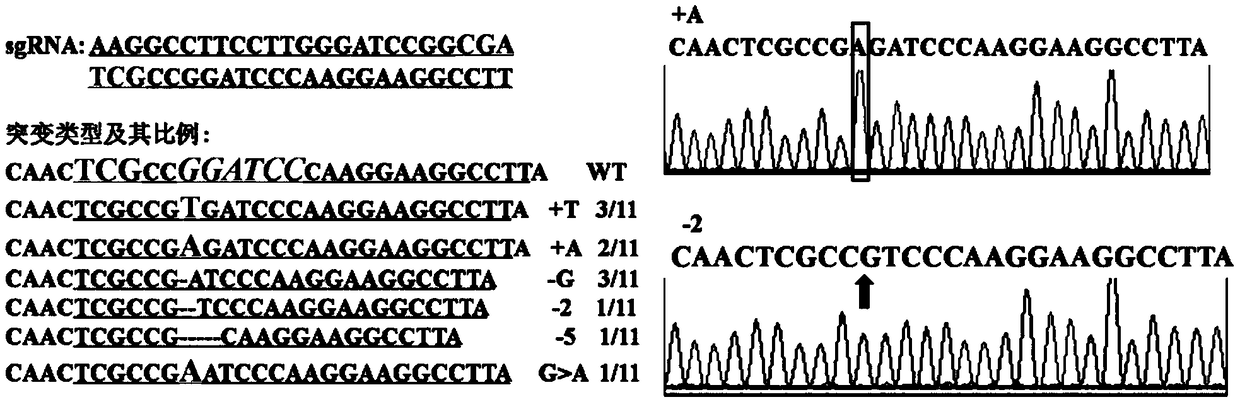
[0079] Example 2: Knockout of rice endogenous gene OsCERK1 using pUbi:Cas9NG
[0080] 2.1 Design and cloning of recognition sequence for OsCERK1 gene
[0081] The transcript sequence and genome sequence of the OsCERK1 (LOC_Os08g42580) gene were obtained from the MSU / TIGR rice genome database ( http: / / rice.plantbiology.msu.edu / ).
[0082] For the OsCERK1 gene, the design contains the target nucleotide sequence (SEQ ID No.16: The underline is the BamH I restriction site, and the bold is the PAM sequence) primers are as follows: gOsCERK1-F1 (SEQ ID No. 26: tgttggccttccttgggatccgg) and gOsCERK1-R1 (SEQ ID No. 27: aaacccggatcccaaggaaggcc). After synthesizing the primers, use T4 polynucleotide kinase to phosphorylate the primers, anneal to form double strands, clone gOsCERK1-F1 / R1 into the BtgZ I restriction site of the pENTR4:sgRNA vector, and confirm that the inserted fragment is complete by sequencing. Correct, named pENTR4:sgRNA-gOsCERK1.
[0083] 2.2 PEG-mediated pUbi:Ca...
Embodiment 3
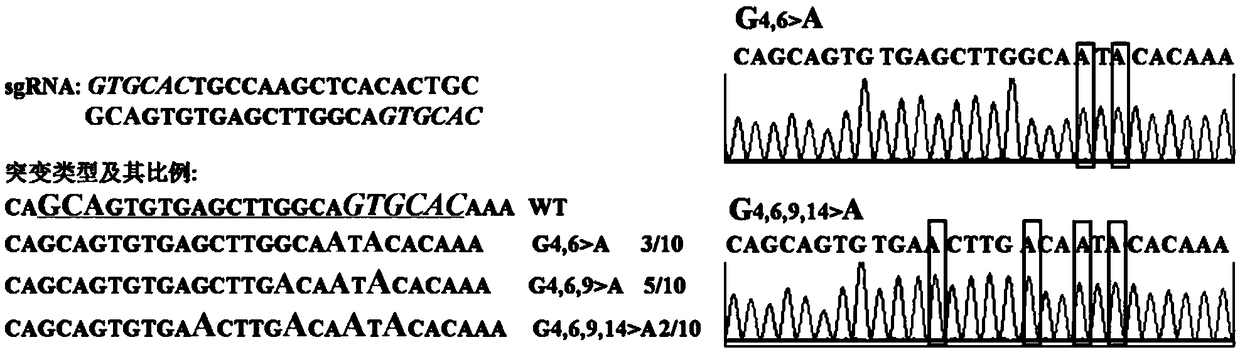
[0090] Example 3: Base C to T substitution of rice endogenous gene OsRLCK185 using pUbi:rBE22
[0091] The transcript sequence and genome sequence of the OsRLCK185 (LOC_Os05g30870) gene were obtained from the MSU / TIGR rice genome database ( http: / / rice.plantbiology.msu.edu / ).
[0092] For the OsRLCK185 gene, the design contains the target nucleotide sequence (SEQ ID No.17: The underline is the restriction site of Alw44I, and the bold is the PAM sequence) primers are as follows: gOsRLCK185-F1 (SEQ ID No. 30: gtgtgtgcactgccaagctcacac) and gOsRLCK185-R1 (SEQ ID No. 31: aaacgtgtgattggcagtgcac). After synthesizing the primers, use T4 polynucleotide kinase to phosphorylate the primers, anneal to form double strands, clone gOsRLCK185-F1 / R1 into the Bsa I restriction site of the pENTR4:sgRNA vector, and sequence to confirm that the inserted fragment is complete. Correct, named pENTR4:sgRNA-gOsRLCK185.
[0093] Other operations are the same as in Example 2.
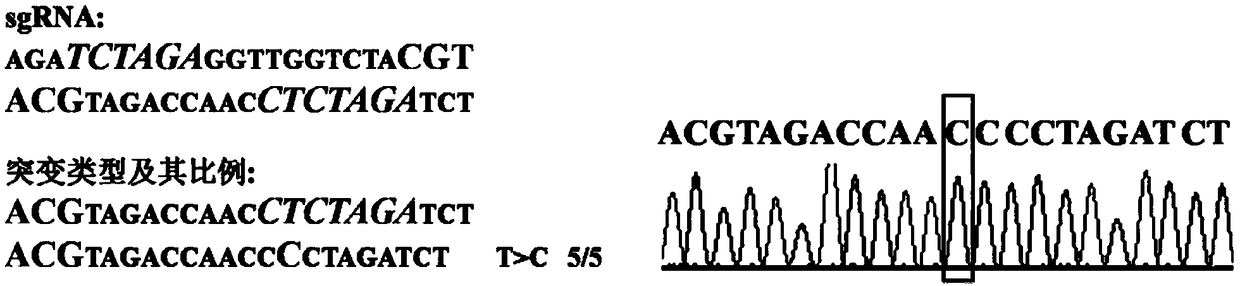
[0094] According to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com