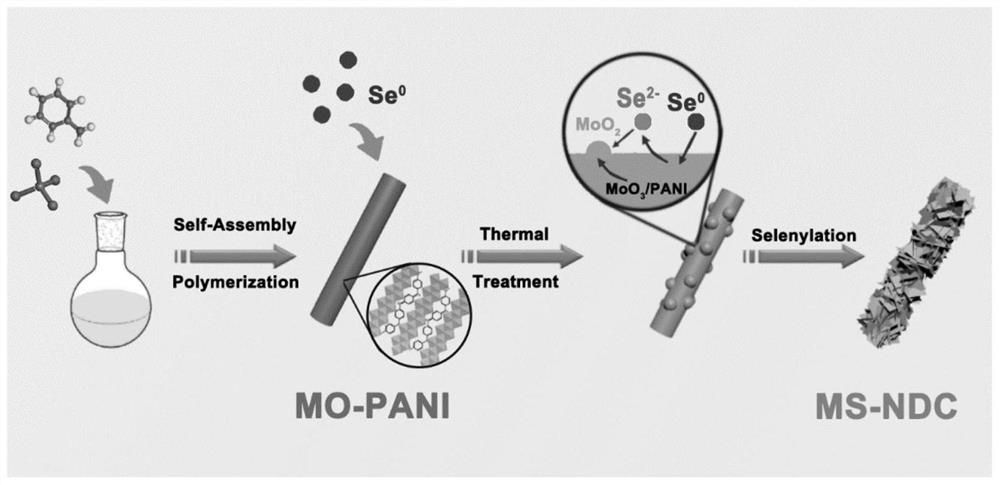
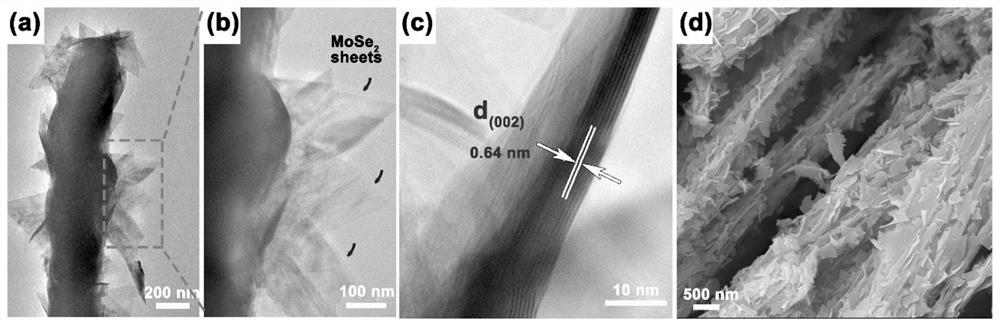
Solid-phase cothermal synthesis of molybdenum diselenide/nitrogen-doped carbon rods
A technology of nitrogen-doped carbon and molybdenum diselenide, applied in structural parts, electrical components, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of high requirements, high toxicity of hydrazine hydrate, unsafe reducing hydrogen, etc., and achieve good ratio performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Step 1: Stir and disperse molybdate and aniline in deionized water at a mass ratio of 3:4;
[0034] The second step: the mixed solution obtained in the second step is placed in a 25°C water bath, and a certain amount of hydrochloric acid is slowly added dropwise until white turbidity appears;
[0035] The third step: put the above white turbid solution in a 50°C water bath for 4 hours, filter and wash to obtain a white precipitate;
[0036] Step 4: Ultrasonic disperse the obtained white precipitate in a certain amount of deionized water, add an appropriate amount of ammonium persulfate and hydrochloric acid solution, and place it in a water bath at 0°C to stir for 20 hours to obtain a polymerization product;
[0037] Step 5: Suction filter, wash, and dry the above-mentioned polymerization product, and mix it evenly with an appropriate amount of selenium powder. In an argon atmosphere, raise the temperature to 500°C at a rate of 2°C per minute, and then keep it warm for ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Step 1: Stir and disperse molybdate and aniline in deionized water at a mass ratio of 3:4;
[0042] The second step: the mixed solution obtained in the second step is placed in a 25°C water bath, and a certain amount of hydrochloric acid is slowly added dropwise until white turbidity appears;
[0043] The third step: put the above white turbid solution in a 50°C water bath for 4 hours, filter and wash to obtain a white precipitate;
[0044] Step 4: Ultrasonic disperse the obtained white precipitate in a certain amount of deionized water, add an appropriate amount of ammonium persulfate and hydrochloric acid solution, and place it in a water bath at 0°C to stir for 20 hours to obtain a polymerization product;
[0045] Step 5: Suction filter, wash, and dry the above-mentioned polymerization product, mix it with an appropriate amount of selenium powder, and in an argon atmosphere, raise the temperature to 600°C at a rate of 2°C per minute and then keep it warm for 3 hours ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Step 1: Stir and disperse molybdate and aniline in deionized water at a mass ratio of 3:4;
[0049] The second step: the mixed solution obtained in the second step is placed in a 25°C water bath, and a certain amount of hydrochloric acid is slowly added dropwise until white turbidity appears;
[0050] The third step: put the above white turbid solution in a 50°C water bath for 4 hours, filter and wash to obtain a white precipitate;
[0051] Step 4: Ultrasonic disperse the obtained white precipitate in a certain amount of deionized water, add an appropriate amount of ammonium persulfate and hydrochloric acid solution, and place it in a water bath at 0°C to stir for 20 hours to obtain a polymerization product;
[0052] Step 5: Suction filter, wash, and dry the above-mentioned polymerization product, and mix it evenly with an appropriate amount of selenium powder. In an argon atmosphere, raise the temperature to 400°C at a rate of 2°C per minute, and then keep it warm for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com