Differentially expressed NACs transcription factor in populus tomentosa under cadmium stress condition as well as obtaining method thereof
A transcription factor and differential expression technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve problems such as affecting crop yield and quality, unclear gene expression regulation mechanism, and plant damage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Obtaining candidate NACs transcription factors differentially expressed in Populus tomentosa under cadmium stress
[0060] The excellent clone plant "1316" [P.tomentosa Carr.(clone'1316')] of Populus tomentosa in that year was used as the experimental material. °47′). Select the young shoots of the excellent clone plants that were born in January to graft in January, and select plants with good growth and basically the same in July of that year to process, that is, to use six-month-old seedlings for experimentation. First the seedlings are taken out from the soil, washed with water and carefully cleaned up the roots, then put into an aqueous solution containing 20 mg / L of cadmium chloride for processing, and after 6 hours, take leaf samples, each sample contains three biological repetitions, after sampling Immediately freeze in liquid nitrogen.
[0061] The total RNA of leaves was extracted with RNAplant Plus Plant Total RNA Extraction Reagent, and the operation steps...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Obtain SNP data of differentially expressed candidate NACs transcription factors
[0068] Genome sequences of 435 Populus tomentosa populations were determined by genome resequencing technology. The genome sequence obtained by sequencing was compared with the genes in the P. tomentosa germplasm resource bank to obtain the genome SNP data of P. tomentosa treated with cadmium stress. Then screen the SNP sites with a minimum allele frequency (Minor allele frequency, MAF) above 5% and missing data within 20%, and finally obtain high-quality SNP data.
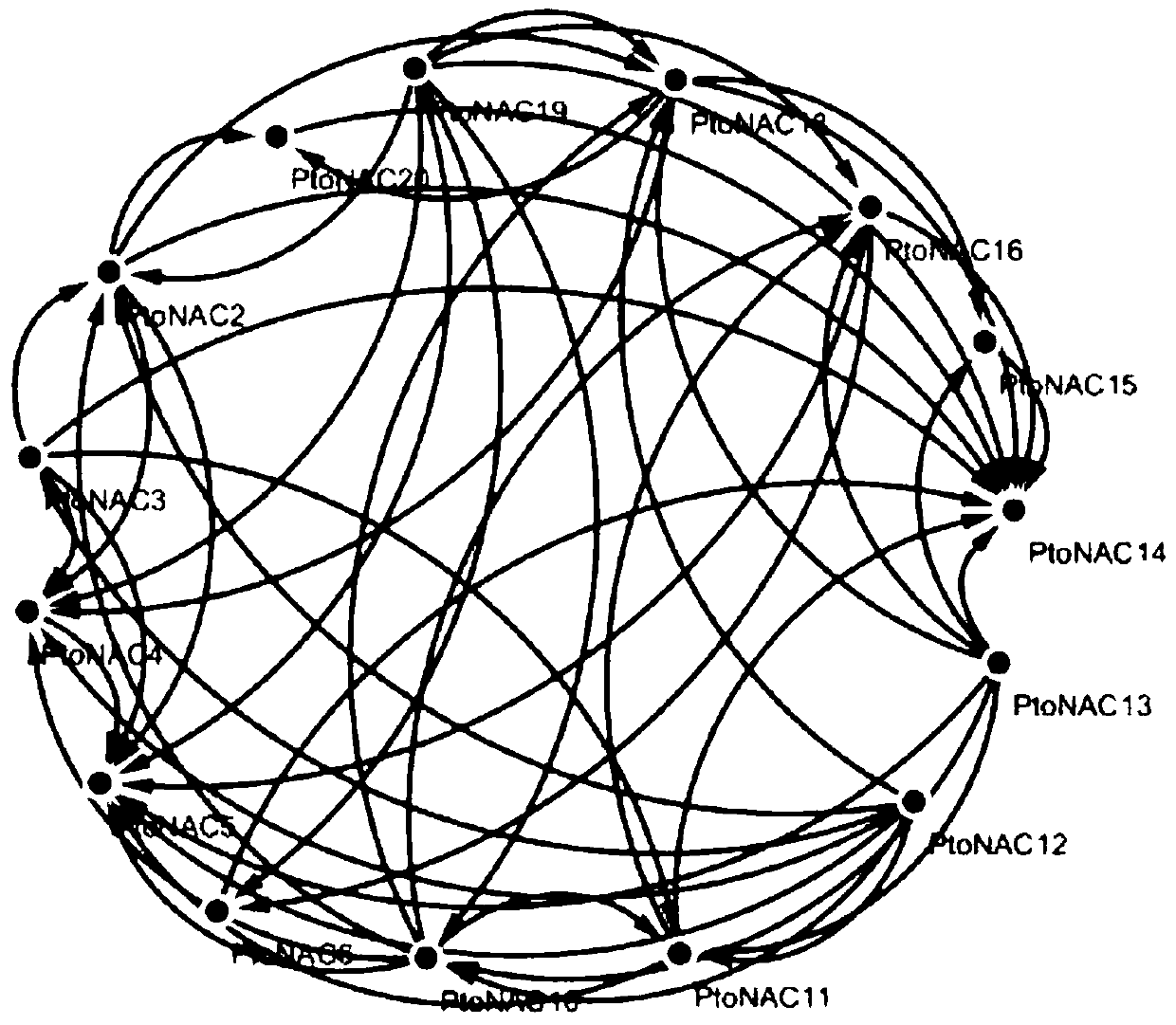
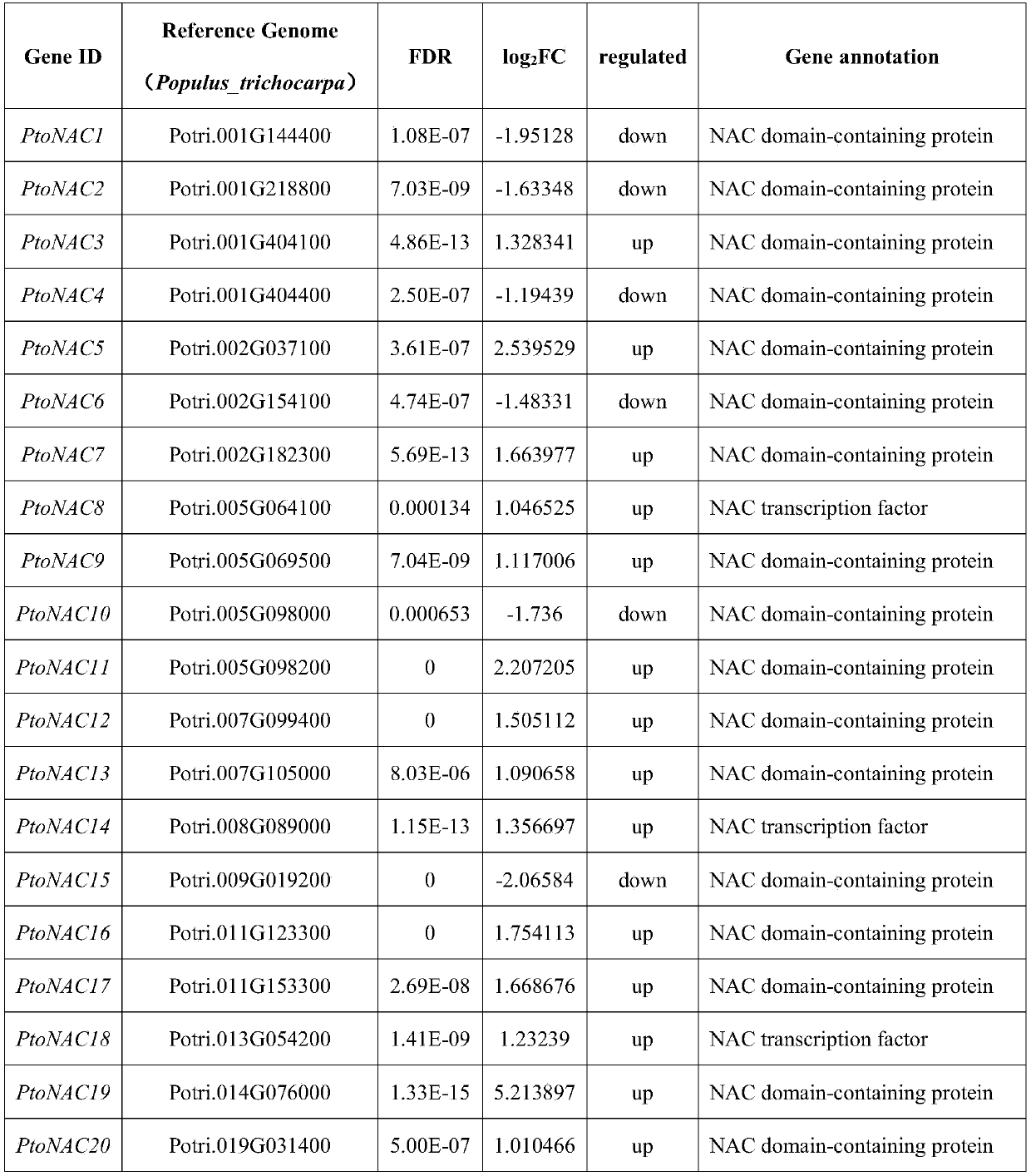
[0069] Based on the population resequencing data, 20 differentially expressed candidate NACs transcription factors were mapped to the corresponding P. tomentosa genes by multiple alignment method, and SNP data were extracted. A total of 889 SNP sites from 20 NACs transcription factors were obtained.
Embodiment 3
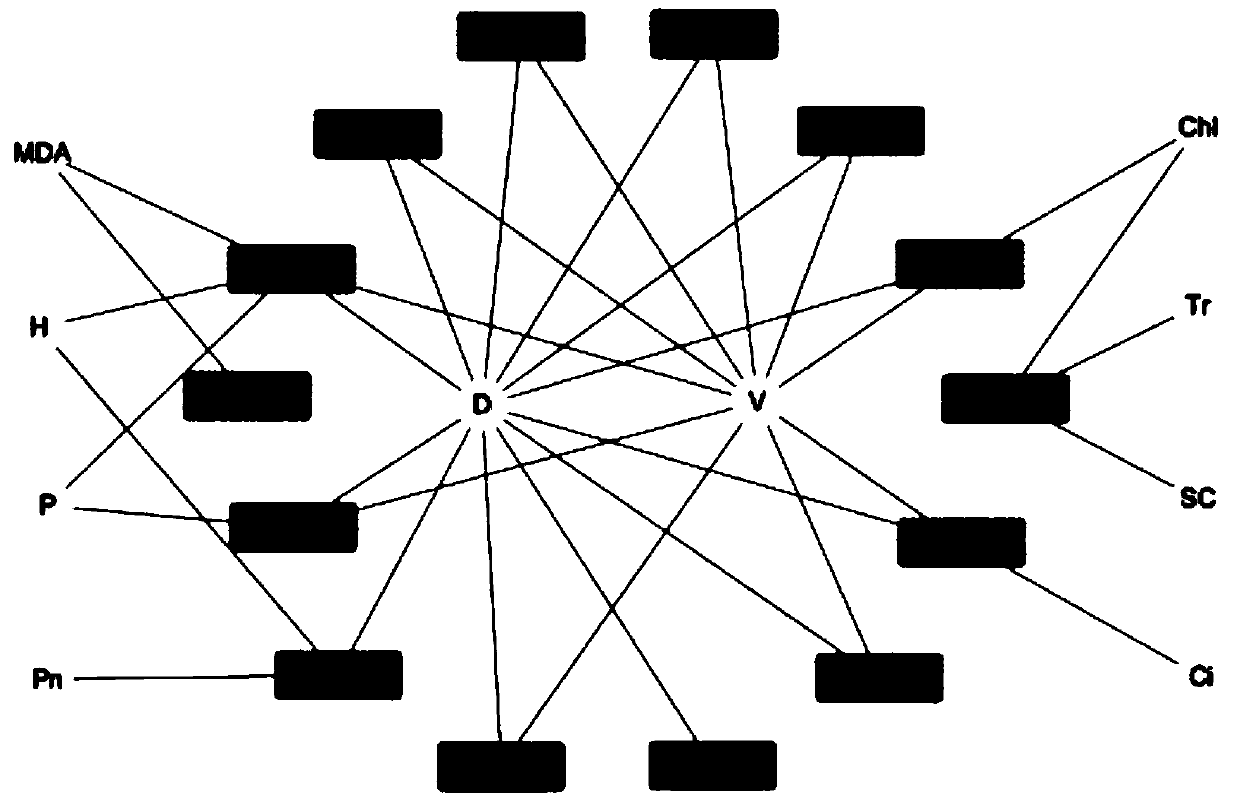
[0071] The 435 Populus tomentosa natural populations adopted in Example 2 were tested for phenotypic traits, including the following 10 population phenotype data related to growth and photosynthesis: tree height (Height, H), diameter at breast height (Diameter atbreast height, D) and Stem volume (V), net photosynthetic rate (Net photosythetic rate, Pn), stomatal conductance (Sromatal conductance, SC), transpiration rate (Transpiration rate, Tr), intercellular CO 2 Concentration (IntercellularCO 2 concentration, Ci), malondialdehyde content (Malondialdehyde Content, MDA) and total protein content (Total Protein Content, P).
[0072] The diameter at breast height, tree height, and volume were measured by the growth traits measurement tool, and the net photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, transpiration rate, and intercellular CO were measured by the LI6400 photosynthetic measuring instrument. 2 Concentration of four photosynthetic traits, using kits to determine malondiald...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com