A yeast-like fungus for suppressing postharvest diseases of fresh fruit and its application
A technology of yeast and fungi, applied in the direction of application, fungi, chemicals for biological control, etc., can solve problems such as shedding, peach damage, and economic loss of fruit farmers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
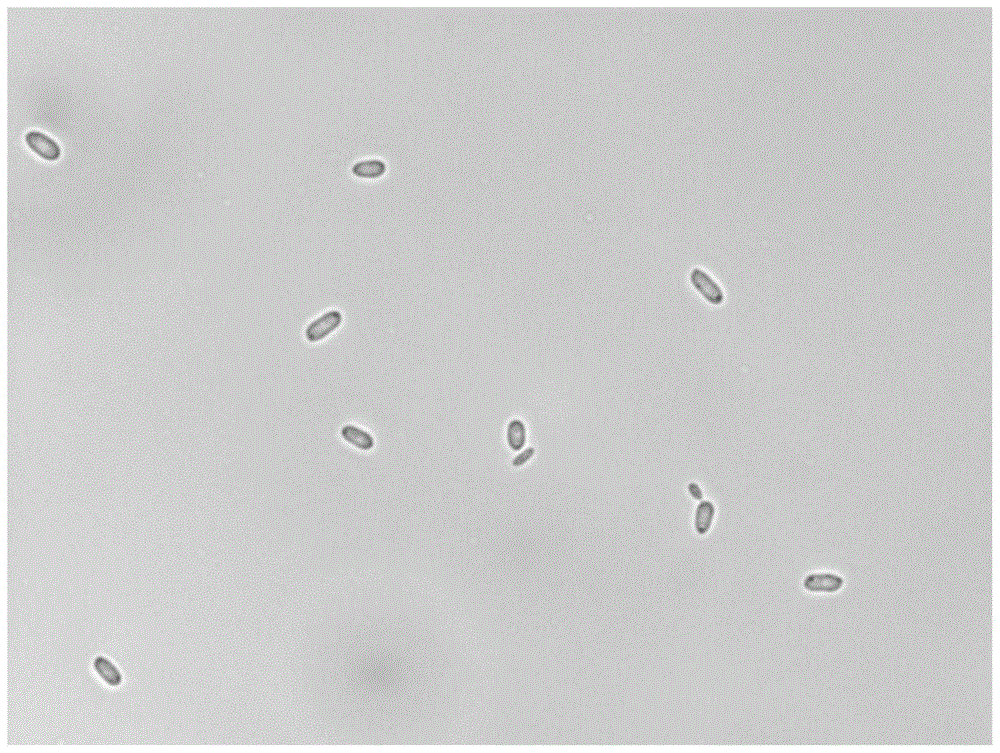
[0046] Example 1. Isolation and strain identification of yeast-like fungi (Pseudozyma fusiformata) SF6 of the present invention
[0047] 1. Sample collection
[0048] Apples are collected from organic orchards in northern China.
[0049] 2. Isolation and screening of strains and antagonistic screening
[0050] Isolate strains from organic fruits, use conventional gradient dilution coating to isolate, use two kinds of media, PDA (containing streptomycin sulfate) and YPD agar (containing streptomycin sulfate), to culture at 28°C respectively, and pick colonies Bacteria with large morphological differences and can be purely cultured were purified and preserved on YPD agar medium, and the primary screening and multiple re-screening of antagonistic bacteria were carried out with Peach brown rot as the target pathogen, and finally a strain with strong antibacterial activity was obtained. Saccharomyces-like strain, named as SF6.
[0051] 3. Identification of strains
[0052] The ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Physiological and biochemical characteristics of SF6: glucose can be fermented, raffinose and lactose can not be fermented; carbon source assimilation: sorbose, sucrose, maltose, trehalose, D-mannitol are positive, galactose, lactose, rhamnose , ribitol, and erythritol were negative. SF6 can grow normally in the medium that contains 5% (mass content) sodium chloride, can not grow in the medium that contains 10% (mass content) sodium chloride, can grow in the medium of pH4.0-5.5 It can grow normally, but the growth potential is weak when the ambient temperature is 4°C, and it cannot grow above 40°C; the optimum growth temperature is 25-30°C. The 5.8S rDNA gene, ITS1 / ITS2 sequence and 26S rDNA D1 / D2 nucleotide sequence of strain SF6 are shown in SEQ ID No.1 and No.2. Embodiment 2, the mensuration of class yeast fungus (Pseudozyma fusiformata) SF6 antibacterial spectrum of the present invention
[0055] Pathogens tested:
Embodiment 3
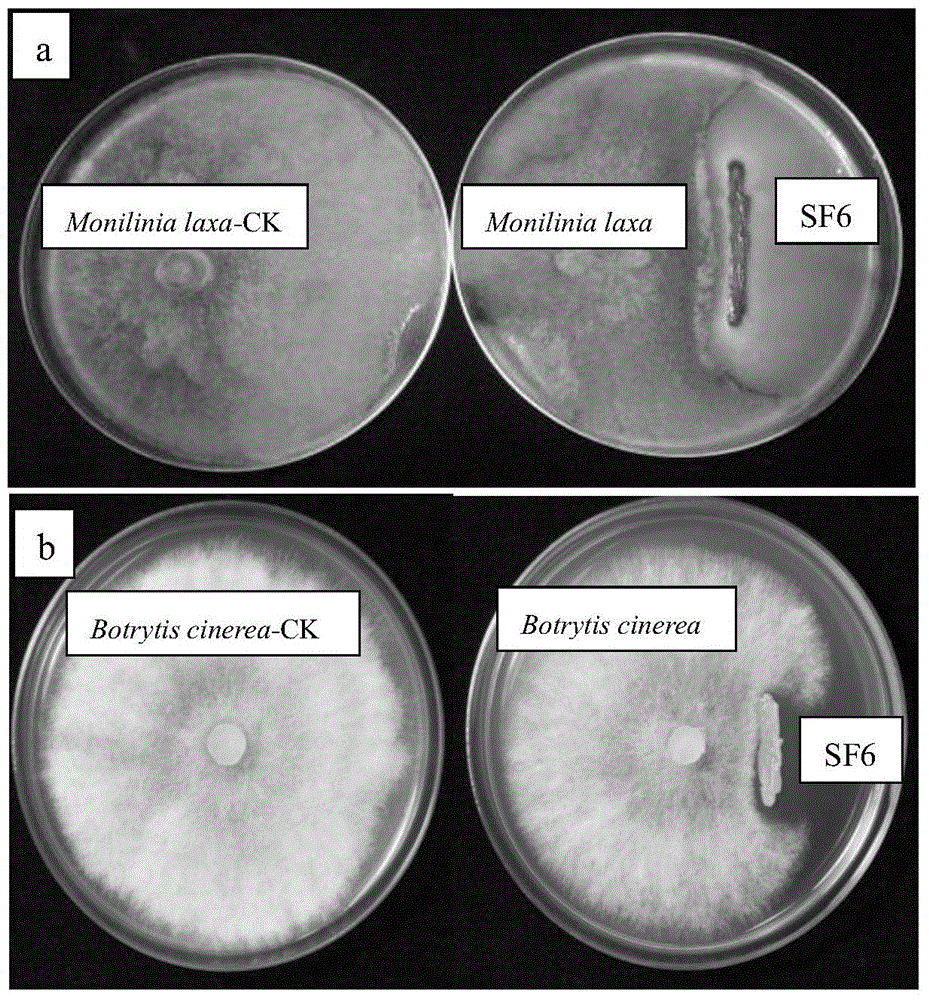
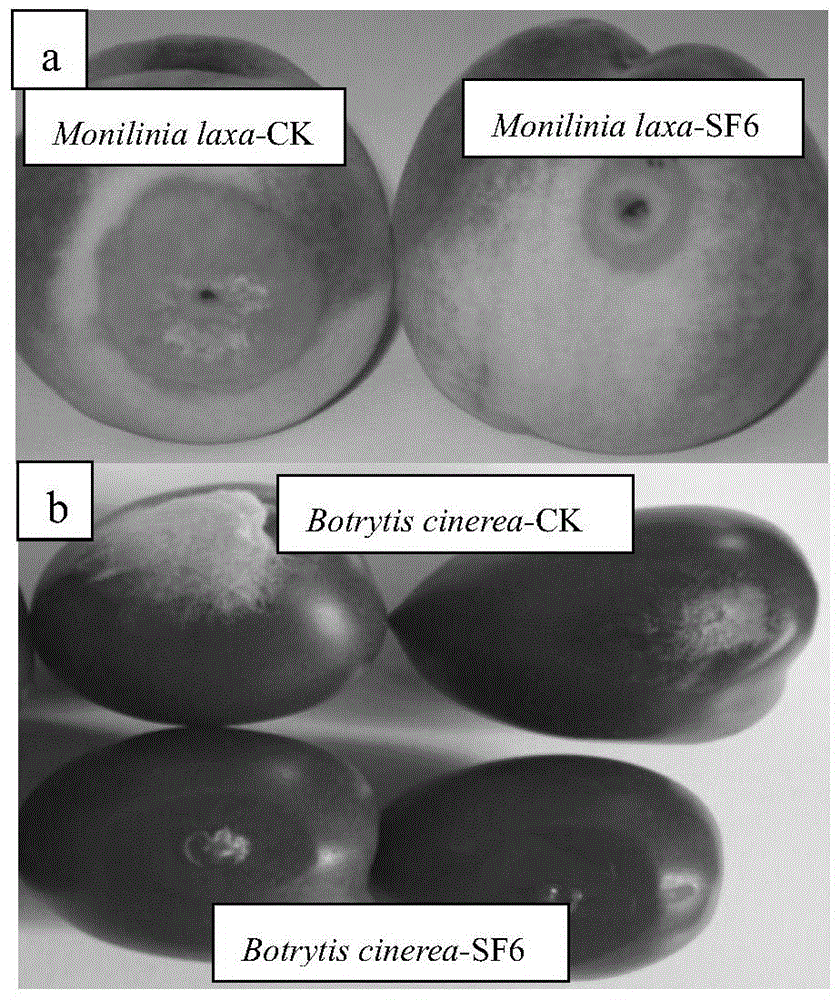
[0065] Example 3 Inhibition of yeast fungus (Pseudozyma fusiformata) SF6 on rot lesions caused by two kinds of plant pathogenic fungi tested.
[0066] After the peaches were picked, they were passed through the SF6 bacterial solution (the concentration of the bacterial solution was 10 7 cfu / ml, 10 8 cfu / ml, 10 9 cfu / ml) for 30-60 seconds, then air-dried at room temperature, and then stored in the dark at a temperature of 1°C and a relative humidity of 95%. After storage for 21 days, compared with the control group, when the bacterial solution concentration was 10 7 cfu / ml, its control effect is 50%, when the concentration of bacteria solution reaches 10 8 When cfu / ml, its control effect is 60%, when the concentration of bacteria solution reaches 10 9 When cfu / ml, its control effect reaches 70%.
[0067] After the tomatoes were picked, the SF6 bacterial liquid (the concentration of the bacterial liquid was 10 7 cfu / ml, 10 8 cfu / ml, 10 9 cfu / ml) soaked for 30-60 seconds,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com