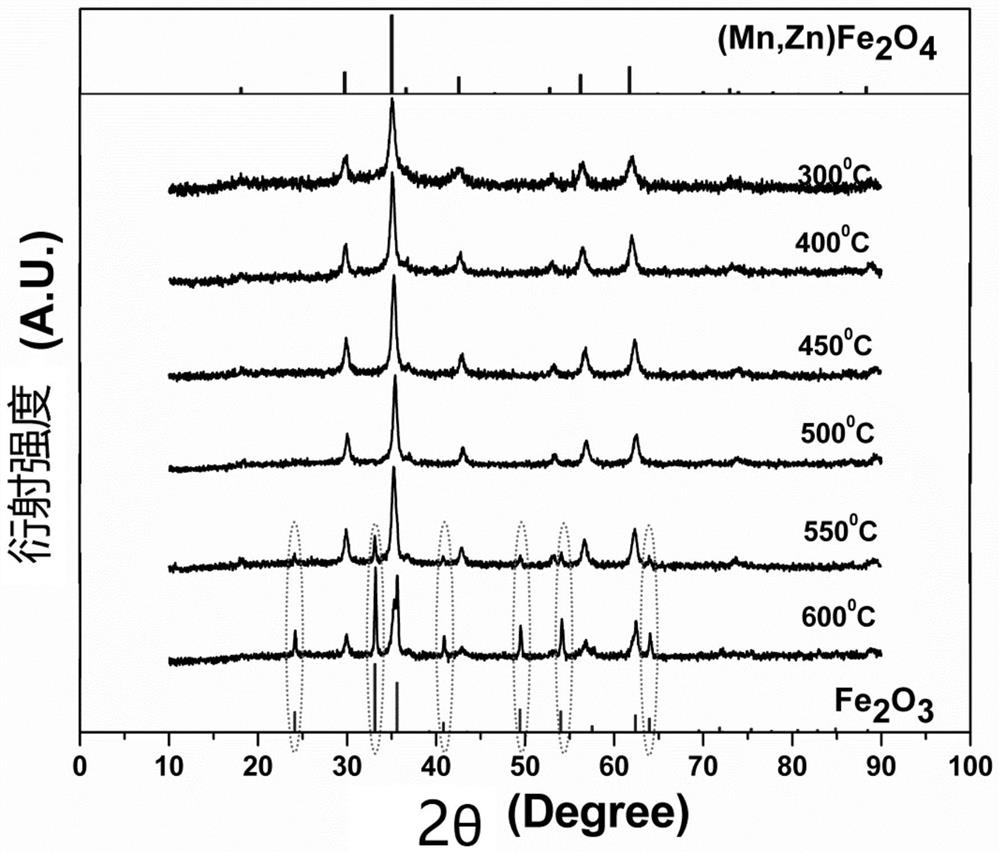
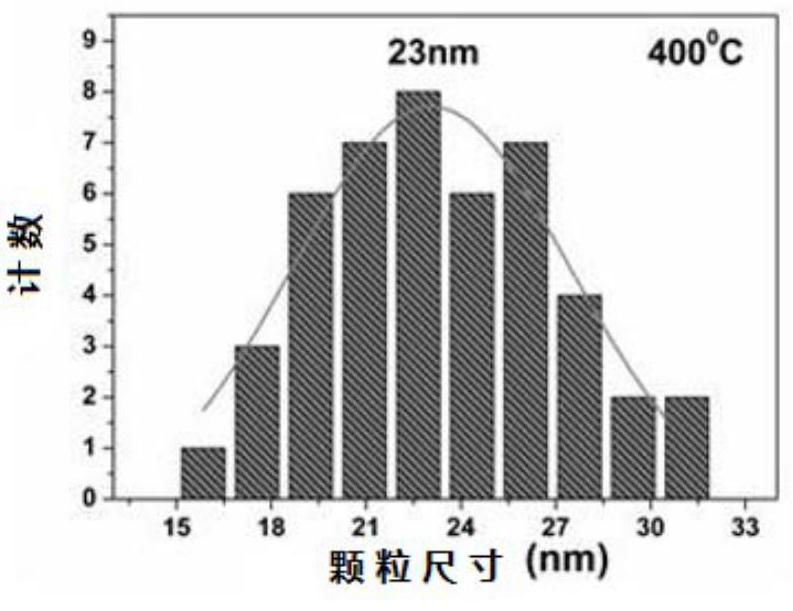
A method for preparing manganese zinc ferrite nanoparticles
A technology of manganese-zinc ferrite and nano-particles, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, chemical instruments and methods, etc., to achieve the effects of high saturation magnetization, suppression of component segregation, and high particle uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Step 1. According to MnZn ferrite (Mn 0.6 Zn 0.4 Fe 2 o 4 ) stoichiometric ratio of manganese nitrate (Mn(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O) 0.006mol, zinc nitrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O) 0.004mol, iron nitrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 (0) 0.02mol, add 100ml deionized water to dissolve, stir at room temperature for 30 minutes to form a clear and transparent solution;
[0028] Step 2. Weigh 0.03 mol of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (the same amount of substance as the total molar amount of metal ions), add it to the above metal ion solution, stir and dissolve at 60-80°C (an appropriate amount of ammonia water can be added Accelerate its dissolving), form the sol that comprises EDTA metal ion chelate after 6~8 hours;
[0029] Step 3. Put the sol into a ventilated drying oven, heat and dehydrate at 100° C. for 5 to 6 hours to obtain a xerogel. Take out the dry gel and grind it thoroughly to obtain the precursor powder;
[0030] Step 4. Put the precursor powder into the muffle ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Step 1. According to MnZn ferrite (Mn 0.6 Zn 0.4 Fe 2 o 4 ) stoichiometric ratio of manganese nitrate (Mn(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2O) 0.006mol, zinc nitrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O) 0.004mol, iron nitrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 (0) 0.02mol, add 100ml deionized water to dissolve, stir at room temperature for 30 minutes to form a clear and transparent solution;
[0034] Step 2. Weigh 0.03 mol of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (the same amount of substance as the total molar amount of metal ions), add it to the above metal ion solution, stir and dissolve at 60-80°C (an appropriate amount of ammonia water can be added Accelerate its dissolving), form the sol that comprises EDTA metal ion chelate after 6~8 hours;
[0035] Step 3. Put the sol into a ventilated drying oven, heat and dehydrate at 100° C. for 5 to 6 hours to obtain a xerogel. Take out the dry gel and grind it thoroughly to obtain the precursor powder;
[0036] Step 4. Put the precursor powder into the muffle f...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Step 1. According to MnZn ferrite (Mn 0.6 Zn 0.4 Fe 2 o 4 ) stoichiometric ratio of manganese nitrate (Mn(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O) 0.006mol, zinc nitrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O) 0.004mol, iron nitrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 (0) 0.02mol, add 100ml deionized water to dissolve, stir at room temperature for 30 minutes to form a clear and transparent solution;
[0040] Step 2. Weigh 0.03 mol of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (the same amount of substance as the total molar amount of metal ions), add it to the above metal ion solution, stir and dissolve at 60-80°C (an appropriate amount of ammonia water can be added Accelerate its dissolving), form the sol that comprises EDTA metal ion chelate after 6~8 hours;
[0041] Step 3. Put the sol into a ventilated drying oven, heat and dehydrate at 100° C. for 5 to 6 hours to obtain a xerogel. Take out the dry gel and grind it thoroughly to obtain the precursor powder;
[0042] Step 4. Put the precursor powder into the muffle ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com