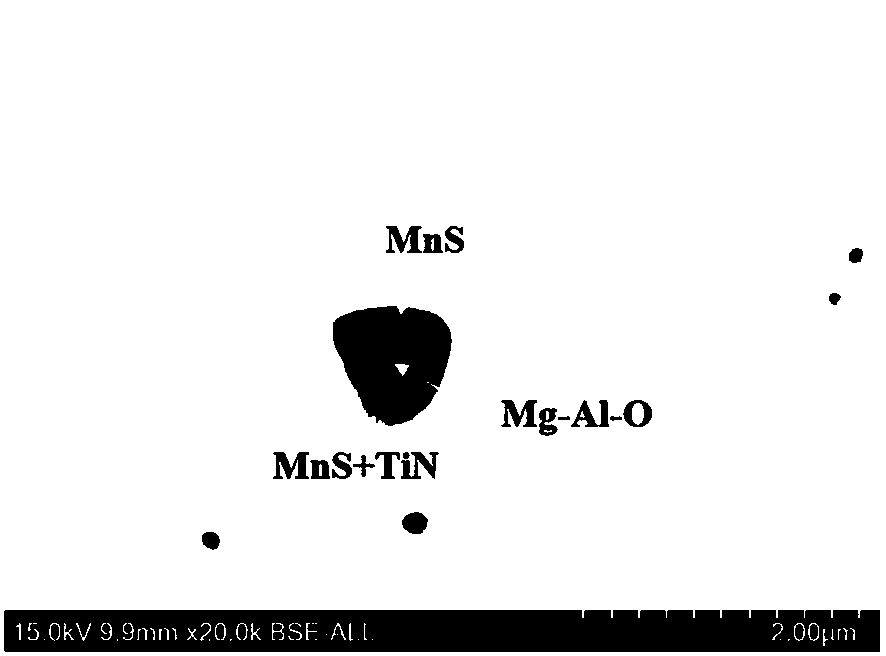
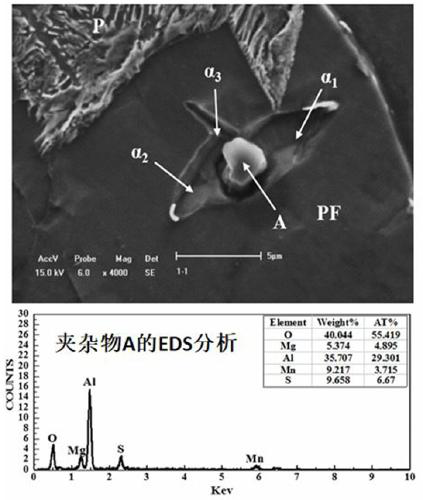
Low-cost magnesium-treated microalloyed steel and preparation method thereof
A low-cost technology for microalloyed steel, applied in the field of low-cost magnesium-treated microalloyed steel and its preparation, can solve the problems of unfavorable structure and performance of low-carbon microalloyed steel, difficulty in controlling inclusions, etc., and achieve significant economic benefits. Crystallization, adding a stable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027]The steel grade is HR60 wheel steel. The 250t converter smelting process is adopted, and Si-Mn weak deoxidation is used after the furnace, and the oxygen content in the steel is controlled at 0.01wt%; then LF slagging is used to raise the temperature, and Al is used for deep deoxidation, and then the alloying design is carried out, and the Nb content in the steel is adjusted during alloying. Reduce from 0.03wt% of the benchmark steel to 0.02wt%, Ti content from 0.02wt% to 0.01wt%, vacuum degassing in RH after alloying, break the vacuum after the treatment, and feed Mg-Al into the ladle - Fe cored wire (where the magnesium content is 10wt%, the Al content is 60wt%, and the Fe content is 30wt%), the wire feeding speed is 3m / s, and the feeding amount is 250m; The conventional continuous casting process casts a slab continuous casting slab with a thickness of 230mm. The continuous casting slab is heated in a high-temperature furnace at a heating temperature of 1220°C, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The production steel grade is X65 pipeline steel. The 250t converter smelting process is adopted, and Si-Mn weak deoxidation is used after the furnace, and the oxygen content in the steel is controlled at 0.015wt%. LF slagging and heating, using Al deep deoxidation, and then alloying design; during alloying, the Nb content in the steel is reduced from 0.045wt% of the benchmark steel to 0.030wt%, and the V content is reduced from 0.045wt% to 0.030wt%. Vacuum degassing in RH after alloying, break the vacuum after treatment, and feed Mg-Al-Fe cored wire into the ladle (the content of magnesium is 15wt%, the content of Al is 55wt%, and the content of Fe is 30wt%) , the feeding line speed is 3m / s, and the feeding amount is 300m. Soft blow for 8 minutes after wire feeding, and then use conventional continuous casting technology to cast slab continuous casting slab with a thickness of 230mm. The continuous casting slab is heated in a high-temperature furnace at a heating tem...
Embodiment 3
[0032] The production steel grade is QSTE500. The 250t converter smelting process is adopted, and Si-Mn weak deoxidation is used after the furnace, and the oxygen content in the steel is controlled at 0.012wt%. LF makes slag and heats up, uses Al deep deoxidation, and then carries out alloying design. During alloying, the Nb content in the steel was reduced from 0.06wt% to 0.04wt%, and the Ti content was reduced from 0.04wt% to 0.025wt%. Vacuum degassing in RH after alloying, break the vacuum after treatment, and feed Mg-Al-Fe cored wire into the ladle (the content of magnesium is 15wt%, the content of Al is 60wt%, and the content of Fe is 25wt%) , the feeding line speed is 3m / s, and the feeding amount is 280m. Soft blow for 8 minutes after wire feeding, and then use conventional continuous casting technology to cast slab continuous casting slab with a thickness of 230mm. The continuous casting slab is heated in a high-temperature furnace at a heating temperature of 1220°C ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com