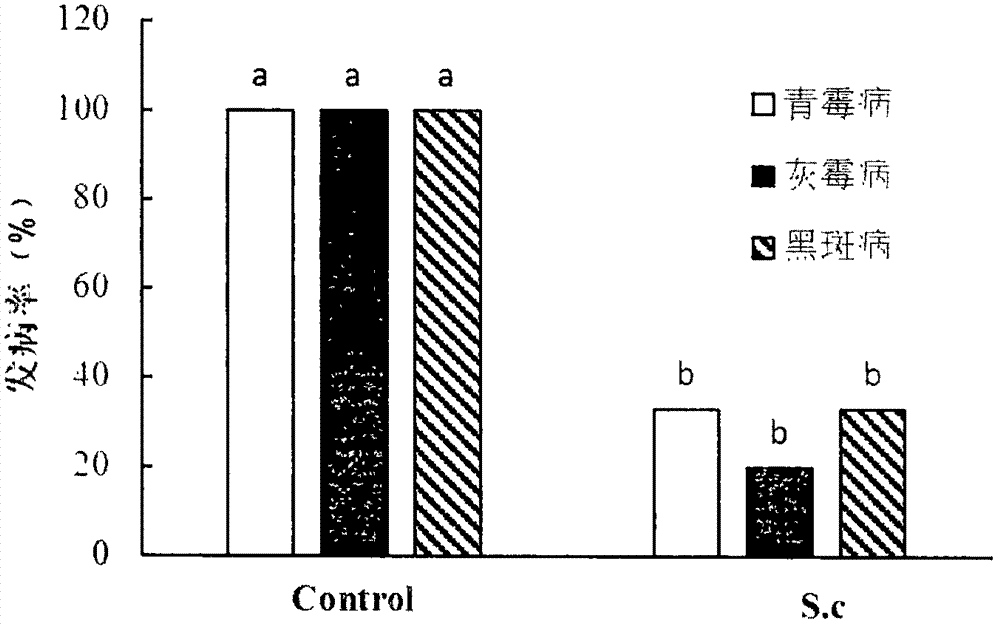
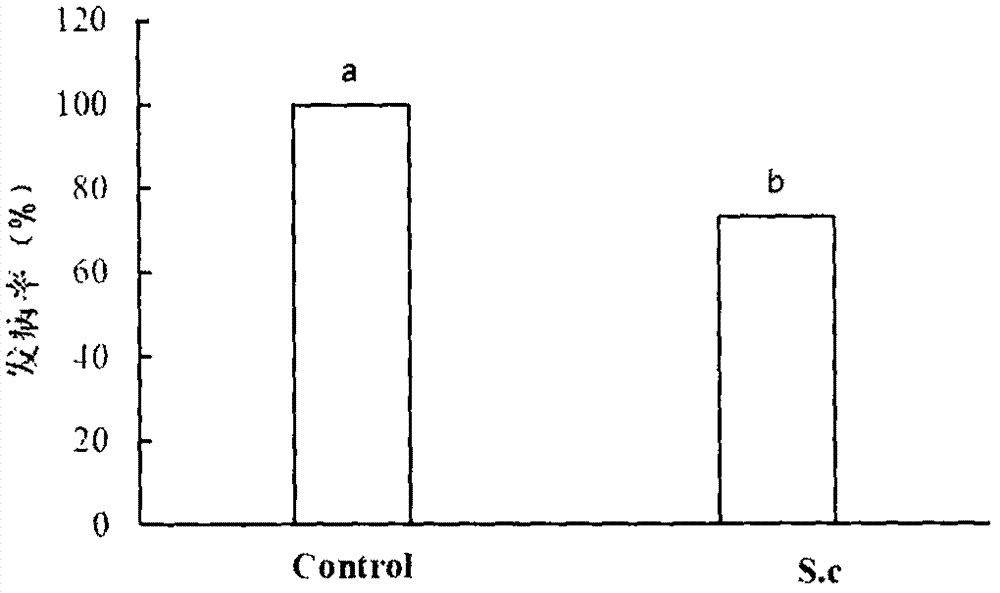
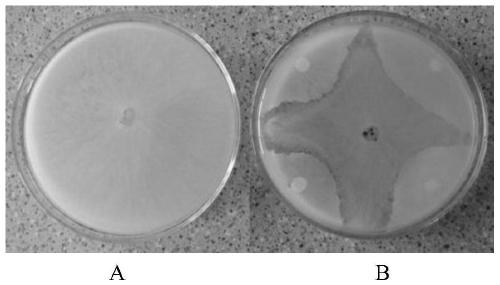
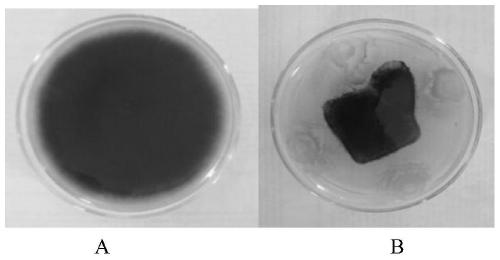
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Donacia cinerea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Donacia cinerea is a species of leaf beetles from a subfamily of Donaciella. It can be found in Czech Republic and Slovakia.
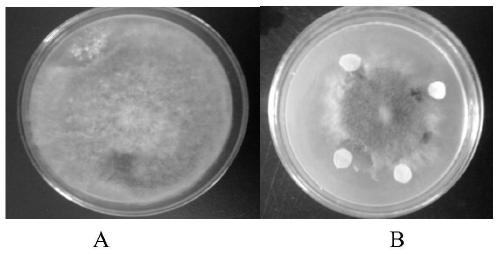
Pseudomonas chlororaphis for preventing and treating crop fusarium disease and applications thereof
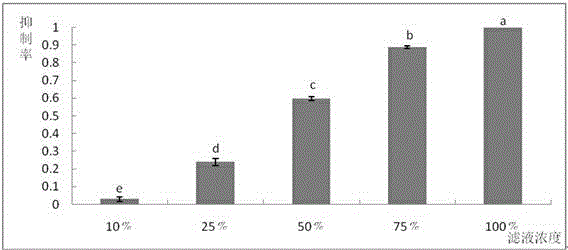
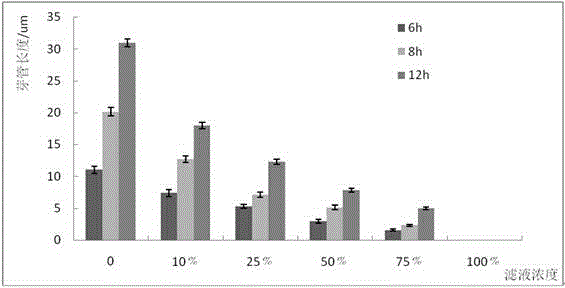
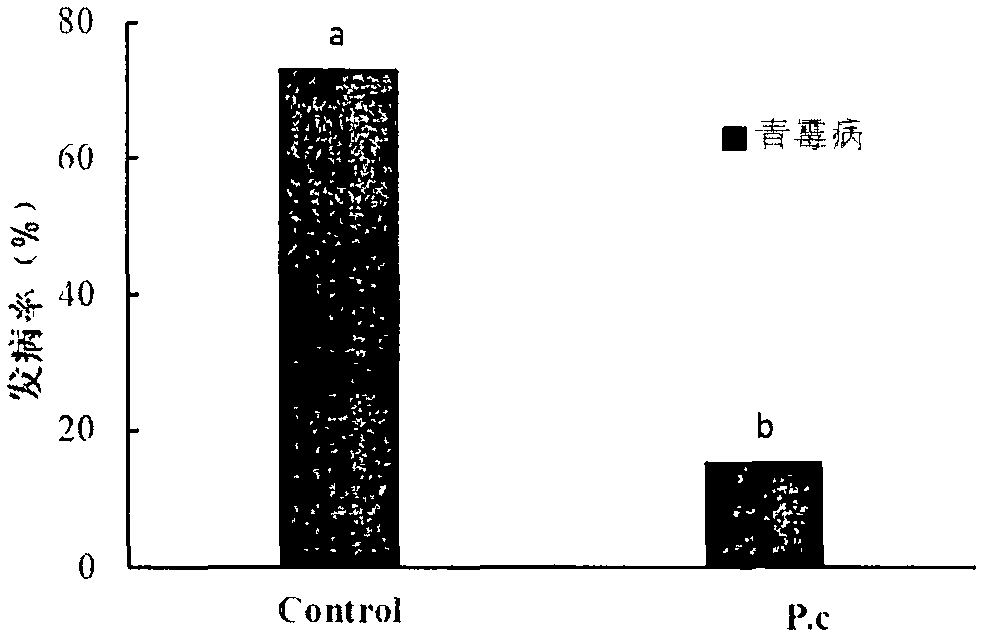
The invention provides pseudomonas chlororaphis for preventing and treating the crop fusarium disease and applications thereof. The preservation number of the pseudomonas chlororaphis is CGMCC No. 7729. The Pcho01 bacterium strain of the pseudomonas chlororaphis has a high effective antagonistic action, is capable of being applied to the preventing and treating wheat scab caused by fusarium, and the preventing and treating efficiency in the field is maintained above 60%. The Pcho01 bacterium strain also has a very good antagonistic action on botrytis cinerea, rice sheath blight fungus, bipolaris maydis, pythium wltmum, rhizopus, and pseudomonas solanacearum, and can be used to prevent and treat the diseases caused by those bacteria mentioned above.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for preventing and treating botrytis cinerea in plants and application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens
InactiveCN107338207APromote colonizationGood biological control effectBiocideBacteriaKnema cinereaPlant disease
The invention relates to bacill us amyloliquefaciens sw17 for preventing and treating botrytis cinerea in plants and an application of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens. The bacterium (the bacillus amyloliquefaciens sw17) is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with preservation number of CGMCC No.14365; and the bacterium can take an inhibitory effect on gray mold of strawberry, gray mold of tomato and gray mold of cucumber caused by botrytis cinerea Pers., with a bacteriostasis rate ranging from 62% to 74%. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens sw17, which is provided by the invention is separated from rhizosphere soil of healthy fruit trees in a demonstration orchard, is free from ecological toxicity, high in safety and good in antibacterial effect, and the bacillus amyloliquefaciens sw17 is simple in culture and short in cycle; and the bacillus amyloliquefaciens sw17 has a quite broad application prospect in biological control of plant diseases.
Owner:MICROBIOLOGY INST OF SHAANXI
Device for rapidly detecting benzimidazole fungicide-resistant botrytis cinerea Pers. based on LAMP
ActiveCN106350588AImprove practicalityGet rid of dependenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenotypeLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
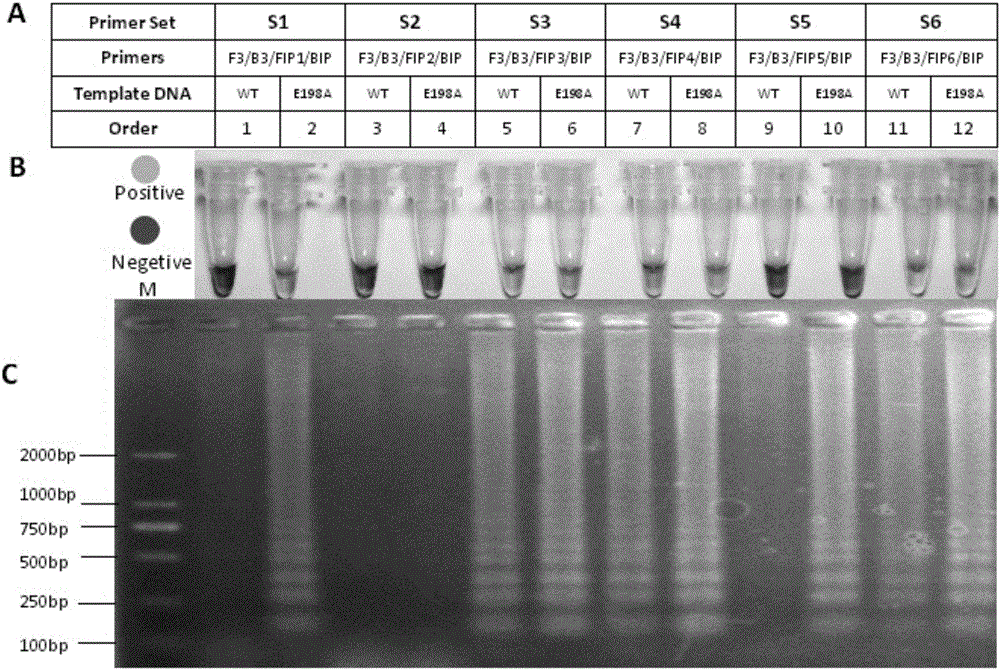
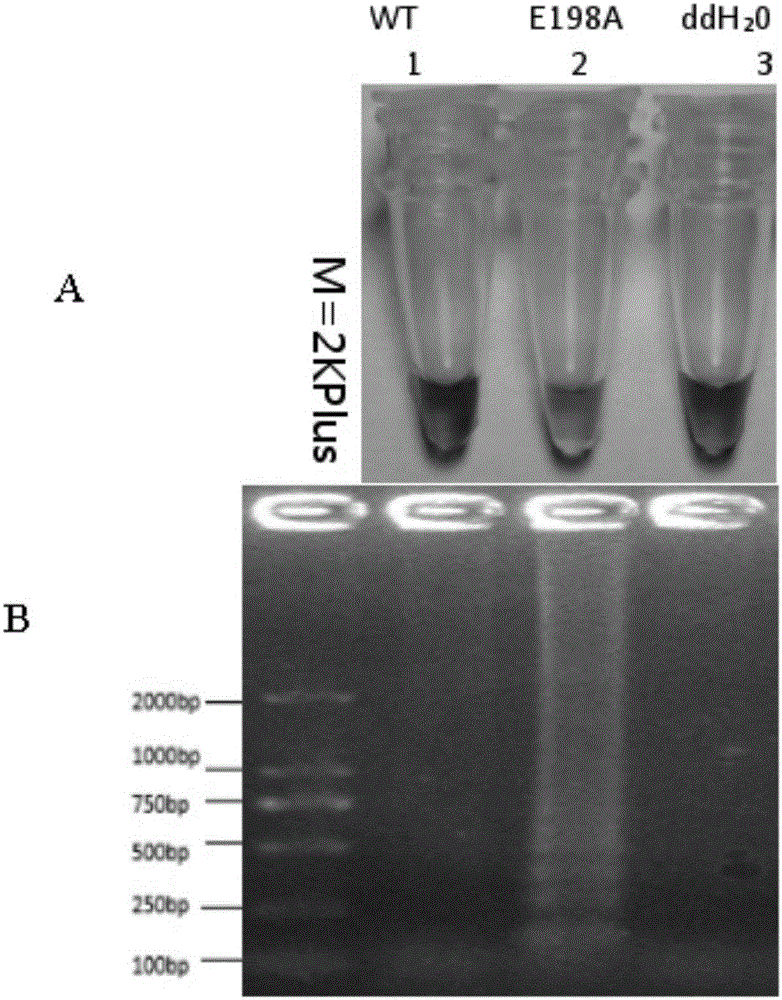
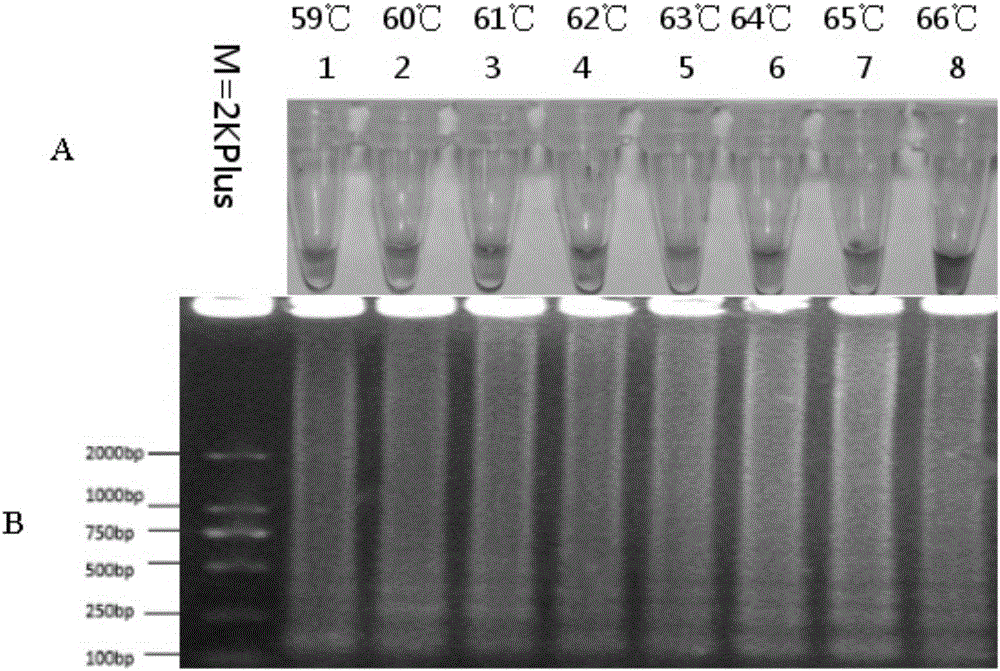
The invention discloses a loop-mediated isothermal amplification primer composition for detecting benzimidazole fungicide E198A genotype-resistant botrytis cinerea Pers.. The LAMP primer composition consists of the following four primers: an F3, a B3, an FIP and a BIP. The primer composition consists of primer groups designed by mismatching a basic group in a mutation region containing a 198 locus of a botrytis cinerea Pers. beta-tubulin gene; loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction is used for detecting the benzimidazole fungicide E198A genotype-resistant botrytis cinerea Pers.. The invention further provides a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for detecting the benzimidazole fungicide E198A genotype-resistant botrytis cinerea Pers. and a kit used thereby.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Botrytis cinerea antagonistic strain and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN106479934AGood inhibitory effectGrowth inhibitionBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesDiffusion methods
The invention belongs to the fields of microbial technology and biological control and particularly relates to bacillus amyloliquefaciens BA-KA4 and a screening method and application thereof. Bacteria are separated from soil, and an agar disk diffusion method is adopted for screening BA-KA4 out of the bacteria, wherein the inhibition ratio of BA-KA4 on cucumber botrytis cinerea is 65%, and BA-KA4 has stable inheritance. Through cultural characteristics, morphology and physiological and biochemical characteristics of the strain in combination with result reanalysis of a 16S rDNA sequence and a gyrB gene sequence, it is preliminarily identified that the strain BA-KA4 is bacillus amyloliquefaciens. The strain is stored with the accession number of CGMCC No.12190 in the Common Microorganism Center of China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The strain has the best control effect on the cucumber botrytis cinerea, a long lasting period and a broad antibacterial spectrum.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF SCI
Broad-spectrum bacteriostatic Lactobacillus plantarum
ActiveCN108220212AEnhanced inhibitory effectBroad-spectrum antibacterialBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesEscherichia coli
Broad-spectrum bacteriostatic Lactobacillus plantarum is disclosed, and the preservation number of the Lactobacillus plantarum MG-1 is CCTCC NO: M2018029. The strain MG-1 and a fermentation broth thereof have obvious inhibitory effects on bacteria and molds, can effectively inhibit grape Botrytis cinerea, grape Coniella diplodiella, Altenaria brassicae, Colletotrichum capsici, Diaporthe Kiwifruit,Capsicum southern blight pathogen, potato southern blight pathogen, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, and has broad-spectrum bacteriostasis.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY23 for controlling postharvest diseases of fruits and preparation and use methods thereof
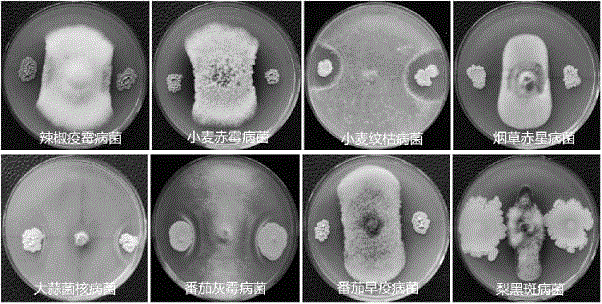
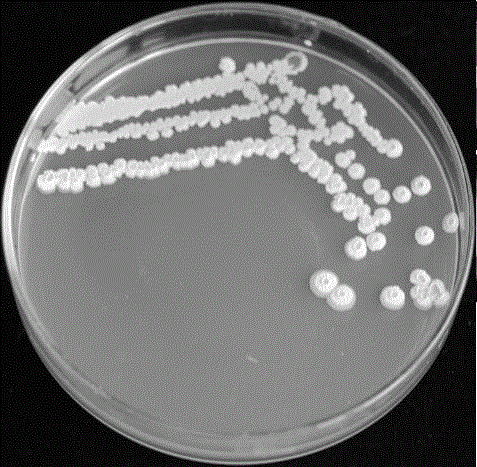
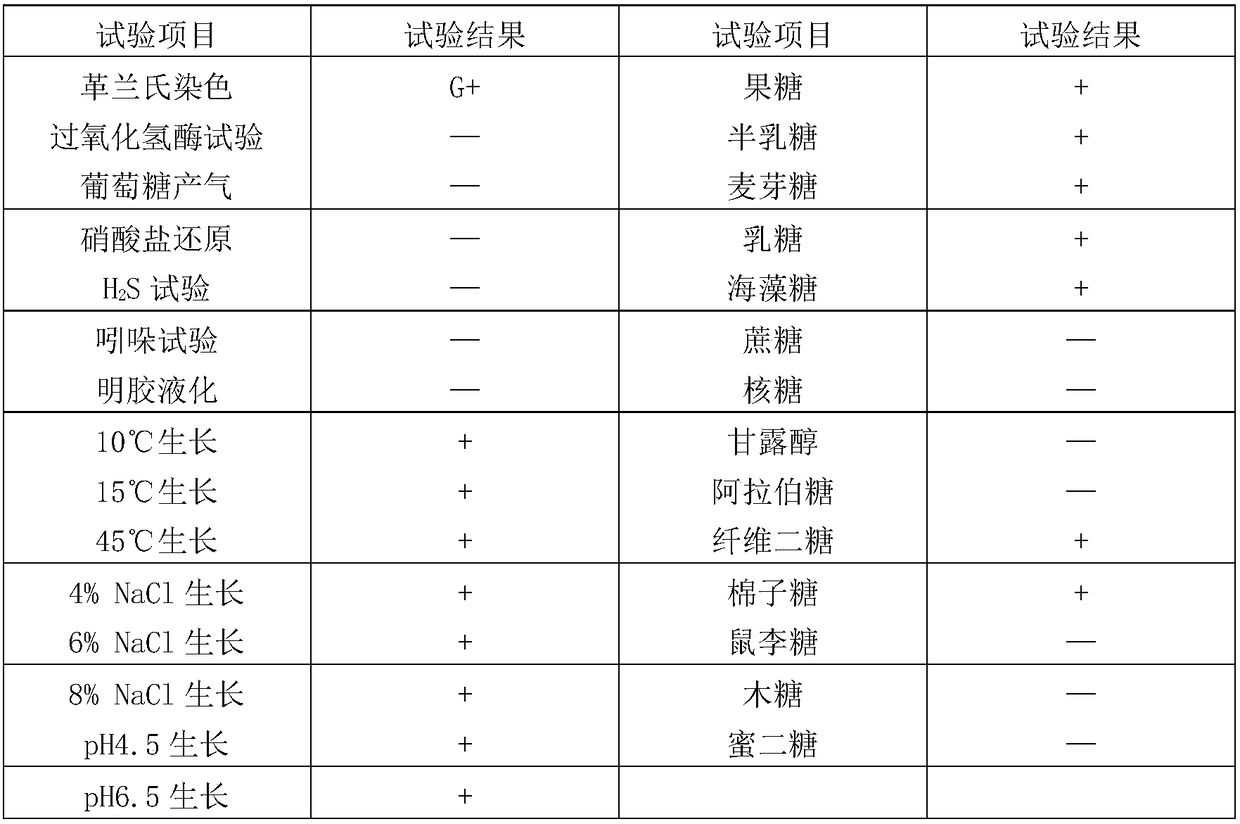
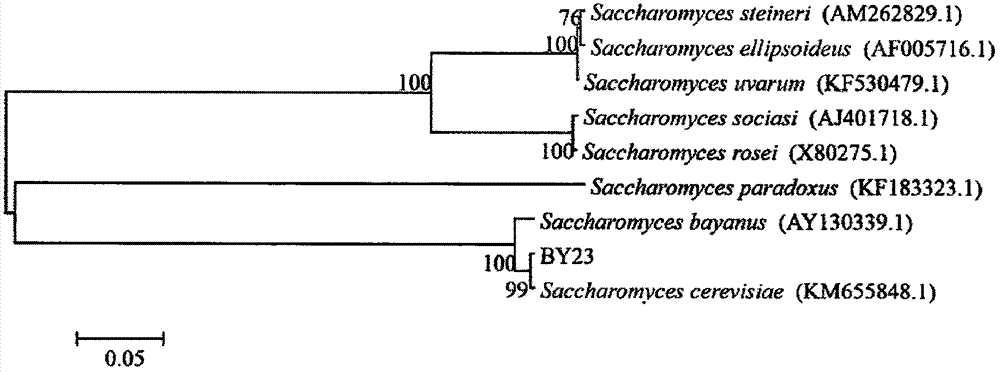
The invention discloses Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY23, with broad bacteriostasis spectrum and stable effect, for controlling postharvest diseases of fruits and a use method and use thereof. The strainhas a collection strain serial number of CGMCC No. 14905 in General Microorganisms Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms. The use method of the saccharomyces cerevisiae comprises the steps: activating the strain, carrying out fermentation culture with YPD, carrying out centrifugation, and preparing a 1*10<8>cell / mL bacterial suspension from thalli and sterile water; placing the fruits such as apples, pears, grapes or oranges into the bacterial suspension, carrying out soaking for 30 seconds, then, taking out the fruits, and drying the fruits in the air; and placing the fruits into a fresh-keeping box, and carrying out storage at normal temperature. The saccharomyces cerevisiae strain can be used for simultaneously controlling blue molds, Botrytis cinerea and black spot of apples, Botrytis cinerea of pears, black spot, Fusarium molds, anthrax and Phoma glomerata of grapes and blue molds of oranges, and loss caused by the postharvest diseases is reduced, sothat the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain has a very good application prospect.
Owner:北京华康信使科技有限公司
Bacillus subtilis strain NH-6 and application thereof
ActiveCN110423707AThe cultivation method is simpleFast growthBiocideBacteriaHigh resistanceMeloidogyne incognita
The invention relates to the field of bacillus, in particular to a bacillus subtilis strain NH-6 and application thereof. The bacillus subtilis strain NH-6 is deposited at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the preservation number of CGMCC 17815. The bacillus subtilis strain NH-6 has the advantages such as simple culture method, high growth rate, wide antibacterial spectrum and high resistance to stress. A biological control preparation prepared by the bacillus subtilis strain NH-6 can be used as a biological pesticide or a biological fertilizer to prevent and controlroot-knot nematode diseases and various plant pathogenic fungi including alternaria brassicae, banded sclerotial blight, botrytis cinerea and the like.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
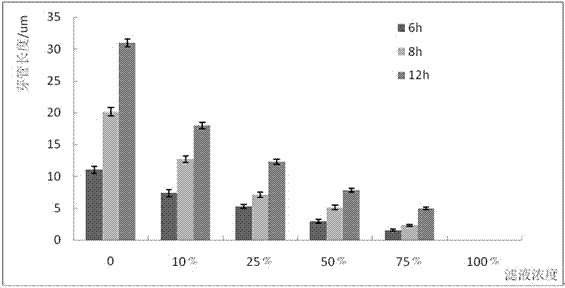
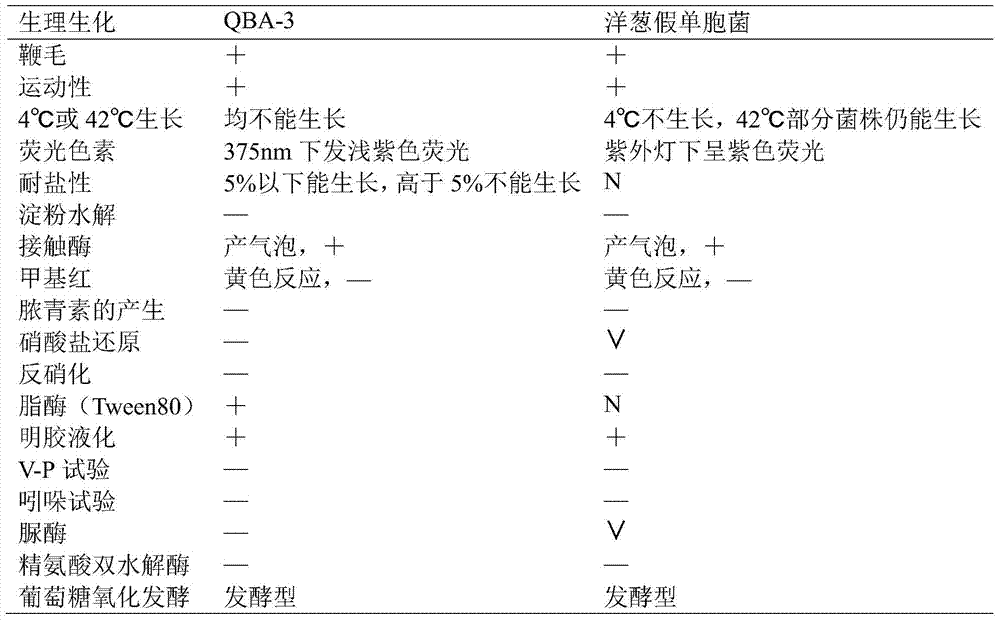
Pseudomonas cepacia strain QBA-3 having function of inhibiting botrytis cinerea and application thereof
The invention discloses a pseudomonas cepacia strain QBA-3 having the function of inhibiting botrytis cinerea and an application thereof. The pseudomonas cepacia strain QBA-3 is obtained through screening, the class name of the QBA-3 is Pseudomonas cepacia, the QBA-3 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation serial number of the QBA-3 is CCTCC M2015402. A botrytis cinerea spore germination experiment, a germinal tube elongation experiment and detached leaf experiment prove that the pseudomonas cepacia strain QBA-3 has the strong inhibiting function on the botrytis cinerea, the pseudomonas cepacia strain QBA-3 can be made into a biocontrol agent preventing the botrytis cinerea and has good market application prospects.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Pichia cactophila capable of effectively controlling fruit postharvest diseases as well as preparation and using method of pichia cactophila
ActiveCN108118004ABroad antibacterial spectrumPromote growthFungiFruit and vegetables preservationDiseasePichia cactophila
The invention discloses a pichia cactophila strain BY35 for effectively controlling fruit postharvest diseases with advantages of wide antibacterial spectrum and stable effect and a using method of pichia cactophila. The strain has a strain collection number of CGMCC No. 14909 in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The using method of the pichia cactophila strain comprises thefollowing steps: activating the strain, performing fermentation culture by YPD, centrifuging, and preparing the culture into bacterium suspension of 1*10<8>cells per mL with sterile water; adding apples, pears, grapes or citrus and the like into the bacterium suspension, soaking for 30 seconds, taking out the fruits, and airing; and putting into a preservation box, and storing at a normal temperature. The pichia cactophila is capable of simultaneously controlling apple penicillium disease and botrytis cinerea, penicilliosis and botrytis cinerea of pear fruits and fusarium wilt disease and anthracnose of grapes as well as blue mold of citrus fruits. Losses caused by the postharvest diseases are decreased, and the strain has excellent application prospects.
Owner:山东凯普菲特生物科技有限公司
Abnormal pichia anomala and application thereof
The invention discloses an abnormal pichia anomala and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of micrograms. The strain of the abnormal pichia anomala disclosed by the invention is YPL6, with the preservation number of CGMCC No.8041. The abnormal pichia anomala YPL6 and a metabolite product of the pichia anomala YPL6 have the inhibition function on peach postharvest monilinia fructicola, apple postharvest botrytis cinerea, apple postharvest penicillium italicum and pear postharvest penicillium italicum, and have the inhibition function on peach postharvest brown rot, apple postharvest botrytis, pear postharvest penicilliosis and apple postharvest penicilliosis.
Owner:北京莱万生物技术有限公司
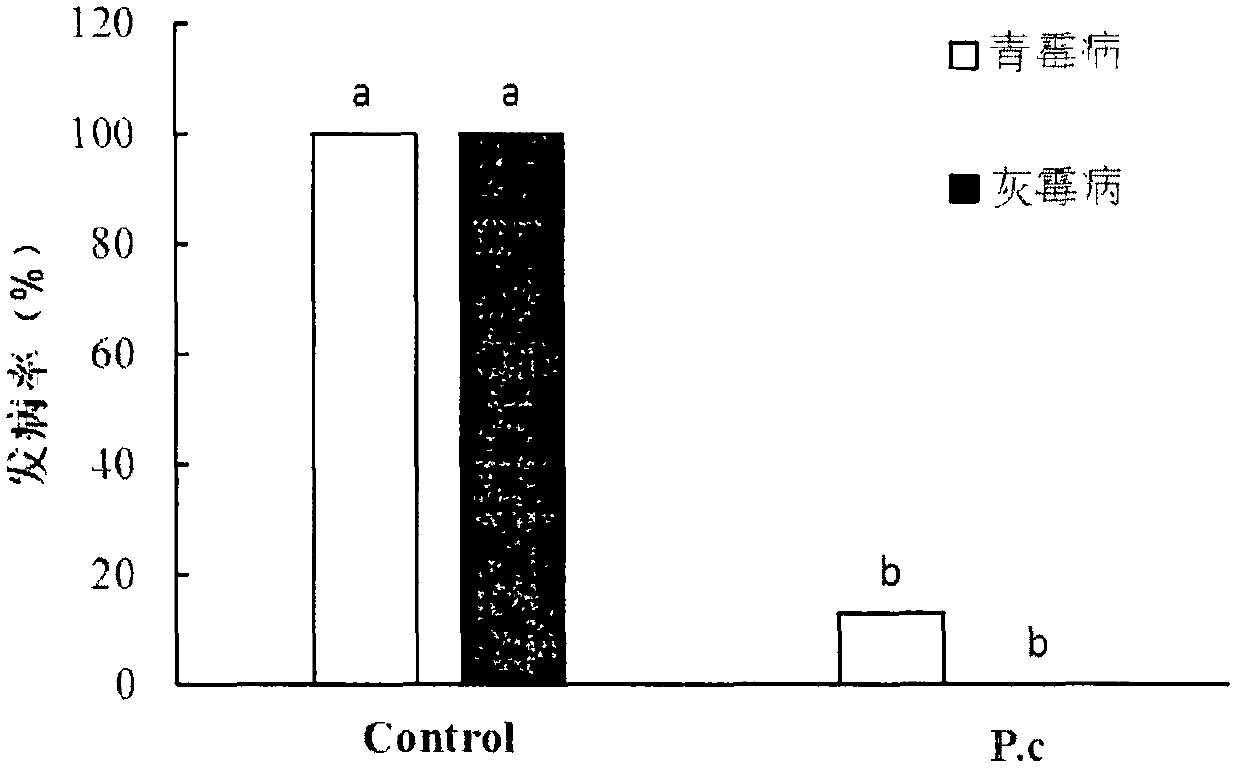
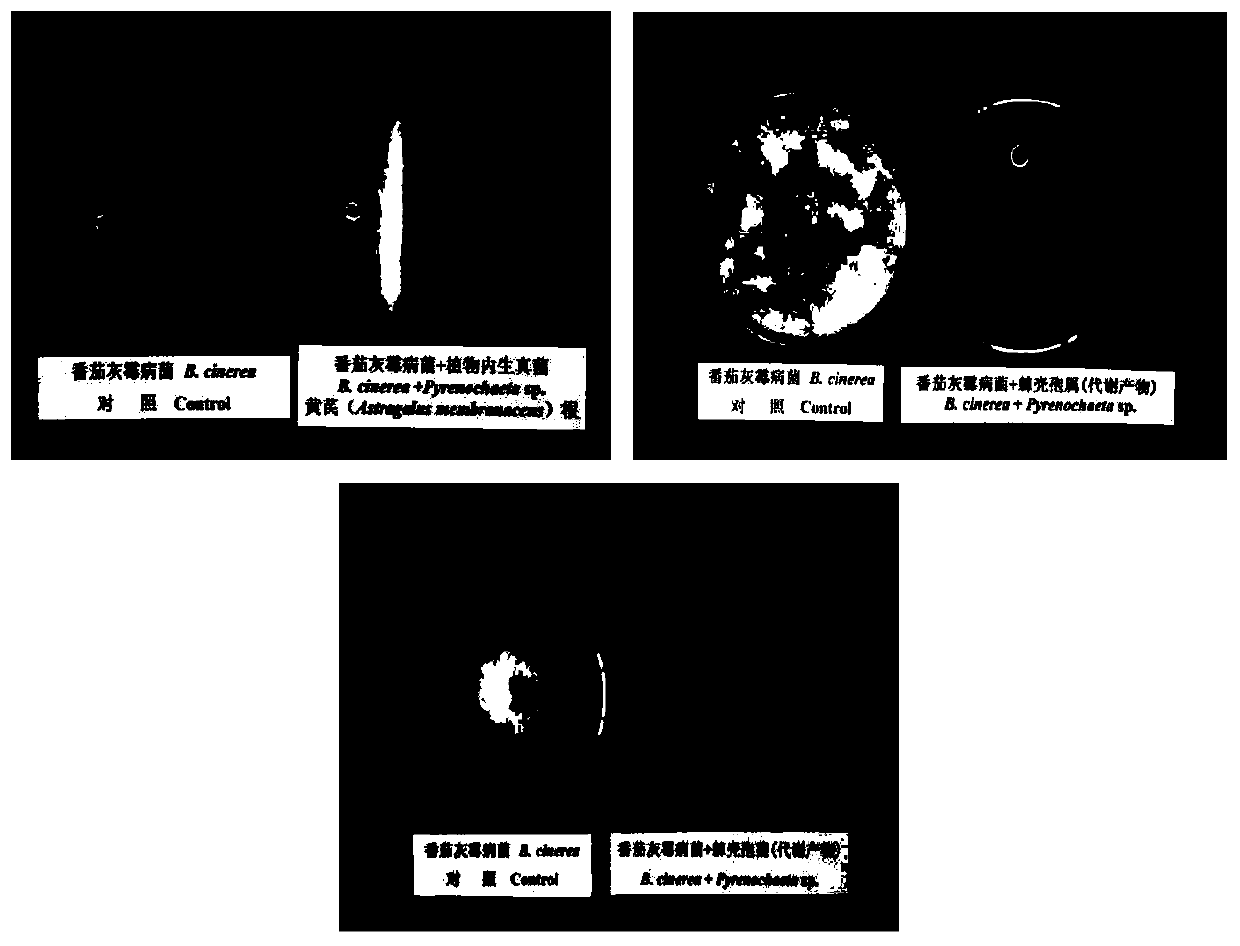
Radix astragali root source pyrenochaeta for efficiently inhibiting botrytis cinerea and application for radix astragali root source pyrenochaeta
ActiveCN110551637AEnhanced inhibitory effectLesion size works wellBiocideFungiMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention discloses radix astragali root source pyrenochaeta for efficiently inhibiting botrytis cinerea and application for the radix astragali root source pyrenochaeta and relates to the technical field of biology. A strain is named as pyrenochaeta nobilis in classification, is named as pyrenochaeta SFJ12-R-5, is deposited in General Microbial Center for China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CGMCC) with a preservation number being CGMCC No.17766 and a preservation date being 31 May 2019, can be used for inhibiting the botrytis cinerea, and thus providing an environmental-friendly and efficient biological control method to prevention and treatment of the botrytis cinerea.
Owner:黑龙江省农业科学院植物保护研究所
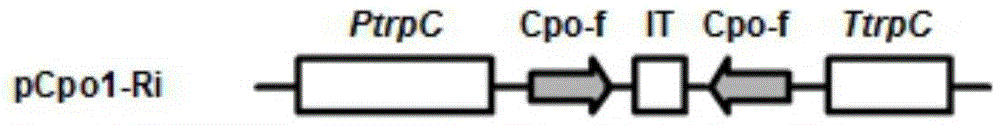
Botrytis cinerea gene BcCpo1 relative to pathogenicity and application of botrytis cinerea gene BcCpo1
InactiveCN105483143AReduce pathogenicityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesAntifungalAmino acid composition
The invention provides a botrytis cinerea gene BcCpo1 relative to pathogenicity and application of the botrytis cinerea gene BcCpo1, and belongs to the technical field of microbiological genetic engineering. The DNA sequence of the gene BcCpo1 sourced from botrytis cinerea and used for controlling pathogenicity is shown in SEQ ID No:1, and comprises 1074 nucleotides. The amino acid sequence of protein coded by the gene BcCpo1 is shown in SEQ ID No:2, and comprises 339 amino acids. The gene BcCpo1 can be applied to the field of gene engineering of plant botrytis cinerea-resisting gray molds. Deletion, mutation or modification is conducted on the protein coded by the gene BcCpo1 used for controlling the pathogenicity of botrytis cinerea to ensure that the pathogenicity of protein is flawed, and the flawed protein can be applied to design and screening of antifungal medicaments while serving as a target.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method and application of hypocrellin A in inhibiting botrytis cinerea of tomatoes
InactiveCN106259334APlay an inhibitory roleInhibitory activityBiocideFungicidesMicroorganismDonacia cinerea
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbes and relates to a method and application of hypocrellin A in inhibiting botrytis cinerea of tomatoes. The method comprises the step of contact of a hypocrellin A solution with botrytis cinerea of tomatoes and / or an object infected with botrytis cinerea of tomatoes; and when the hypocrellin A solution is in contact with the botrytis cinerea of tomatoes and / or object infected with the botrytis cinerea of tomatoes, the botrytis cinerea of tomatoes and / or object infected with the botrytis cinerea of tomatoes is irradiated under light intensity of 12000LX for 10-24h. The invention provides a nontoxic and nuisance-free method for inhibiting the botrytis cinerea of tomatoes.
Owner:胡莉莉
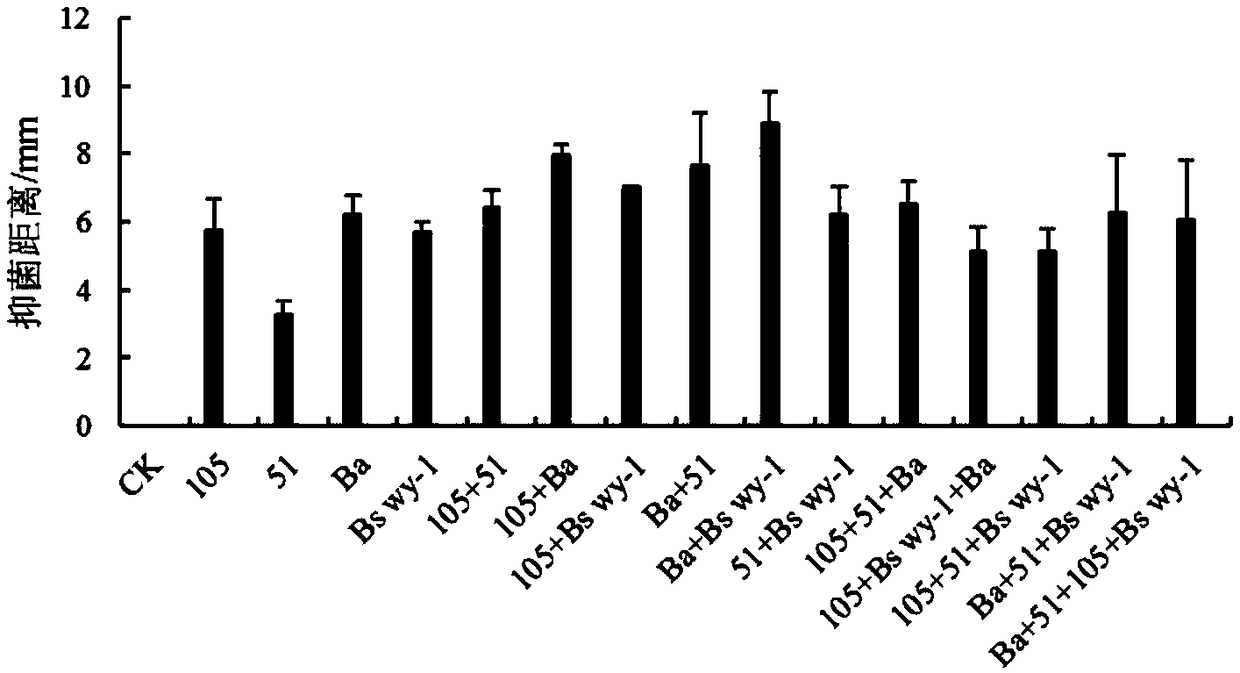
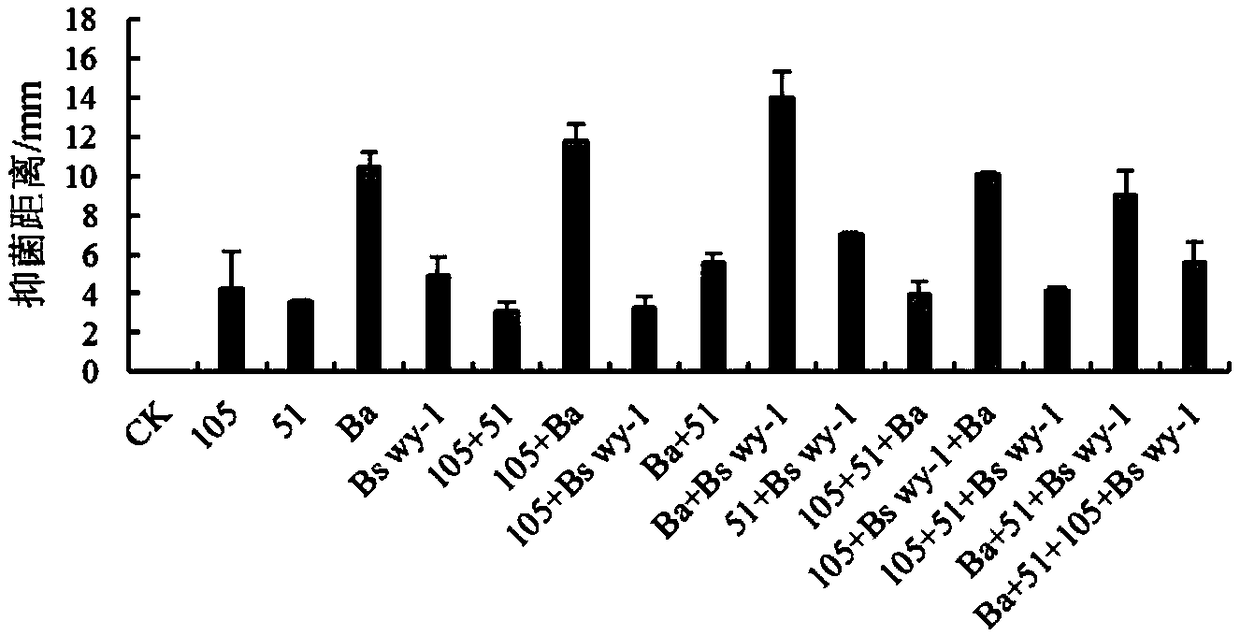
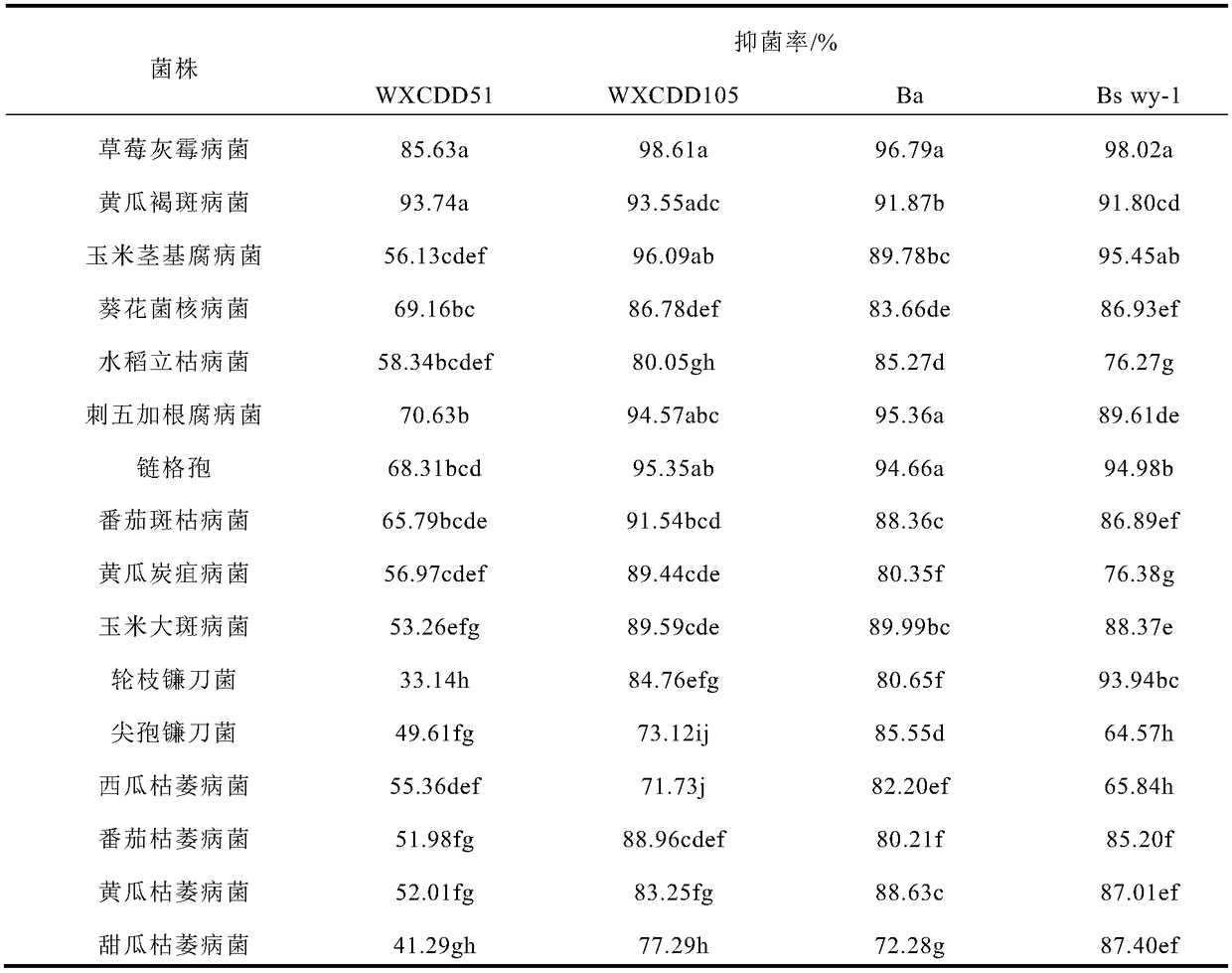
Biocontrol microbial inoculum composition for controlling gray mold and leaf mold of tomatoes
The invention discloses a biocontrol microbial inoculum composition for controlling gray mold and leaf mold of tomatoes, and belongs to the field of biocontrol of the gray mold and the leaf mold of the tomatoes. The compound biocontrol microbial inoculum composition comprises a bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba strain and a bacillus sp Bs wy-1 strain, wherein the microbial inoculum composition comprising the bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba strain and the bacillus sp Bs wy-1 strain according to a mass ratio of 1:3 has the highest rate of inhibiting gray mold bacteria; the microbial inoculum composition obtained by mixing the bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba strain and the bacillus sp Bs wy-1 strain according to a mass ratio of 3:1 has the highest rate of inhibiting leaf mold bacteria. The biocontrolmicrobial inoculum composition has a significant preventive or therapeutic effect on both the gray mold and the leaf mold of the tomatoes, and the disease preventing effect thereof is significantly better than that of a single strain and that of a combination of other strains.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof. The strain number of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens is MH71, and the register number of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No.6978. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens has obvious inhibition effect on multiple pathogenic fungi such as botrytis cinerea, fusarium disease, brown rot, root rot and colletotrichum acutatum on fruits and vegetables and pathogenic bacteria such as black rot of Chinese cabbage, brown blotch diseases of oyster mushroom and angular leaf spot of cucumber. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens MH71 is fast in breeding speed, can be artificially cultured and has strong stress resistance capacity and important significance for prevention and treatment of soil-borne diseases such as cabbage wilt disease caused by fungi.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
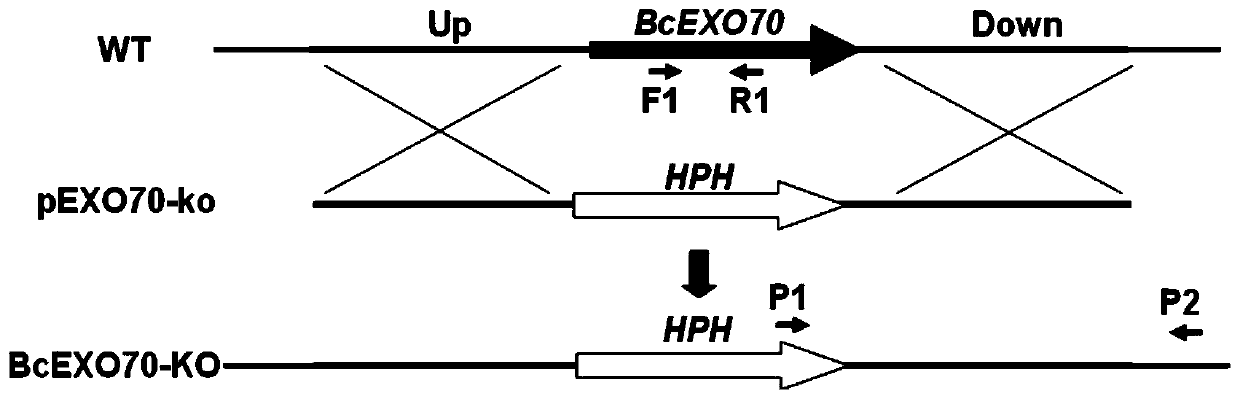
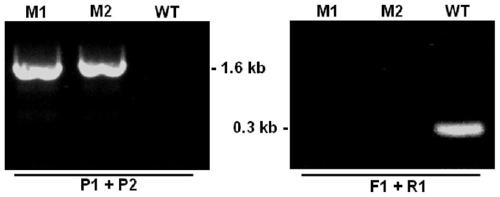
Pathogenicity-related botrytis cinerea gene BcEXO70 and application thereof
InactiveCN109868282AReduce pathogenicityStable introduction of DNADepsipeptidesBiotechnologyMicrobial genetics
The invention discloses a pathogenicity-related botrytis cinerea gene BcEXO70 and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial genetic engineering. The pathogenicity-controlledgene BcEXO70 from botrytis cinerea has a DNA sequence as shown in SEQ ID No:1 and consists of 2067 nucleotides. An amino acid sequence of a protein coded by the BcEXO70 gene is shown as SEQ ID No:2,and the protein is composed of 654 amino acids. The BcEXO70 gene can be applied to the field of plant botrytis cinerea resistance genetic engineering; the gene BcEXO70 for controlling the pathogenicity of the botrytis cinerea is knocked out, so that the pathogenicity of the gene BcEXO70 is defective, and the gene BcEXO70 can be applied to reducing the pathogenicity of the botrytis cinerea.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
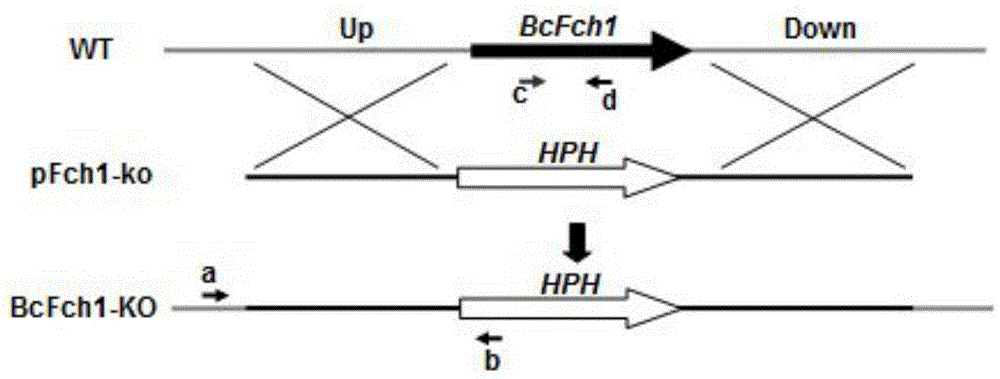
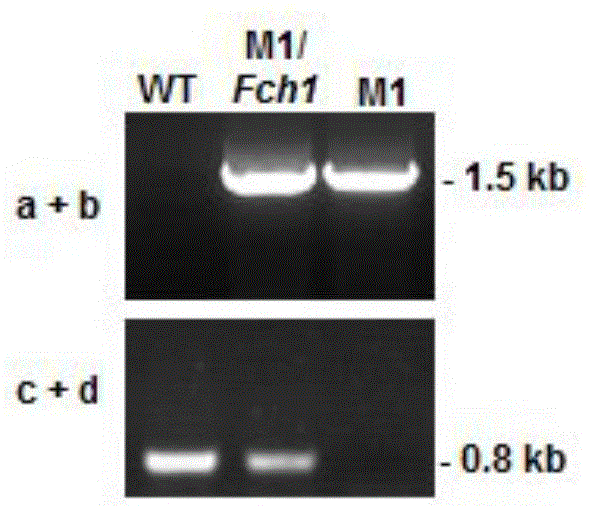
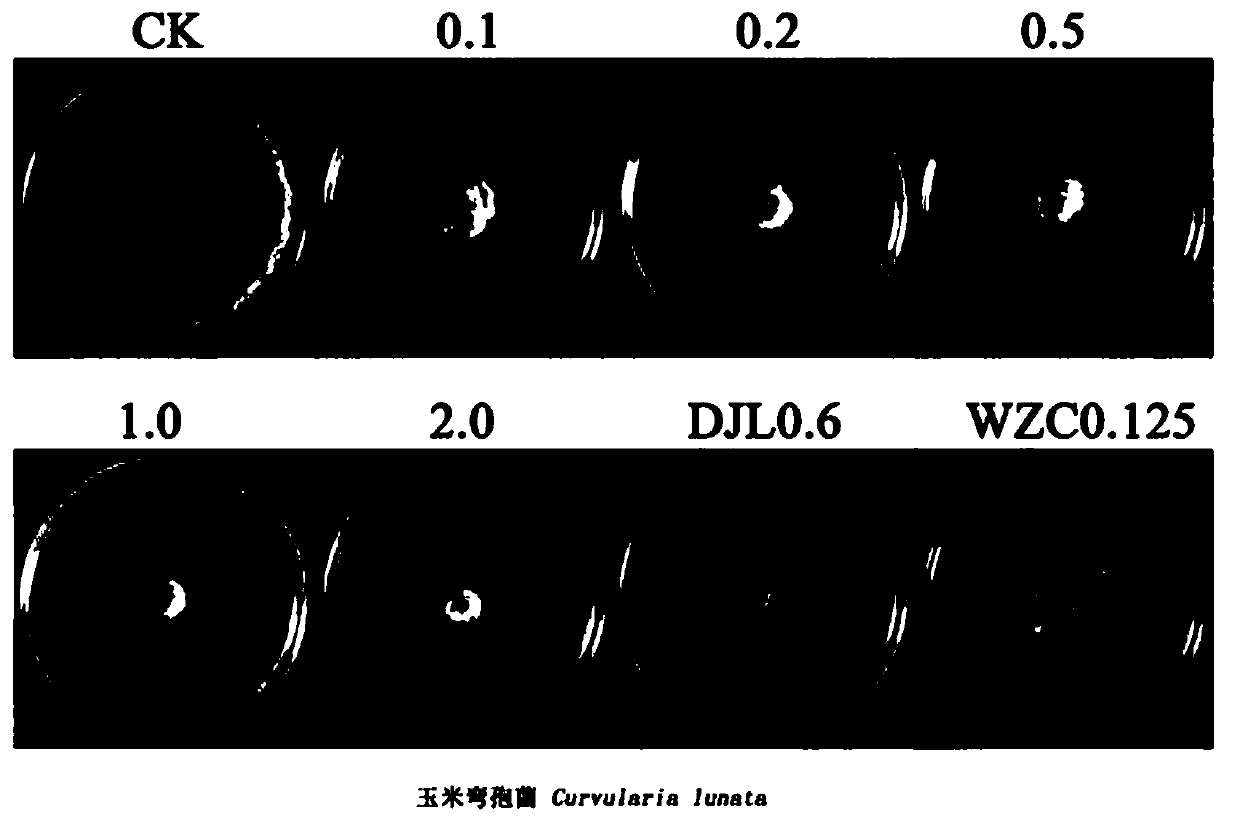
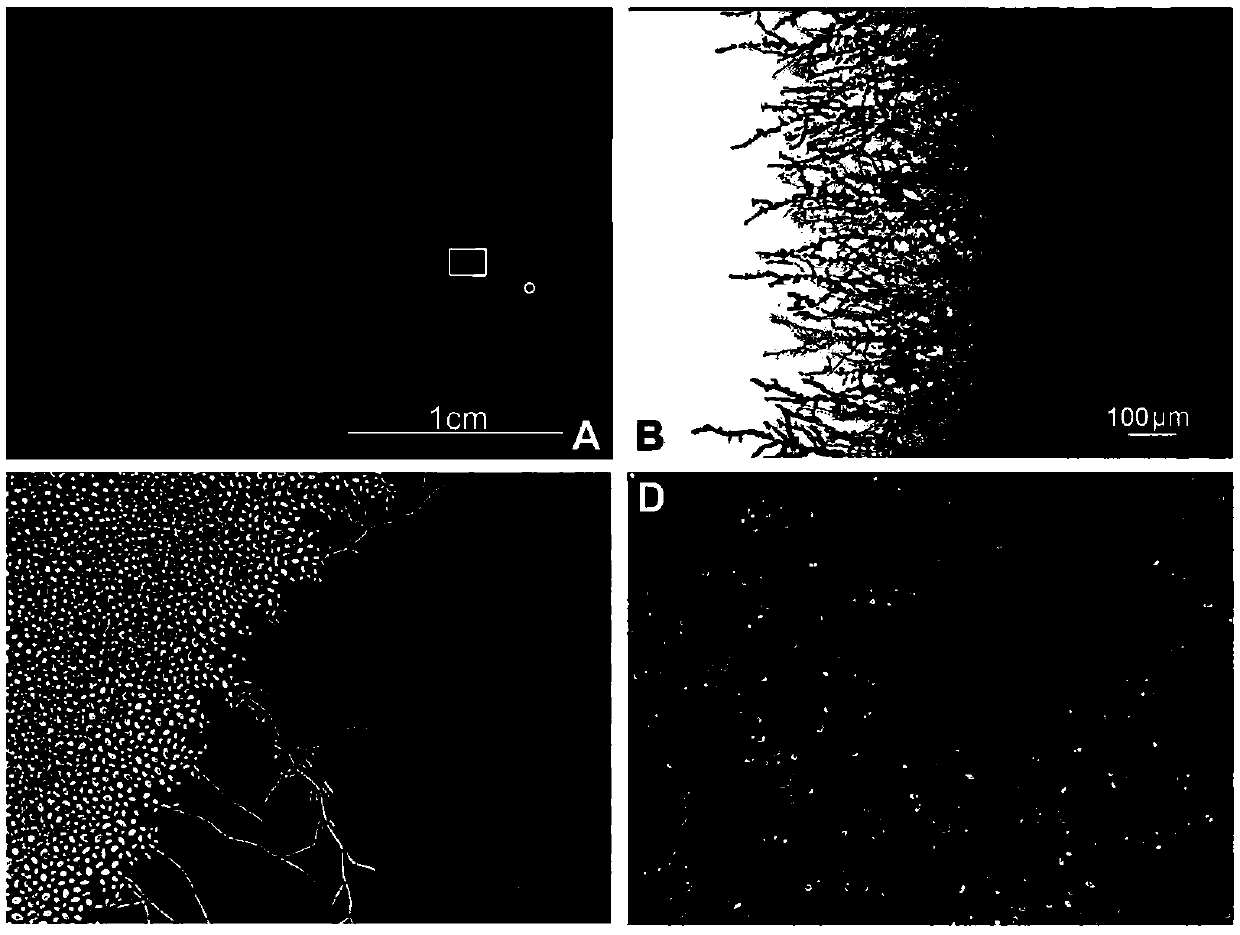
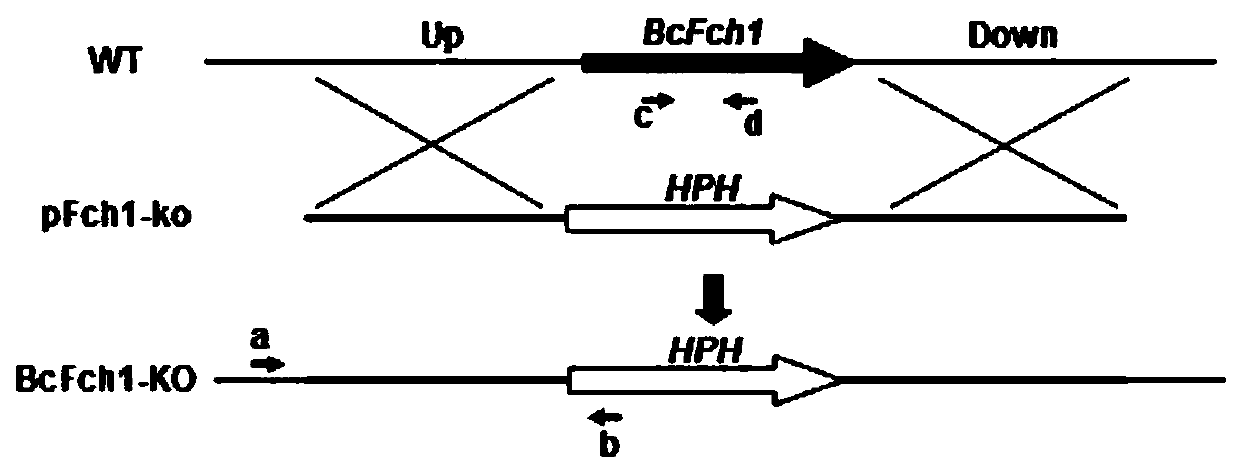
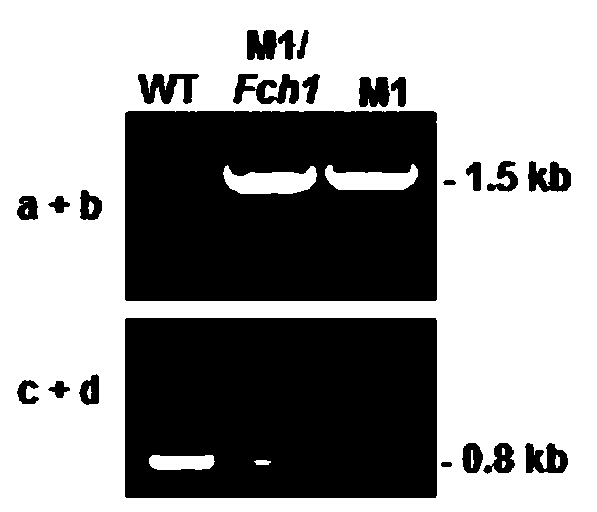
Botrytis cinerea gene BcFch1 relative to pathogenicity and application of botrytis cinerea gene BcFch1
The invention provides a botrytis cinerea gene BcFch1 relative to pathogenicity and application of the botrytis cinerea gene BcFch1, and belongs to the technical field of microbiological genetic engineering. The DNA sequence of the gene BcFch1 sourced from botrytis cinerea and used for controlling pathogenicity is shown in SEQ ID No:1, and comprises 1409 nucleotides. The amino acid sequence of protein coded by the gene BcFch1 is shown in SEQ ID No:2, and comprises 435 amino acids. The gene BcFch1 can be applied to the field of gene engineering of plant botrytis cinerea-resisting gray molds. Deletion, mutation or modification is conducted on the protein coded by the gene BcFch1 used for controlling the pathogenicity of botrytis cinerea to ensure that the pathogenicity of protein is flawed, and the flawed protein can be applied to design and screening of antifungal medicaments while serving as a target.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Application of posaconazole to preparation of bactericide for controlling plant pathogenic bacteria
PendingCN109673650AStrong inhibitory activityConforms to residual toxicity criteriaBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyAlternaria helianthi
The invention discloses application of posaconazole to preparation of a bactericide for controlling plant pathogenic bacteria. Determination of indoor drug sensitivity proves that the posaconazole hasgood activity in inhibiting main diseases of important food crops, including wheat scab-causing fusarium graminearum, rice blast-causing magnaporthe oryzae, sheath blight-causing rhizoctonia cerealisand corn leaf spot-causing maize curvularia, has good activity in inhibiting botrytis cinerea, physalospora piricola, valsa ceratosperma and alternaria tenuissima, and has relatively good activity ininhibiting soil-borne diseases such as fusarium oxysporum, which are extremely difficult to control in agricultural production, and the bacteriostatic activity of the posaconazole is even superior tothose of the conventional bactericides carbendazim and tebuconazole. The invention proposes screening of the green small molecular compound posaconazole from the three-dimensional structure of targetprotein for the first time, and the posaconazole is applied to control of important plant diseases in the agricultural production and has a broad market application prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Biocontrol bacterium candida intermedia C410 for preventing and controlling gray mold and suspending agent and application thereof
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A yeast-like fungus for suppressing postharvest diseases of fresh fruit and its application
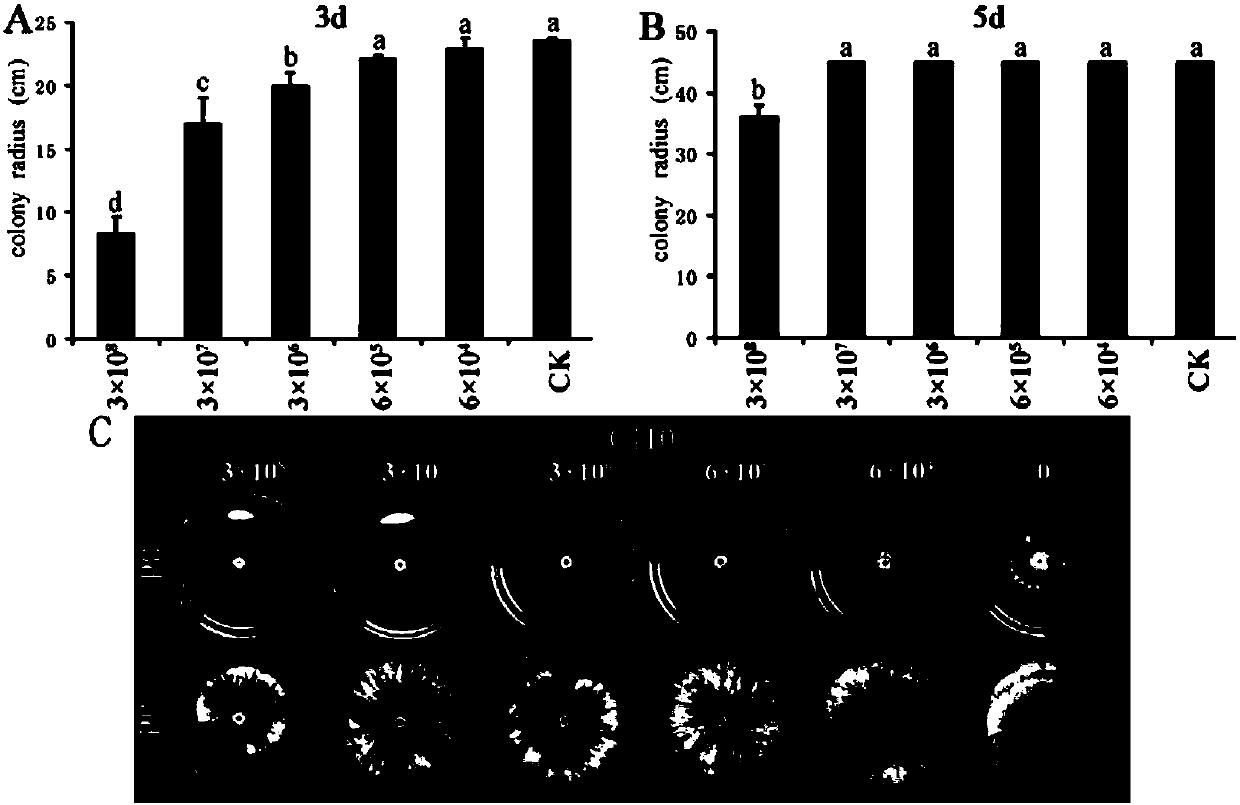
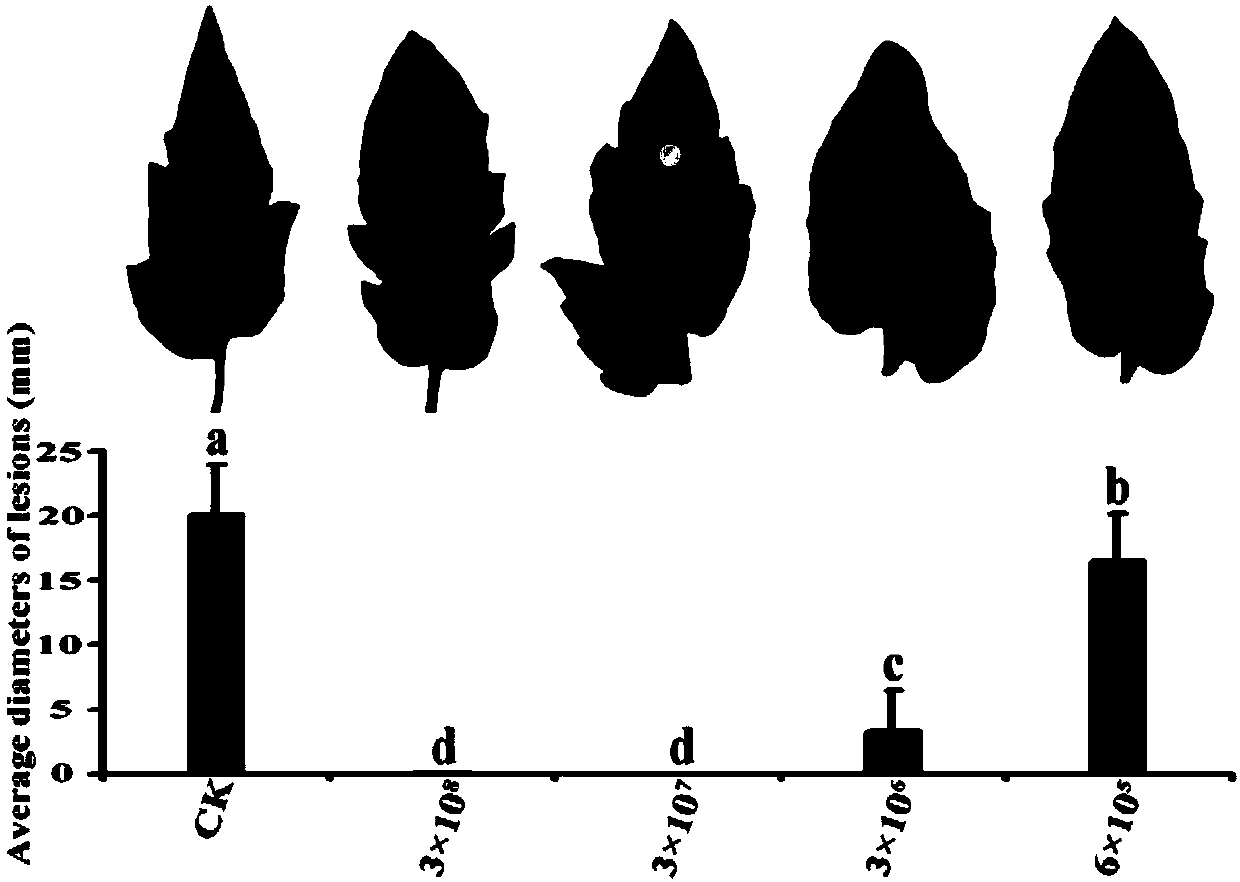
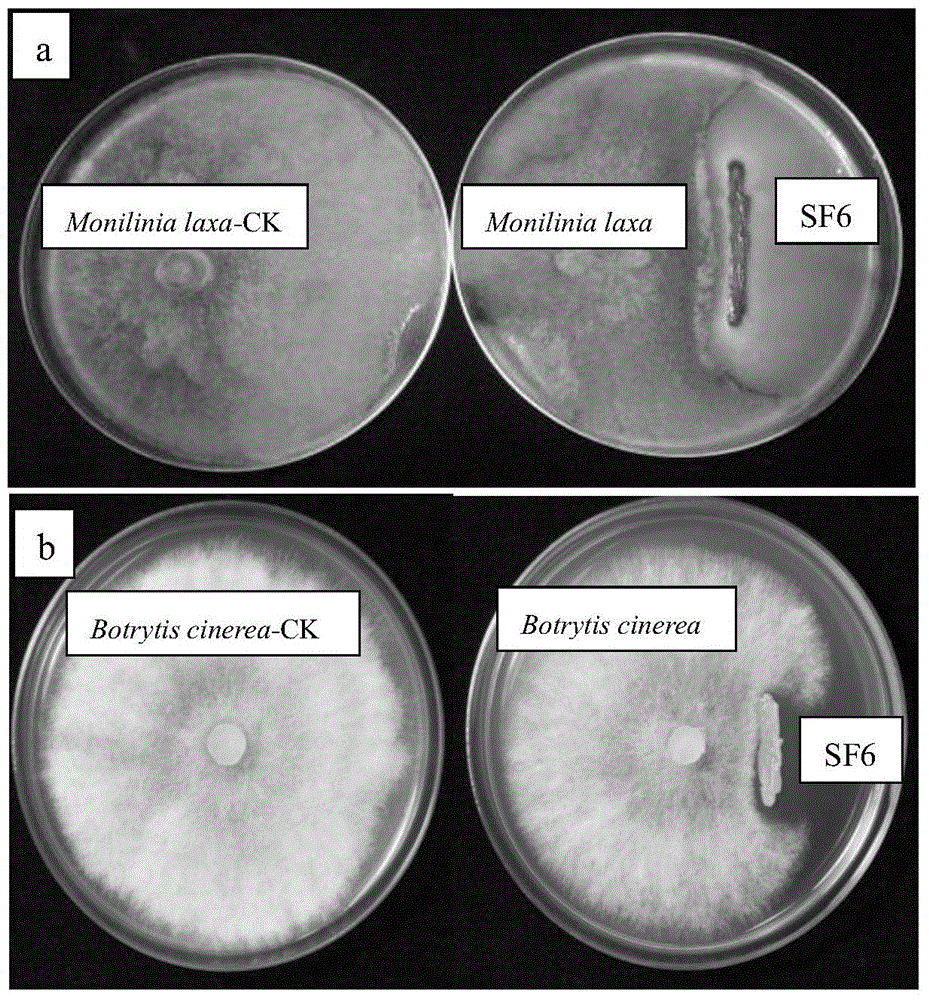
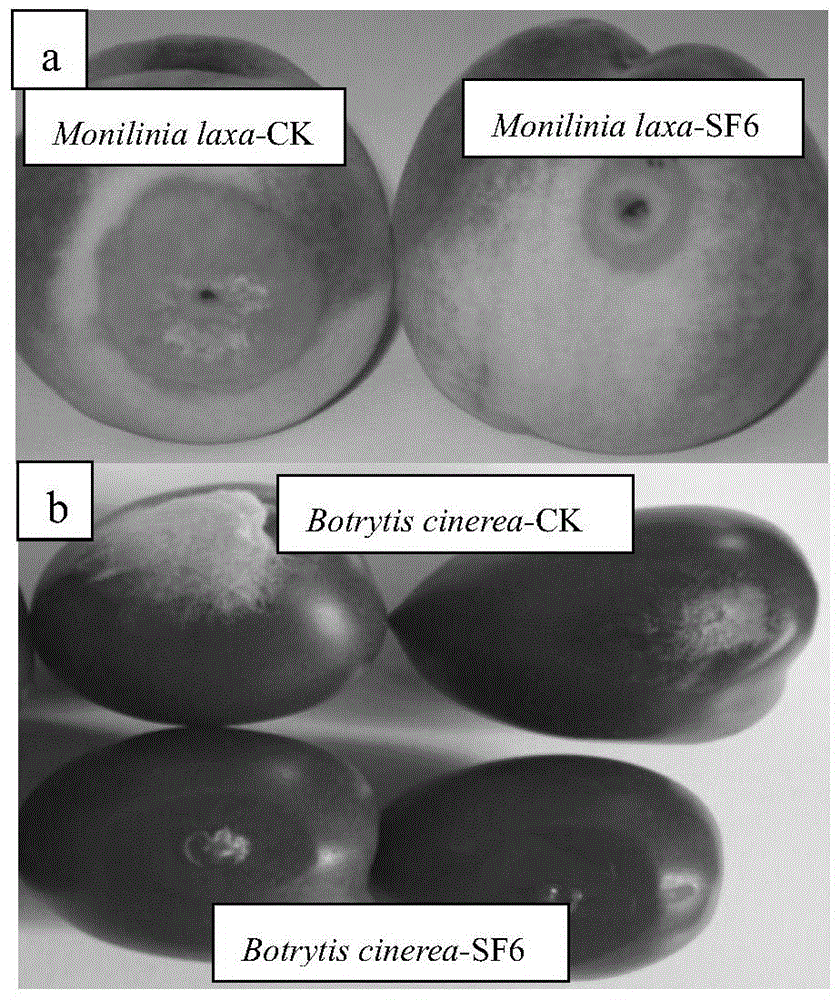
The invention discloses pseudozyma fusiformata for inhibiting diseases after fresh fruit collection and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of microorganism application. The pseudozyma fusiformata SF6 disclosed by the invention has the preservation number of CGMCC No.8577, has inhibiting effects on monilinia after peach collection and botrytis cinerea after tomato collection, has inhibiting effects on the brown rot after peach collection and the grey mould after tomato collection, and has the most obvious inhibiting effect on the monilia, and the diameter of the inhibition zone is more than 15mm. The pseudozyma fusiformata has stable, efficient and broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties, and can be applied to prevention and treatment of the germs or diseases.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
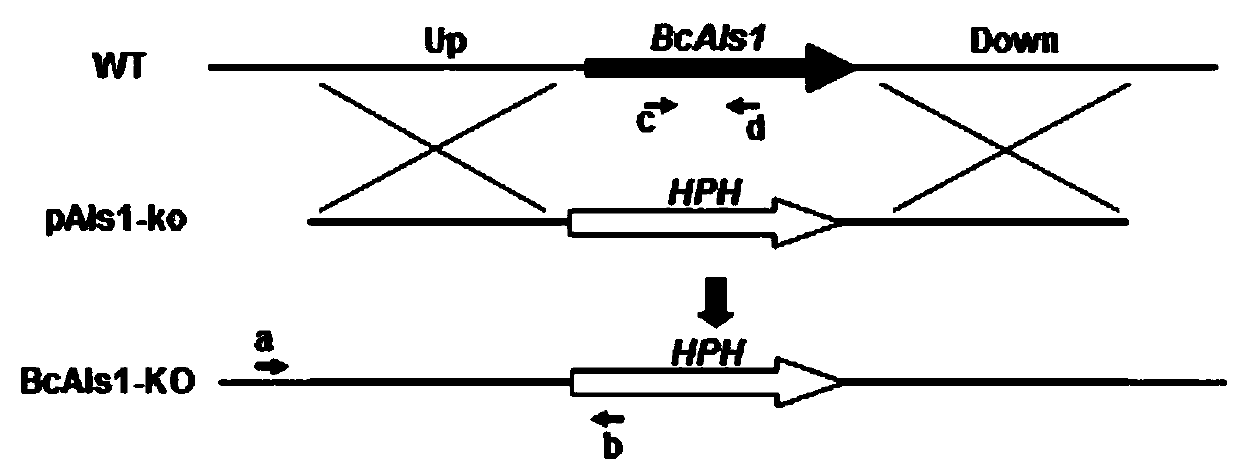
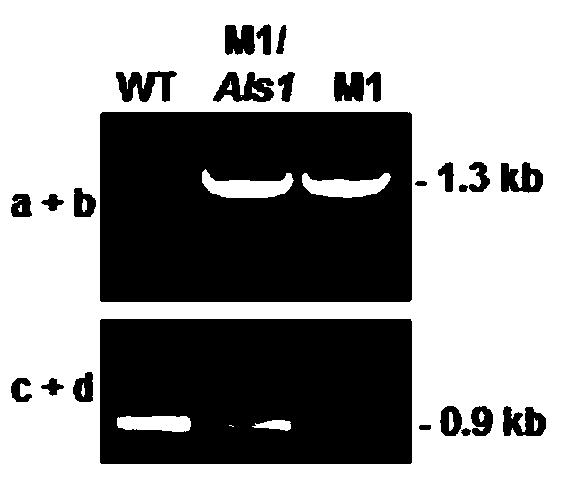
A Botrytis cinerea gene bcals1 related to pathogenicity and its application
The invention provides a botrytis cinerea gene BcAls1 relative to pathogenicity and application of the botrytis cinerea gene BcAls1, and belongs to the technical field of microbiological genetic engineering. The DNA sequence of the gene BcAls1 sourced from botrytis cinerea and used for controlling pathogenicity is shown in SEQ ID No:1, and comprises 1918 nucleotides. The amino acid sequence of protein coded by the gene BcAls1 is shown in SEQ ID No:2, and comprises 616 amino acids. The gene BcAls1 can be applied to the field of gene engineering of plant botrytis cinerea-resisting gray molds. Deletion, mutation or modification is conducted on the protein coded by the gene BcAls1 used for controlling the pathogenicity of botrytis cinerea to ensure that the pathogenicity of protein is flawed, and the flawed protein can be applied to design and screening of antifungal medicaments while serving as a target.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
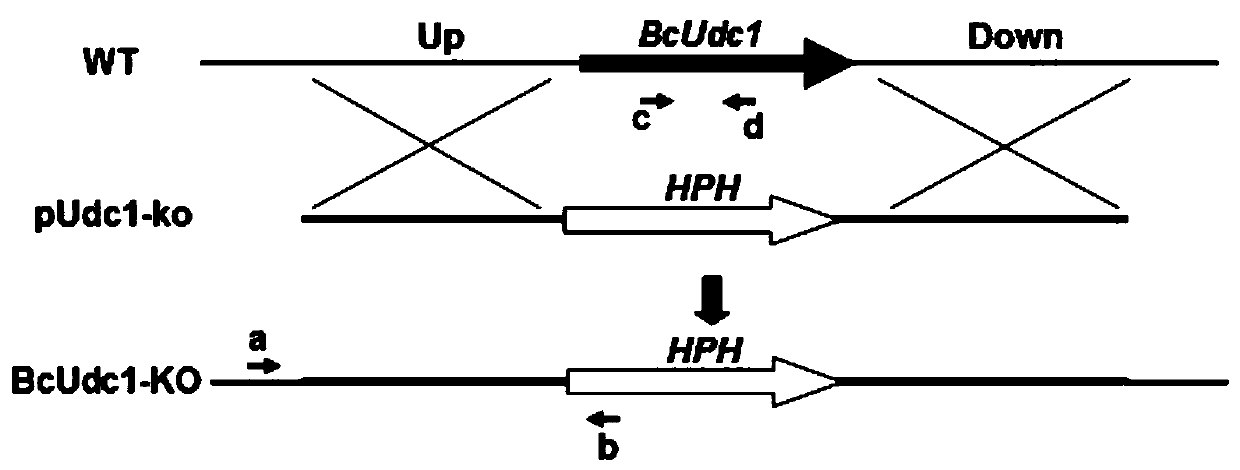
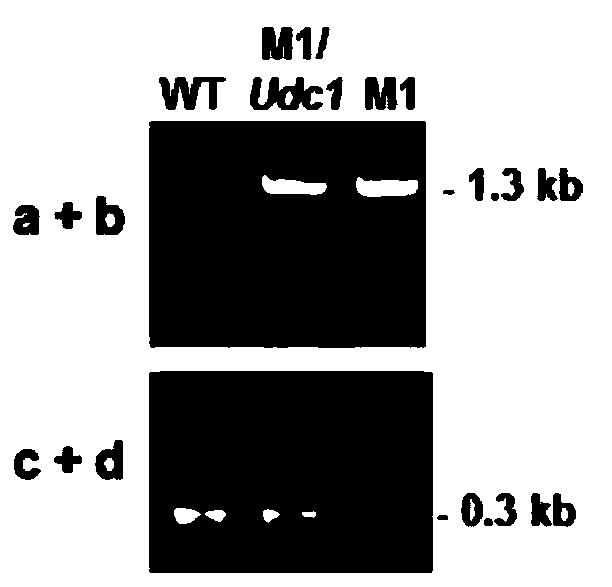
A Botrytis cinerea gene bcudc1 related to pathogenicity and its application
InactiveCN105483147BReduce pathogenicityMicroorganism based processesGenetic engineeringAntifungalAmino acid composition
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Application of tioconazole in preparation of bactericide for preventing and controlling phytopathogenic fungi and bacteria
InactiveCN110537545AStrong inhibitory activityConforms to residual toxicity criteriaBiocideFungicidesAlternaria tenuissimaFusarium
The invention discloses application of tioconazole in preparation of a bactericide for preventing and controlling phytopathogenic fungi and bacteria. Through indoor agent sensitivity determination, itproves that the tioconazole has good inhibitory activity on main diseases of important grain crops including fusarium graminearum causing wheat scab, maize curvularia causing maize leaf spot, rhizoctonia cerealis causing sheath blight and magnaporthe grisea causing rice blast; moreover, the tioconazole has good inhibition activity on botrytis cinerea of gray mold causing main diseases of fruits and vegetables, Physalospora piricola Nose causing ring rot of apples and alternaria tenuissima causing leaf spot of the fruits and vegetables; and moreover, the tioconazole also has good inhibitory activity on soil-borne diseases which are extremely difficult to control in agricultural production, such as fusarium oxysporum causing fusarium wilt, and the antibacterial activity of the tioconazole is even better than that of carbendazim and tebuconazole which are traditional bactericides. The invention provides application of the tioconazole in prevention and control of important plant diseasesin agricultural production for the first time, and the tioconazole has wide market application prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
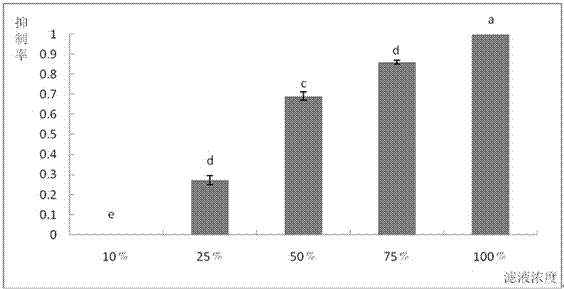
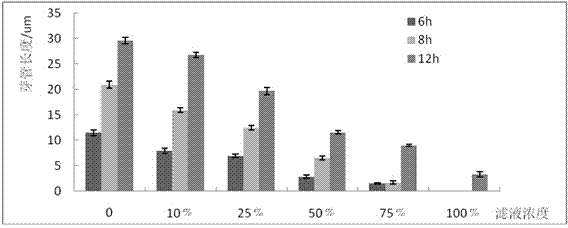
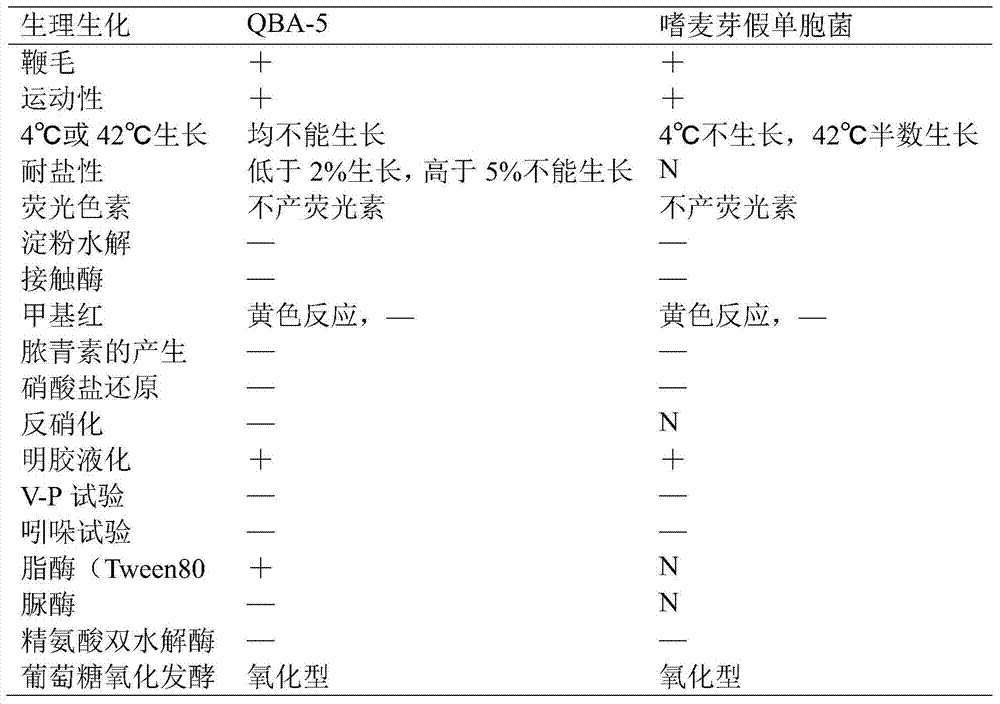
A Pseudomonas maltophilia strain qba-5 with inhibitory effect on Botrytis cinerea and its application
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas maltophilia strain QBA‑5 which has an inhibitory effect on Botrytis cinerea and its application. The strain QBA‑5 obtained by the present invention is classified as Pseudomonas maltophilia , preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and its preservation number is CCTCC M 2015403. Specifically, the present invention proves that the bacterial strain QBA-5 obtained by the present invention has a strong inhibitory effect on Botrytis cinerea through experiments on Botrytis cinerea spores, germ tube elongation and isolated leaves, and it can be prepared as a product for preventing and treating Botrytis cinerea. Biocontrol agents have good market application prospects.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
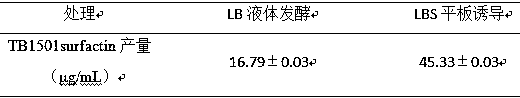
Method for preparing biocontrol bacillus secondary metabolite surfactins
PendingCN110628851AIncrease productionImprove efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFungicidesSucroseMetabolite
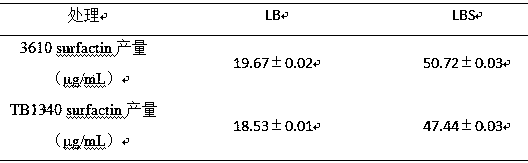
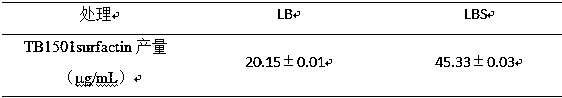
The invention discloses a method for preparing biocontrol bacillus secondary metabolite surfactins. The method comprises the steps of plate induction, LBS plate induction, solvent extraction, HPLC detection and the like. The biocontrol bacillus strain adopted by the method is TB1501 with a preservation number of CGMCC No.16069. According to the method, the yield of the secondary metabolite surfactins induced by sucrose is increased, and the control effect of the biocontrol bacteria is remarkably improved. Particularly, a botrytis cinerea bioassay result shows that after the sucrose is added, and the control effect of the biocontrol bacteria on the botrytis cinerea is remarkably improved. In combination with the phenomenon that the surfactins produced by the biocontrol bacteria after sucrose induction are increased, the invention speculates that the synergistic effect of the sucrose-induced biocontrol bacteria on the botrytis cinerea depends on the increase of the yield of the surfactins.
Owner:天津市农业科学院
Bacteria cinerea prevention actinomycete strain W15 and actinomycete agent thereof
InactiveCN109423464AConducive to pollution-free productionMeet the requirements of sustainable developmentBiocideBacteriaBrickStreptomyces
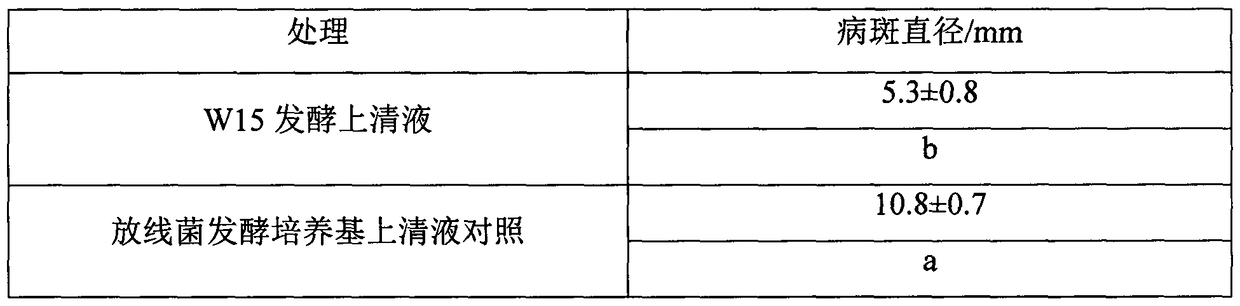
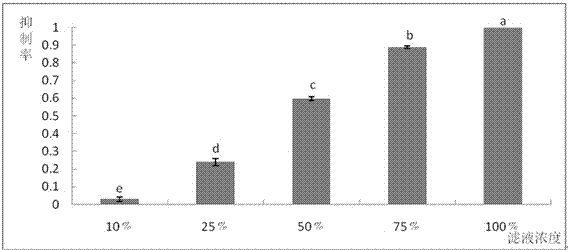
The invention discloses a bacteria cinerea prevention actinomycete strain, and belongs to the technical field of plant protection. The strain is a Streptomyces sp. and named as an actinomycete W15. The single colony of the actinomycete strain is circular and brick-red, the surface of the strain is dry and non-transparent, hyphae are thin and slowly grow, and the colony is compact in texture and has muddy and fishy smell. The actinomycete strain is gram-stained to be purple and positive. The prevention effect of the W15 agent on gray mold is 60% or more. Bacteria cinerea cannot easily generateresistance, the bacteria cinerea prevention actinomycete strain and the actinomycete agent thereof are environmentally friendly, and the agent can be used by root-irrigation after tomatoes germinate.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
A Pseudomonas cepacia strain qba-3 with inhibitory effect on Botrytis cinerea and its application
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas cepacia strain QBA-3 which has an inhibitory effect on Botrytis cinerea and its application. The QBA-3 obtained by screening in the present invention is classified as Pseudomonas cepacia and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, its collection number is CCTCC M 2015402. The present invention proves that the bacterial strain QBA-3 obtained by the present invention has a strong inhibitory effect on Botrytis cinerea through experiments on Botrytis cinerea spore germination, germ tube elongation, and isolated leaves, and can be prepared as a product for preventing and treating Botrytis cinerea. Biocontrol agents have good market application prospects.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
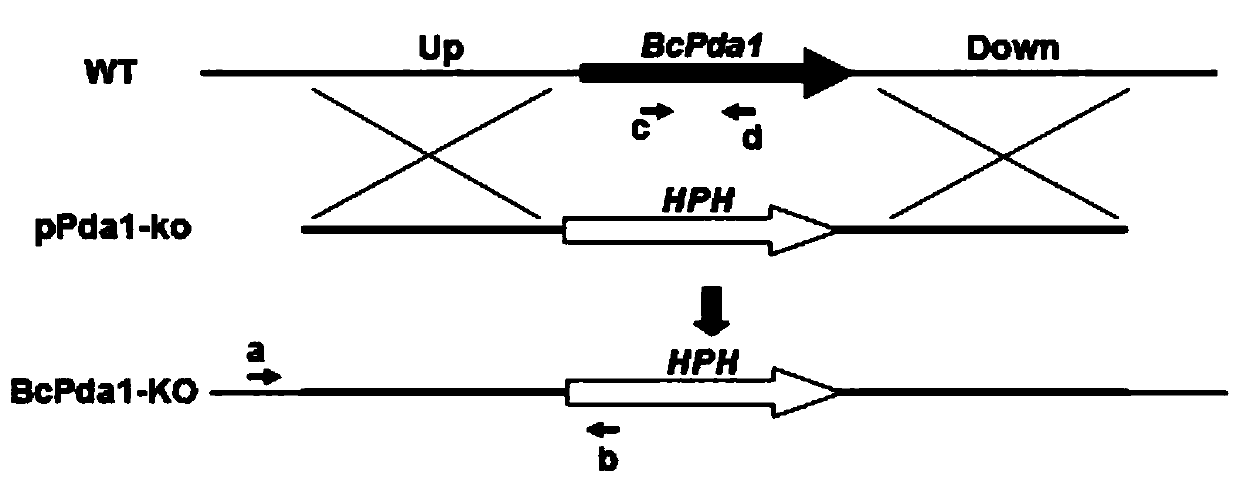
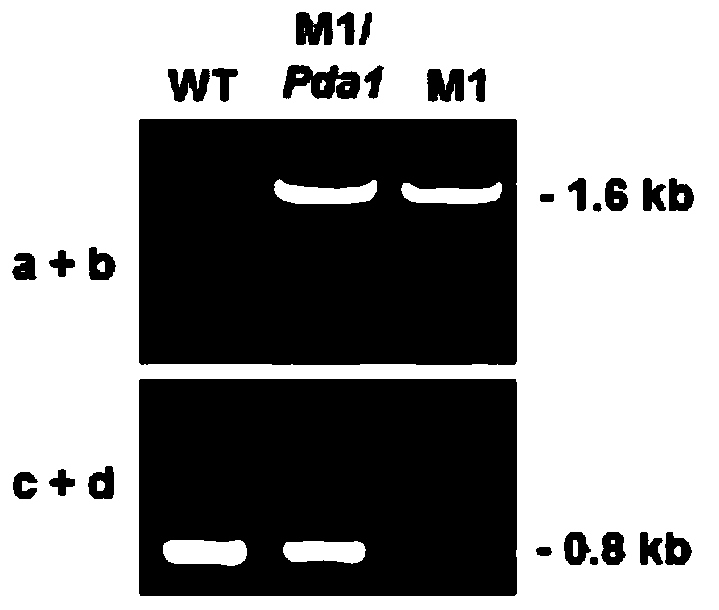
A Botrytis cinerea gene bcpda1 related to pathogenicity and its application
The invention discloses a pathogenicity-related botrytis cinerea gene BcPda1 and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microbiological genetic engineering. The DNA sequence of the gene BcPda1 which is from botrytis cinerea and controls pathogenicity is as indicated in SEQ ID No: 1 and composed of 1140 nucleotides; the amino acid sequence of protein encoded by the gene BcPda1 is as indicated in SEQ ID No: 1 and composed of 379 amino acids; the gene BcPda1 can be applied to the field of plant botrytis-cinerea-resistance genetic engineering; the protein BcPda1 controlling panthogenicity of the botrytis cinerea is subjected to deficiency or mutation or modification, so that pathogenicity of the botrytis cinerea has defects, and the pathogenicity-related botrytis cinerea gene BcPda1 can serve as a target to be applied to design and screening of antifungal medicament.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A Botrytis cinerea gene bcfch1 related to pathogenicity and its application
The invention provides a botrytis cinerea gene BcFch1 relative to pathogenicity and application of the botrytis cinerea gene BcFch1, and belongs to the technical field of microbiological genetic engineering. The DNA sequence of the gene BcFch1 sourced from botrytis cinerea and used for controlling pathogenicity is shown in SEQ ID No:1, and comprises 1409 nucleotides. The amino acid sequence of protein coded by the gene BcFch1 is shown in SEQ ID No:2, and comprises 435 amino acids. The gene BcFch1 can be applied to the field of gene engineering of plant botrytis cinerea-resisting gray molds. Deletion, mutation or modification is conducted on the protein coded by the gene BcFch1 used for controlling the pathogenicity of botrytis cinerea to ensure that the pathogenicity of protein is flawed, and the flawed protein can be applied to design and screening of antifungal medicaments while serving as a target.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
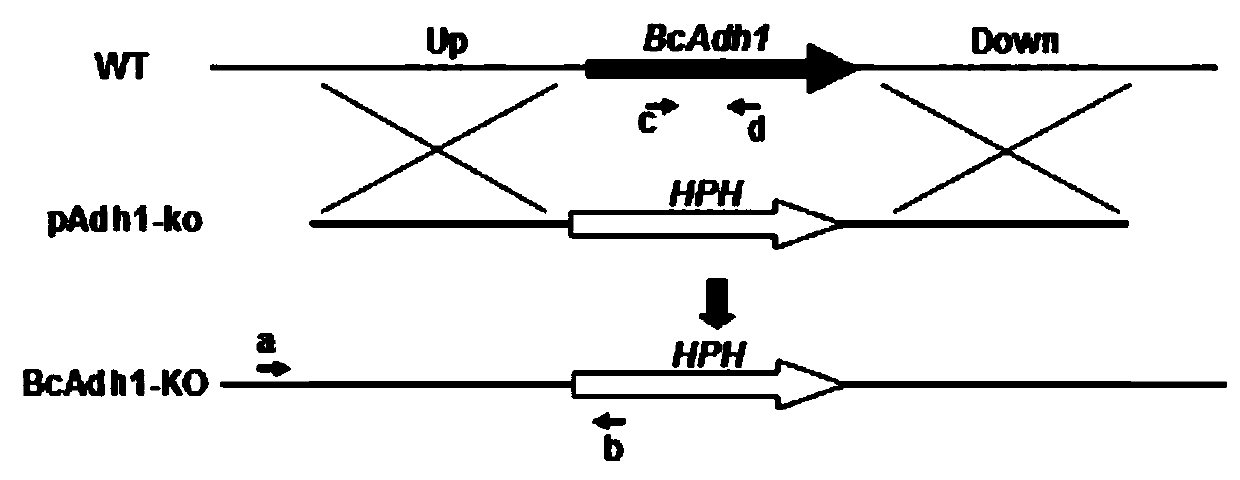
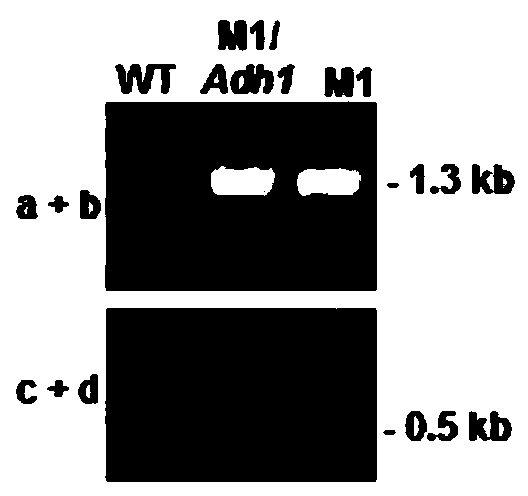
A Botrytis cinerea gene bcadh1 related to pathogenicity and its application
The invention provides a botrytis cinerea gene BcAdh1 relative to pathogenicity and application of the botrytis cinerea gene BcAdh1, and belongs to the technical field of microbiological genetic engineering. The DNA sequence of the gene BcAdh1 sourced from botrytis cinerea and used for controlling pathogenicity is shown in SEQ ID No:1, and comprises 1172 nucleotides. The amino acid sequence of protein coded by the gene BcAdh1 is shown in SEQ ID No:2, and comprises 372 amino acids. The gene BcAdh1 can be applied to the field of gene engineering of plant botrytis cinerea-resisting gray molds. Deletion, mutation or modification is conducted on the protein coded by the gene BcAdh1 used for controlling the pathogenicity of botrytis cinerea to ensure that the pathogenicity of protein is flawed, and the flawed protein can be applied to design and screening of antifungal medicaments while serving as a target.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com