Application of molecular target in prognosis prediction and treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
A technique for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and prognosis evaluation, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of poor prognosis of esophageal cancer, inability to evaluate the prognosis with molecular markers, lack of accurate detection and treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, etc., and achieve the effect of accurate detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 Screening lncRNAs that play a key role in the occurrence and development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
[0047] 1.1 TCGA database screening
[0048] Using bioinformatics technology to screen lncRNAs highly expressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma from the TCGA database.
[0049] 1.2 siRNA library construction and screening
[0050] Using the top 50 highly expressed LncRNAs in cancer tissues analyzed from the database, an siRNA library was established and transfected into esophageal cancer cell lines EC9706 and KYSE30. By detecting MTS and lactic acid production, LncRNAs that can significantly affect cell proliferation and glucolysis were observed.
[0051] 1.3 Large sample tissue verification
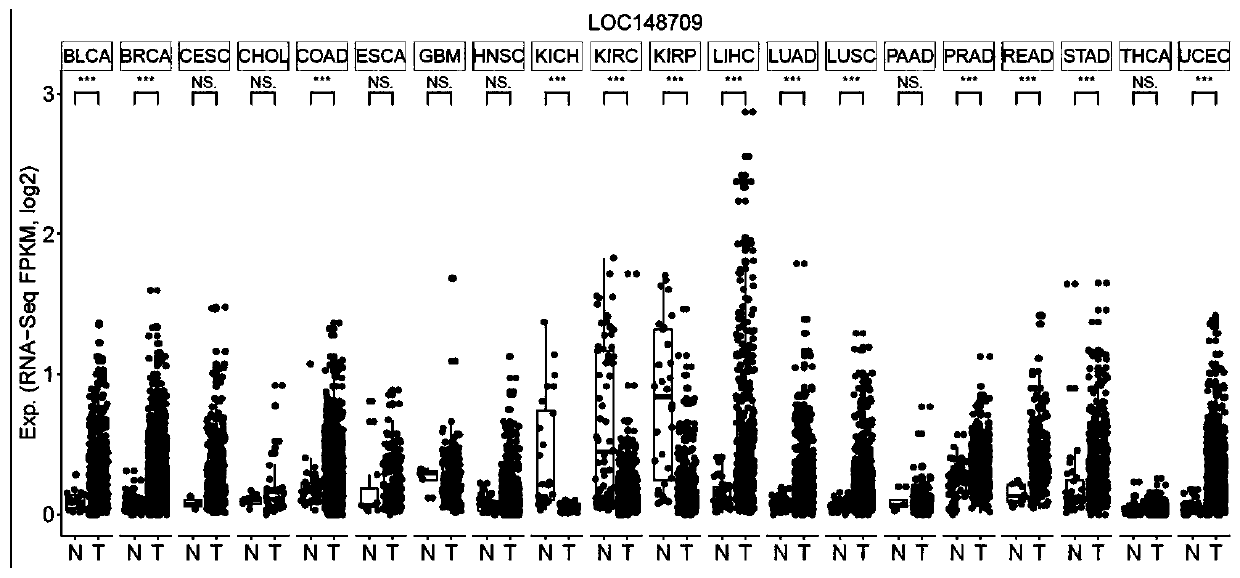
[0052] The TCGA database was used to analyze the expression level of lncRNA APGG in large samples of cancers such as esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, and colorectal cancer. The analysis results are as follows: figure 1 shown by figure 1 It can be se...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2 uses the kit to verify the expression level of lncRNA APGG through RT-PCR technology
[0054] 2.1 Acquisition of cDNA
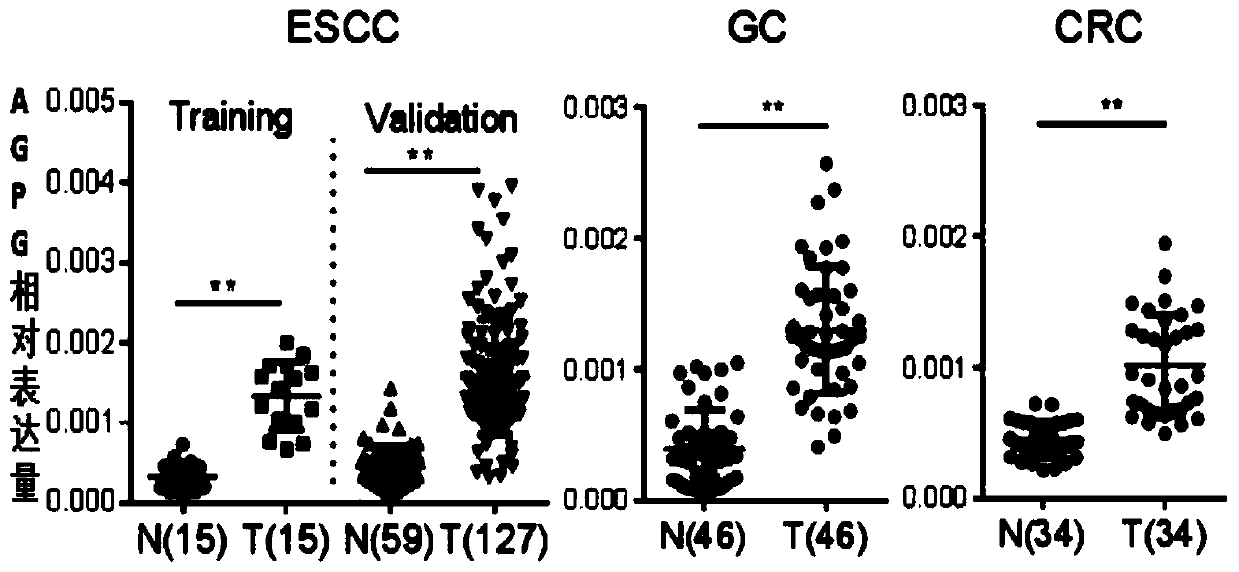
[0055] RNA extraction: Take relevant samples of esophageal cancer (ESCC), gastric cancer (GC), and colon cancer (CRC) tissues. These samples have obtained the consent of relevant personnel, and the total RNA of animal tissues is extracted using RNA extraction kit NEP019-1, and then Use Bio-Red ultraviolet spectrophotometer to measure the optical density value of total RNA at 280nm and 260nm, measure OD 260 / OD 280 The value is 1.87, indicating that the RNA purity is reliable and can be used for the next test,
[0056] Acquisition of cDNA: Use the Revert Aid First Strand cDNA synthesis Kit to reverse transcribe RNA into cDNA;
[0057] 2.2 Primer design
[0058] The sequence information of the APGG gene (that is, LOC148709) was screened out from the TCGA database, and the amplification primers for RT-PCR were designed using PrimerPrimier5.0...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 Using RNA scope in situ hybridization technology to verify the expression level of lncRNA APGG
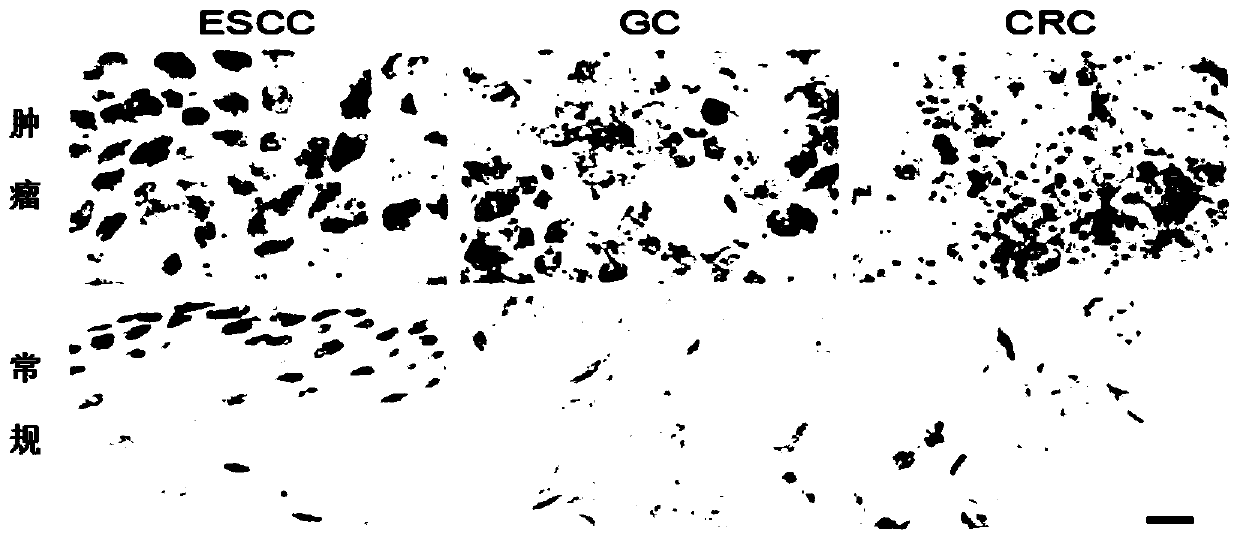
[0066] RNAscope is a new type of ultra-sensitive RNA in situ hybridization detection technology. It has a unique specific probe design and signal amplification system, which can extremely reduce background noise. Its main operation steps include: (1) Pretreatment of tissue sections to increase Its permeability; (2) target RNA hybridizes with specific probe; (3) signal amplification system hybridizes with probe; (4) observes the result under bright field or fluorescent microscope.
[0067] For the specific results of APGG, see image 3 ,Depend on image 3 It can be seen that lncRNA APGG is highly expressed in cancer tissues such as esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, and colorectal cancer.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com