Method for fermenting production of feed enzyme preparation by immobilized cell technology
A technology for immobilizing cells and feed enzyme preparations, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, immobilization on/in organic carriers, etc., can solve the problems of low production efficiency, high production cost, and production technology. complex problems, to achieve the effect of improving production efficiency, prolonging service life, and easy mass transfer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0045] 1) Preparation of crude enzyme solution: After the cultivation, the filtrate separated by filtration from the fermentation broth was centrifuged at 5000r / min for 20min, and the obtained supernatant was the crude enzyme solution.
[0046] 2) Carboxymethyl cellulase: take 0.5mL of crude enzyme solution, mix it with 1.5mL of 1% CMC-Na and citrate buffer (pH5.0), react in a water bath at 50°C for 30min, and measure it by DNS method after reaction Reducing sugar produced by enzymatic hydrolysis. The amount of enzyme required to generate 1 μmol of glucose from the substrate per hour under the above conditions is defined as an enzyme activity unit U.
[0047] 3) α-amylase: Mix 2.0mL of crude enzyme solution with 2.0mL of citric acid buffer (pH5.5), add 2.0mL of 1% starch solution, shake well, heat in a water bath at 40°C for 5min, then add 4.0mL of 0.4 M NaOH solution to terminate the reaction, take 2.0mL of the reacted solution, mix it with 2.0mL DNS solution, heat in a boil...
Embodiment 1
[0050] Test according to the technical scheme of using immobilized cell technology to ferment and produce feed enzyme preparation provided by the present invention, the steps are as follows:
[0051] Activation and expansion of S1 strain
[0052] 1) Aspergillus niger and Trichoderma konii: Take the preserved strains of Aspergillus niger and Trichoderma konii, inoculate them on PDA medium plates respectively, and culture them at 30°C for 3-5 days, whichever is full of spores; inoculate the spores with sterile After washing with normal saline, prepare a concentration of about 1×10 7 spore suspension per ml, put the spore suspension into the PDB medium with 5% inoculum amount, cultivate it on a rotary shaker at 30°C and 150rpm for 24-30h, and obtain the bacterial suspensions of these two bacteria respectively;
[0053] 2) Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus natto: Take the preserved strains of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus natto, inoculate them on the slant of LB solid medium, cultu...
Embodiment 2
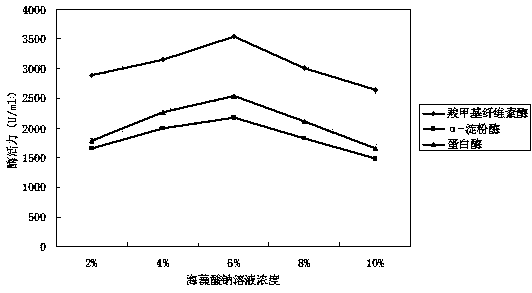
[0062] Example 2 Effect of concentration of sodium alginate solution on enzyme production
[0063] According to the method of Example 1, the concentration of the sodium alginate solution used in step S2 is set to 2%, 4%, 6%, 8%, 10%, and the other operations are the same, and the crude enzyme liquid is prepared after the fermentation enzyme production is completed. The activities of three representative enzymes, carboxymethyl cellulase, α-amylase and protease, were measured, and the results were as follows: figure 1 shown. The results showed that too high a concentration of sodium alginate solution would reduce the porosity of the carrier, thereby affecting the diffusion of enzyme molecules from the carrier into the fermentation broth, while too low a concentration would reduce the strength of the carrier, and the carrier would be easily broken under the action of shear force. Making the bacteria free in the fermentation broth will affect the effect of enzyme production and f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com