Gene sequencing chip and gene sequencing method
A gene sequencing and chip technology, applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, biochemical instruments, etc., can solve the problem of fluorescence detection technology, expensive labeling reagents or autofluorescence reaction system, sequence analysis continuity and simultaneous monitoring and reflection Insufficient quantity, cost reduction and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving integration and stability, reducing excitation area and reducing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
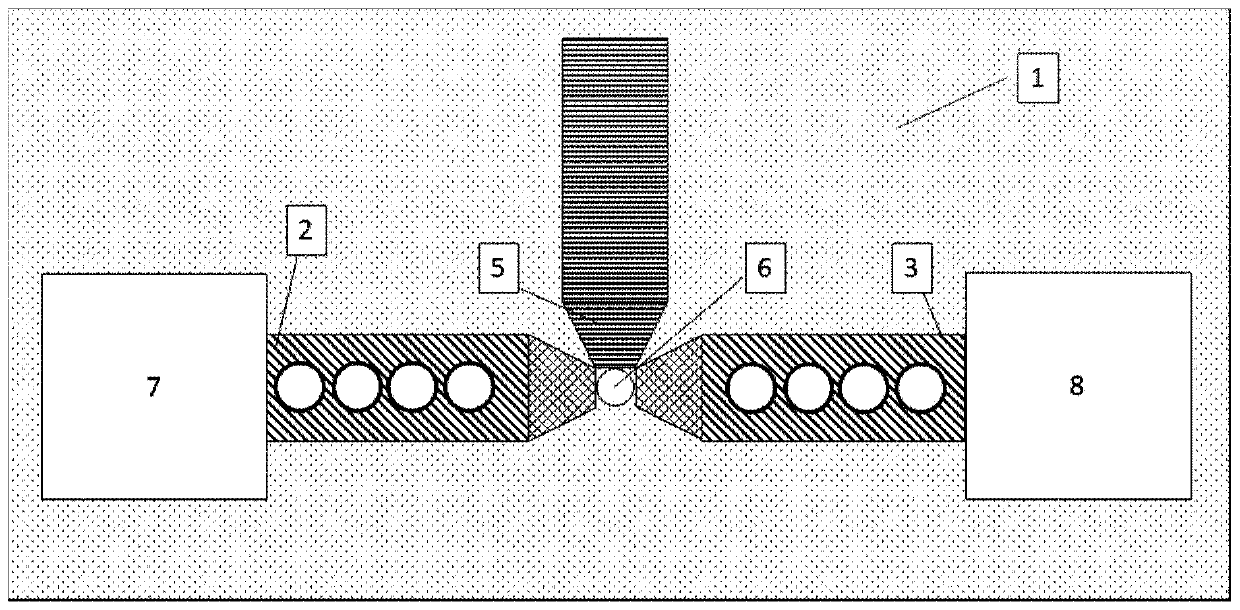
[0046] figure 1 A schematic structural diagram of a gene sequencing chip based on tip-enhanced Raman effect in Example 1 of the present invention is shown. Such as figure 1 As shown, the chip includes:
[0047] A substrate 1 , a first optical waveguide 2 , a second optical waveguide 3 , a metal tip 5 , a nanohole 6 , a light source coupling module 7 , and a first signal acquisition module 8 . The first optical waveguide 2 , the second optical waveguide 3 , the metal needle tip 5 , the nanohole 6 , the light source coupling module 7 , and the first signal acquisition module 8 are all formed on the substrate 1 .
[0048] The substrate 1 is a silicon substrate, the first optical waveguide 2, the second optical waveguide 3 and the metal needle point 5 are relatively distributed on the silicon substrate in a T shape, and the nanohole 6 is arranged on the first optical waveguide 2 and the second optical waveguide 3 The area in contact with the metal needle tip 5 runs through the ...
Embodiment 2
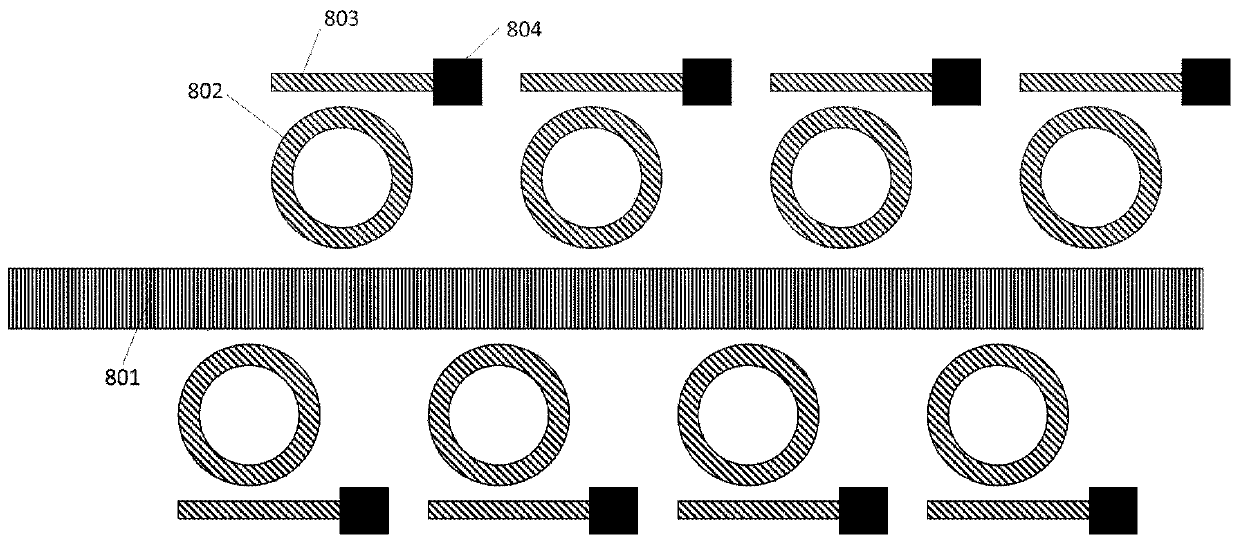
[0053] On the basis of the gene sequencing chip based on the tip-enhanced Raman effect described in Example 1, this example adds a second Raman signal acquisition method, such as Figure 4 As shown, the gene sequencing chip also includes a third optical waveguide 4 and a second collector 9, which are formed on the substrate 1, and the third optical waveguide 4 is opposite to the T-shaped first optical waveguide 2 and the second optical waveguide. 3 and the metal needle point 5 form a cross-shaped structure, the nanohole 6 is placed in the middle of the cross, the third optical waveguide 4 has a three-dimensional gradient structure, and one end is opposite to the metal needle point 5, and the second collector 9 is located on the third optical waveguide 4 and has a three-dimensional gradient structure. One end of the structure is opposite to the other end, the third optical waveguide 4 is a MIM structure, and the metal material in the MIM structure is a metal with a strong surfac...
Embodiment 3
[0056] This embodiment proposes a gene sequencing method based on a gene sequencing chip, such as Figure 5 As shown, the methods include:
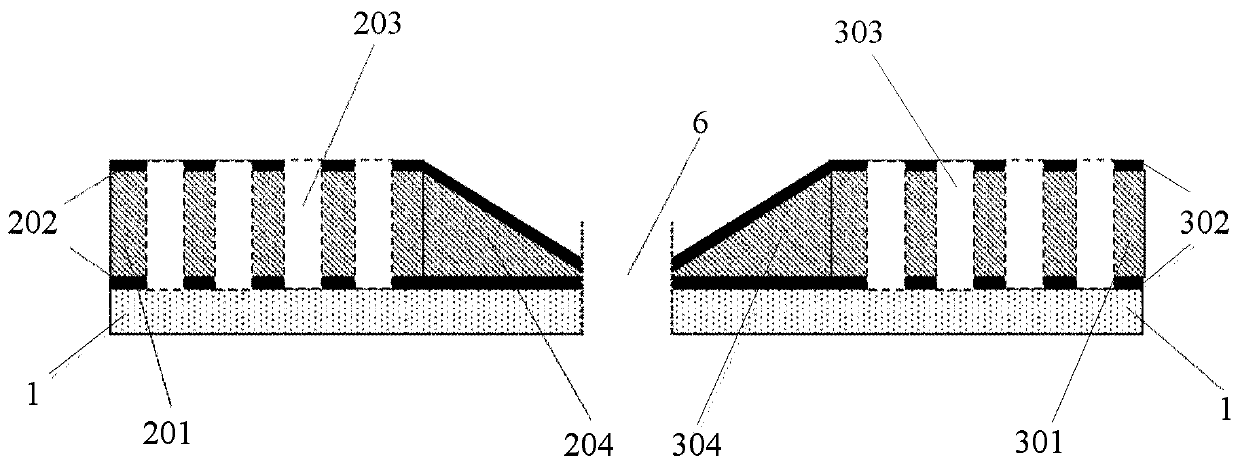
[0057] S1, the optical field of the optical signal generated by the light source coupler 7 passes through the first optical waveguide 2 and the second optical waveguide 3 for compression enhancement and resonance enhancement to form excitation light.
[0058] Specifically, the optical signal sent by the light source coupler 7 is reflected back and forth by at least one Bragg periodic structure 203 (303) on the first optical waveguide 2 and the second optical waveguide 3, realizing resonance enhancement, and passing through the three-dimensional tapered structure 204 (304) The optical signal light field is further compressed and enhanced to form excitation light.
[0059] S2, controlling the base chain of the gene to be tested to pass through the nanopore 6 in the form of a single strand;
[0060] Because the size of the nanopore 6 is la...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com