Bacteria cinerea prevention actinomycete strain W15 and actinomycete agent thereof
A technology of botrytis cinerea and actinomycetes, applied in the field of microorganisms, to achieve the effect of reducing and saving costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Identification of the 16S rRNA molecule of the strain
[0024] Actinomycetes strain W15 was activated and cultured on Gaoshi No. 1 plate at a temperature of 28°C. Gaoshi No. 1 medium: soluble starch 19.9-20.1g, sodium chloride 0.49-0.51g, potassium nitrate 0.9-1.1g , dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.49-0.51g, magnesium sulfate 0.49-0.51g, ferrous sulfate 0.009-0.011g, agar 15-20g composition, pH is 7.2-7.4, the above components are distilled to 1000ml with distilled water.
[0025] After culturing for 2-4 days, it was found that the single colony of W15 was round, brick red, and the surface was dry and opaque; the mycelium was thin, the growth was slow, and the colony was dense in texture and had a muddy smell. Gram staining of strain W15 was purple and positive.
[0026] The morphological characteristics of strain W15 were most similar to those of Streptomyces sp. in the identification manual of common bacterial systems.
Embodiment 2
[0030] The invention relates to an actinomycete strain for preventing and treating Botrytis cinerea, the strain is Streptomyces sp., and the name is Actinomyces W15.
[0031] The single colony of the actinomycete strain is round, brick red, and the surface is dry and opaque; the hyphae are thin, the growth is slow, and the colony is dense in texture and has a muddy smell. The Gram staining of the actinomycetes strain is purple, which is positive.
[0032] The actinomycete bacterial agent for preventing and treating Botrytis cinerea prepared by the actinomycete of the present invention. Its active ingredient is at least one of the following (a), (b) and (c):
[0033] (a) actinomycetes described in claim 1;
[0034] (b) the fermentation supernatant of actinomycetes described in claim 1;
[0035] (c) the fermentation culture of actinomycetes described in claim 1.
[0036] The preparation method of the actinomycetes bacterial agent of preventing and treating botrytis cinerea o...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Determination of control effect of detached leaves
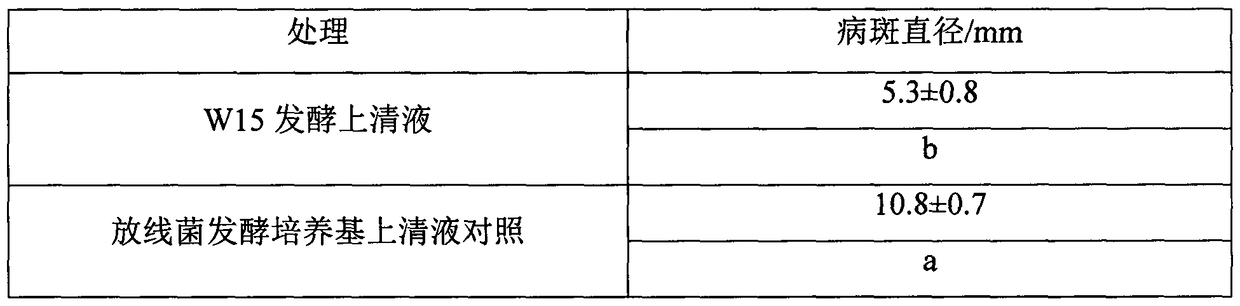
[0048] Cultivate the actinomycetes until the predetermined time for use. Healthy leaves of the same size were collected from neatly growing tomato plants, soaked in 0.5% Tween 20 for about 10 seconds, rinsed gently with sterile water, took them out and dried them in an ultra-clean workbench. After the leaves are dried, soak them in the actinomycetes agent for 1 min, take them out and dry them in the ultra-clean workbench (leaves soaked in the supernatant of the actinomycetes fermentation medium are used as a control), and inoculate the leaves with tomato ash with a diameter of 5 mm. For fungus fungi, each treatment was repeated 8 times. At 25°C, relative humidity 80-90%, and dark conditions for 48 hours, measure the diameter of the lesion and evaluate the control effect. The formula for calculating the control effect is: control effect (%)=(the lesion diameter of the control group−the lesion diameter of the treatmen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com