Titanium dioxide product
A titanium dioxide, selected technology, applied in the direction of titanium dioxide, titanium oxide/hydroxide, ink, etc., to achieve the effect of providing environmental benefits and reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0120] Electron microscopy image analysis was performed on 140 conventional pigmentary titanium dioxide materials to determine their crystal size and geometric weight standard deviation (GWSD). Minimum, maximum and average values were determined.
[0121] Image analysis was also performed on three commercially available macrocrystalline titania products. Their crystal size and geometric standard deviation are recorded.
[0122] Table 1 shows the results of the image analysis
[0123]
[0124] The crystal size distribution of products with different values of mean crystal size and geometric weight standard deviation was then calculated based on the material with lognormal distribution. The values taken for mean crystal size and geometric weight standard deviation are intended to be illustrative and not directly reflective of individual prior art products.
[0125] Table 2 shows the differences in the distribution of crystals within the materials based on the mean cr...
Embodiment 2
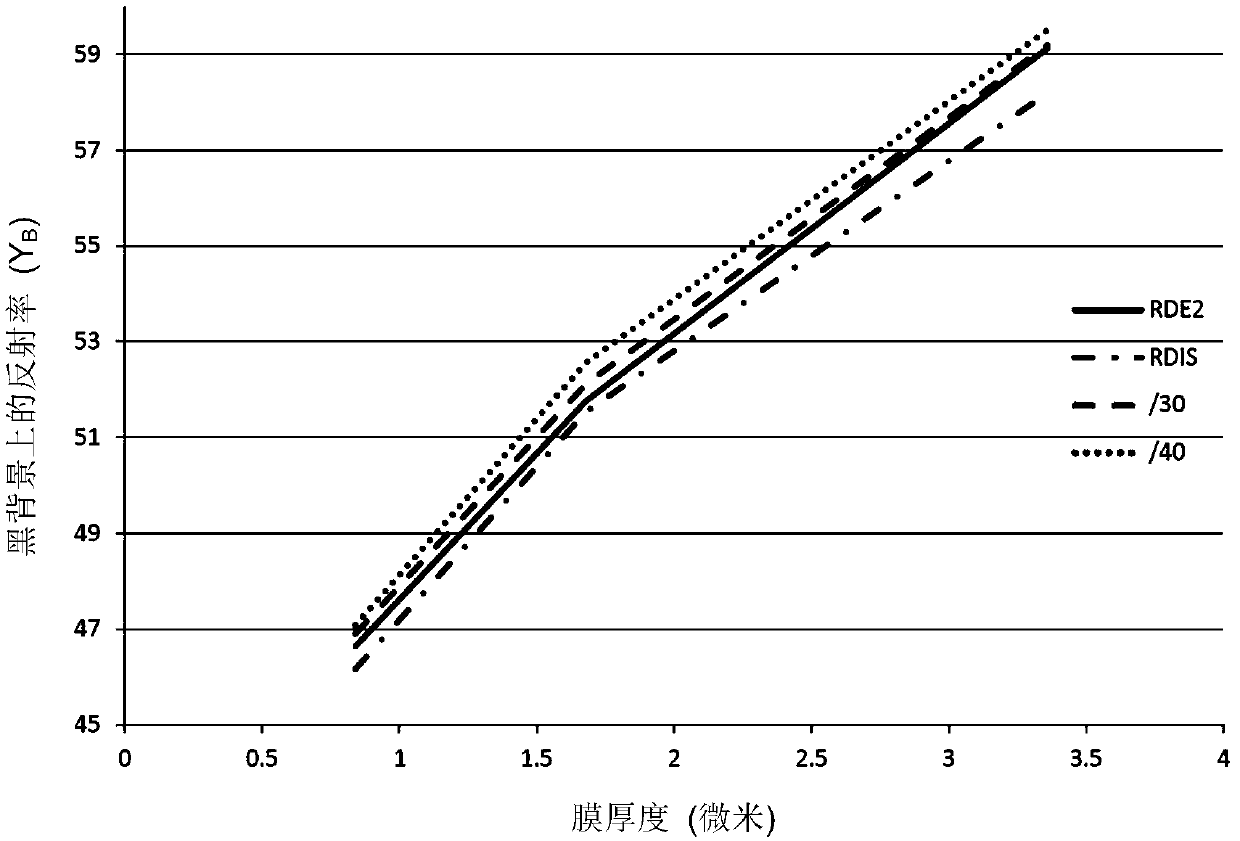
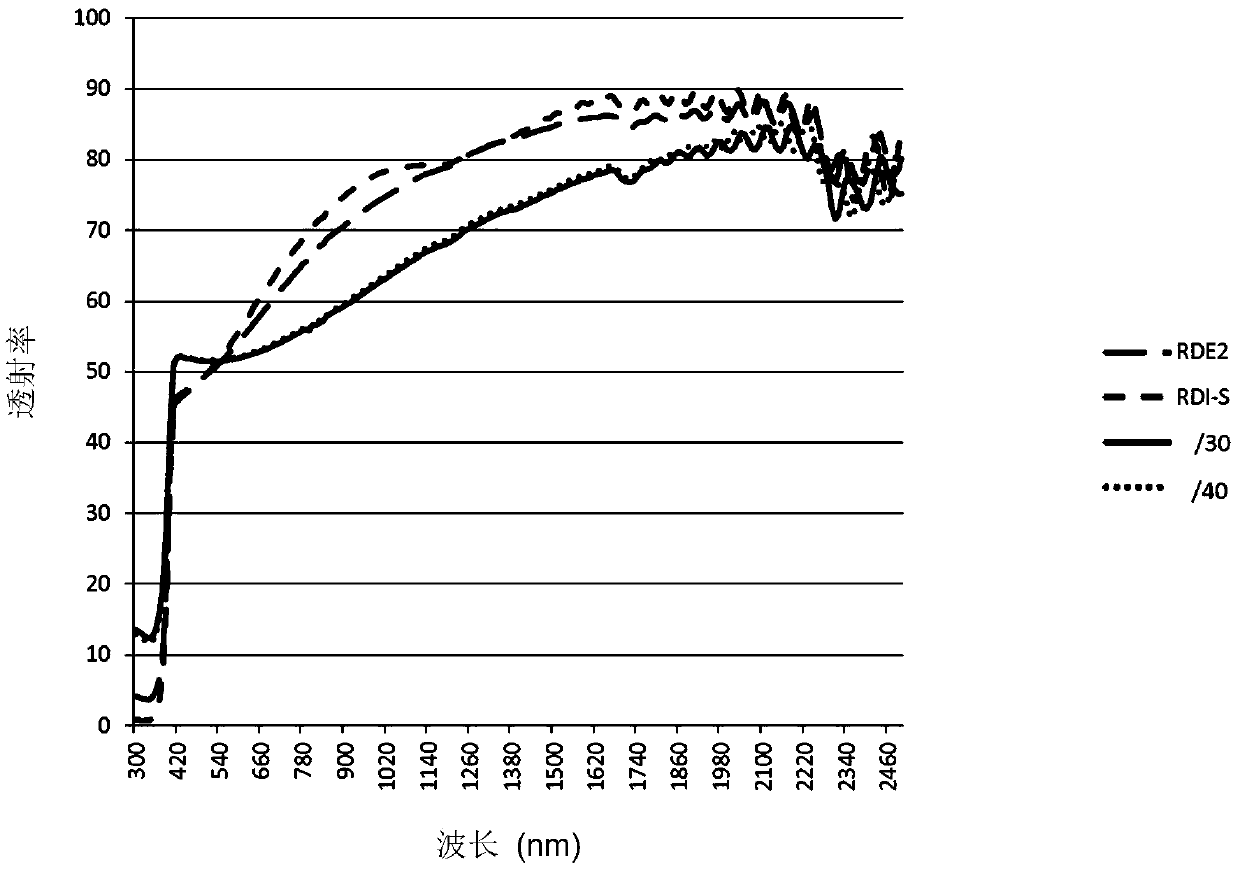
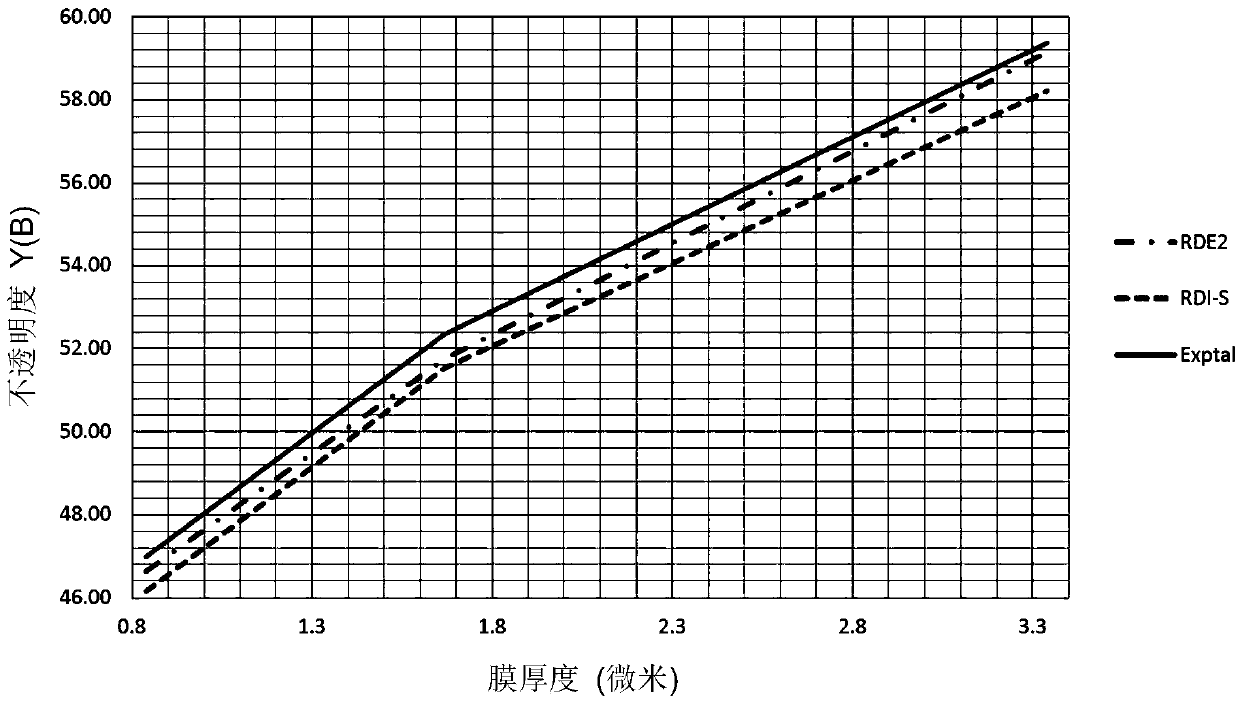
[0129] prepared TiO with average crystal sizes of 0.397 μm and 0.386 μm, respectively 2 particles and tested in white ink.
[0130] method:
[0131] The rutile titanium dioxide material is produced using the sulfate method (Blumenfeld variant). Conventional processing takes place during the ore grinding, digestion, purification, precipitation and leaching stages. The metatitanic acid slurry from filtration was spiked with 1.00% Blumenfeld rutile cores (prepared from sodium titanate) since the goal was to produce larger than conventional crystal sizes. To this nucleation material was further added 0.10% Al 2 o 3 (as aluminum sulfate) and 0.2% K 2 O (as potassium sulfate). The resulting material was calcined to a temperature of 960 degrees Celsius over a period of about 12 hours.
[0132] The calciner effluent was pulverized, dispersed and sand milled to a particle size of about 0.45 microns, then coated with 2.7% dense silica and 2.4% alumina.
[0133]The coated materia...
Embodiment 3
[0173] prepared TiO with average crystal sizes of 0.28, 0.32 and 0.36 microns 2 particles and tested in alkyd paints.
[0174] method:
[0175] A certain amount of metatitanic acid from the sulfate process was divided into three portions. 1.88%, 1.26% and 0.89% rutile cores were added to these portions respectively.
[0176] Each part also uses 0.07% Al 2 o 3 (as aluminum sulfate), 0.20% K 2 O (as potassium sulfate) and 0.20% P 2 o 5 (as monoammonium phosphate).
[0177] Each of the three parts was calcined separately, increasing the temperature by 1 degree per minute until a rutile content of >99% was measured. At this point, the calcination was stopped.
[0178] The three fractions have titanium dioxide with average crystal sizes of 0.28, 0.32 and 0.36 microns, respectively.
[0179] The properties of these titania materials are listed in Table 6 below:
[0180] Table 6
[0181]
[0182] Each of the three calciner effluents was ground to three different partic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average crystal size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average crystal size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com